File
... Tamoxifen and raloxifene inhibit activation of the estrogen receptor, used in treatment of breast cancer (selective estrogen receptor modulators - SERMs) ...
... Tamoxifen and raloxifene inhibit activation of the estrogen receptor, used in treatment of breast cancer (selective estrogen receptor modulators - SERMs) ...
Gene Section MYST3 (MYST histone acetyltransferase (monocytic leukemia) 3
... 2004 amino acids; 225 kDa; composed from N-term of: a NEMM domain (N-term region of ENOK, MOZ or MORF) including a H15 (linker H1 and H5 like) nuclear localization domain, 2 PHD (plant homeodomain, also known as LAP (leukemia ...
... 2004 amino acids; 225 kDa; composed from N-term of: a NEMM domain (N-term region of ENOK, MOZ or MORF) including a H15 (linker H1 and H5 like) nuclear localization domain, 2 PHD (plant homeodomain, also known as LAP (leukemia ...
Chapter 6
... remodeling complexes that use energy provided by hydrolysis of ATP. • The SWI/SNF, RSC, and NURF complexes all are very large; – there are some common subunits. ...
... remodeling complexes that use energy provided by hydrolysis of ATP. • The SWI/SNF, RSC, and NURF complexes all are very large; – there are some common subunits. ...
An Investigation into the Genomic Evolution of the Histone Gene
... conversion - have been documented to occur, and are understood in molecular detail, but their role in concerted evolution is primarily based on theoretical and/or mathematical models with limited data from actual genome sequence to support them. It is the hypothesis of this research that if unequal ...
... conversion - have been documented to occur, and are understood in molecular detail, but their role in concerted evolution is primarily based on theoretical and/or mathematical models with limited data from actual genome sequence to support them. It is the hypothesis of this research that if unequal ...
Breanna Perreault D145 Presentation 2/23/17 Background
... CpGs: Consecutive C and G nucleotides, sequence that can be directly methylated ...
... CpGs: Consecutive C and G nucleotides, sequence that can be directly methylated ...
Chapter 7C
... and cells, 2) regulation of TF activity via a signal transduction pathway coupled to a receptor for a hormone or growth factor, and 3) direct binding of the TF to certain small molecules, e.g., steroid hormones, in the case of nuclear receptors. Examples of hormones that regulate nuclear receptor ac ...
... and cells, 2) regulation of TF activity via a signal transduction pathway coupled to a receptor for a hormone or growth factor, and 3) direct binding of the TF to certain small molecules, e.g., steroid hormones, in the case of nuclear receptors. Examples of hormones that regulate nuclear receptor ac ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Effects of Chromatin Structure DNA Methylation • DNA Methylation (adding -CH3) can occur on cytosines at CpG groupings near transcription start sites •Inactive genes have methylated cytosines •Active genes have demethylated cytosines • Acetylation of histones is associated with ...
... Effects of Chromatin Structure DNA Methylation • DNA Methylation (adding -CH3) can occur on cytosines at CpG groupings near transcription start sites •Inactive genes have methylated cytosines •Active genes have demethylated cytosines • Acetylation of histones is associated with ...
Epigenetics Glossary FINAL
... Allele: Human genes occur in pairs, one on each chromosome of a chromosome pair. The paired genes are called "alleles" and can have a differing form and significance. For instance, in the case of some flowers, the allele on one chromosome may produce a red petal color and the other a white petal col ...
... Allele: Human genes occur in pairs, one on each chromosome of a chromosome pair. The paired genes are called "alleles" and can have a differing form and significance. For instance, in the case of some flowers, the allele on one chromosome may produce a red petal color and the other a white petal col ...
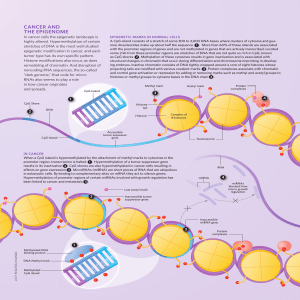
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... with the promoter regions of genes and are not methylated in genes that are actively transcribed. Located some 2 kb from these promoter regions are stretches of DNA that are not quite so rich in CpG, known as CpG shores 2 . Methylation of these cytosines results in gene inactivation and is associa ...
... with the promoter regions of genes and are not methylated in genes that are actively transcribed. Located some 2 kb from these promoter regions are stretches of DNA that are not quite so rich in CpG, known as CpG shores 2 . Methylation of these cytosines results in gene inactivation and is associa ...
Review (12/13/16)
... • Name two different consequences that histone modifications can have when present on a nucleosome. – Do the different chemical modifications on histones have the same effect regardless of which amino acid they are added to on the histone? – What histone modifications are associated with active or ...
... • Name two different consequences that histone modifications can have when present on a nucleosome. – Do the different chemical modifications on histones have the same effect regardless of which amino acid they are added to on the histone? – What histone modifications are associated with active or ...
Document
... • core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) are small (11 to 14 kD), highly basic proteins • they are evolutionarily highly conserved (from yeast to humans) ...
... • core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) are small (11 to 14 kD), highly basic proteins • they are evolutionarily highly conserved (from yeast to humans) ...
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
... Histones – What are they??? Small proteins 102-135 AA Similar structural motif Three a-helices Connected by two loops Histone-fold H3-H4 dimer H2A-H2B dimer ...
... Histones – What are they??? Small proteins 102-135 AA Similar structural motif Three a-helices Connected by two loops Histone-fold H3-H4 dimer H2A-H2B dimer ...
Cancer Genetics
... A relationship between histone acetylation and transcriptional activation was first suggested more than 30 years ago35, but the molecular machinery engaged in this process has only been identified in the past few years29–33. HATs can be divided into several families on the basis of a number of highl ...
... A relationship between histone acetylation and transcriptional activation was first suggested more than 30 years ago35, but the molecular machinery engaged in this process has only been identified in the past few years29–33. HATs can be divided into several families on the basis of a number of highl ...
Nessun titolo diapositiva
... There are several chromatin remodeling complexes that use energy provided by hydrolysis of ATP. The SWI/SNF, RSC, and NURF complexes all are very large; there are some common subunits. A remodeling complex does not itself have specificity for any particular target site, but must be recruited by a co ...
... There are several chromatin remodeling complexes that use energy provided by hydrolysis of ATP. The SWI/SNF, RSC, and NURF complexes all are very large; there are some common subunits. A remodeling complex does not itself have specificity for any particular target site, but must be recruited by a co ...
Next lectures: Differential Gene expression
... initiation complex assembled at the promoter is thought to regulate transcription • Enhancers are modular. Particular combinations of factors (rather than any one factor) determines enhancer function ...
... initiation complex assembled at the promoter is thought to regulate transcription • Enhancers are modular. Particular combinations of factors (rather than any one factor) determines enhancer function ...
Document
... genes to be transcribed. It is not known, if HMTs and HATs have a direct connection to each other. (B) In the postulated 'switch' hypothesis, phosphorylation of serines or threonines adjacent to lysines displaces histone methyl-binding proteins, accomplishing a binding platform for other proteins wi ...
... genes to be transcribed. It is not known, if HMTs and HATs have a direct connection to each other. (B) In the postulated 'switch' hypothesis, phosphorylation of serines or threonines adjacent to lysines displaces histone methyl-binding proteins, accomplishing a binding platform for other proteins wi ...
Epigenetics
... • The methylation pattern of the genome is established anew every generation. In that sense methylation is an epigentic phenomenon - it influences the genetic material but it is not inherited from one generation to another. • All methylation (or at least almost all) is erased during early embryogene ...
... • The methylation pattern of the genome is established anew every generation. In that sense methylation is an epigentic phenomenon - it influences the genetic material but it is not inherited from one generation to another. • All methylation (or at least almost all) is erased during early embryogene ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... • An enhancer binds regulators responsible for activating the gene at the given time and place. • Insulators block activation of the promoter by activators bound at the enhancer. • A silencer binds regulators responsible for repressing the gene at the given time and place. ...
... • An enhancer binds regulators responsible for activating the gene at the given time and place. • Insulators block activation of the promoter by activators bound at the enhancer. • A silencer binds regulators responsible for repressing the gene at the given time and place. ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... Describe the Endosymbiotic hypothesis. Essentially, modern cells are a product of ancient eukaryotes engulfing free-living mitochondria and/or chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria ...
... Describe the Endosymbiotic hypothesis. Essentially, modern cells are a product of ancient eukaryotes engulfing free-living mitochondria and/or chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria ...
Slide 1
... modifications) serves as a bar code for many nuclear factors • Three necessary components: writers, erasers, and readers of the code • Covalent modifications of histone tails act as docking sites for reader proteins that: – Stamp new modifications on neighboring nucleosomes – Remodel neighboring nuc ...
... modifications) serves as a bar code for many nuclear factors • Three necessary components: writers, erasers, and readers of the code • Covalent modifications of histone tails act as docking sites for reader proteins that: – Stamp new modifications on neighboring nucleosomes – Remodel neighboring nuc ...
Slide 1
... DNA methylation II - effects of DNA methylation on gene expression, Methyl-binding proteins and mechanisms of inhibition of gene expression, distribution of DNA methylation within genes and mammalian genomes. ...
... DNA methylation II - effects of DNA methylation on gene expression, Methyl-binding proteins and mechanisms of inhibition of gene expression, distribution of DNA methylation within genes and mammalian genomes. ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;22)(q23;q13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Chimeric mRNAs from both derivative chromosomes are found. ...
... Chimeric mRNAs from both derivative chromosomes are found. ...
Epigenetics - Hospital Melaka Department of Medicine Haematology
... The $3-billion project was formally founded in 1990 by the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
... The $3-billion project was formally founded in 1990 by the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
Histone acetyltransferase

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.In general, histone acetylation is linked to transcriptional activation and associated with euchromatin. When it was first discovered, it was thought that acetylation of lysine neutralizes the positive charge normally present, thus reducing affinity between histone and (negatively charged) DNA, which renders DNA more accessible to transcription factors. Research has emerged, since, to show that lysine acetylation and other posttranslational modifications of histones generate binding sites for specific protein–protein interaction domains, such as the acetyllysine-binding bromodomain. Histone acetyltransferases can also acetylate non-histone proteins, such as nuclear receptors and other transcription factors to facilitate gene expression.