8 Reaction and Physical Properties
... with a globin protein. Dioxygen is transported in blood by being coordinated to ferrous ions in the hem iron unit. The Fe (II) ion is penta-coordinate with four nitrogen atoms of porphyrin and a nitrogen atom of the polypeptide histidine, and becomes hexa-coordinate when a dioxygen coordinates to it ...
... with a globin protein. Dioxygen is transported in blood by being coordinated to ferrous ions in the hem iron unit. The Fe (II) ion is penta-coordinate with four nitrogen atoms of porphyrin and a nitrogen atom of the polypeptide histidine, and becomes hexa-coordinate when a dioxygen coordinates to it ...
Biochemistry PPT
... Found in all cells Makes up the cell membrane 2 layers of phospholipids lipid bilayer ...
... Found in all cells Makes up the cell membrane 2 layers of phospholipids lipid bilayer ...
Leah Cooper
... protein) in appropriate proportions. Throughout evolution, we have conserved the pathways necessary for the synthesis of the nonessential amino acids (NEAA) indicating their importance in the body. Nutritionally, there is a dietary requirement for the 9 essential amino acids (EAA) because our body’s ...
... protein) in appropriate proportions. Throughout evolution, we have conserved the pathways necessary for the synthesis of the nonessential amino acids (NEAA) indicating their importance in the body. Nutritionally, there is a dietary requirement for the 9 essential amino acids (EAA) because our body’s ...
Ch 9 Notes Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Basically a transfer of electrons from something less electronegative to something more electronegative. ...
... Basically a transfer of electrons from something less electronegative to something more electronegative. ...
Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... Substances that release hydrogen ions ( H ) when dissolved in water are called __________. Substances that release hydroxide ions ( OH ) when dissolved in water are called __________. pH and Buffers: The measure of concentration of H in a solution is called __________. ...
... Substances that release hydrogen ions ( H ) when dissolved in water are called __________. Substances that release hydroxide ions ( OH ) when dissolved in water are called __________. pH and Buffers: The measure of concentration of H in a solution is called __________. ...
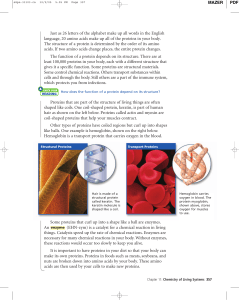
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
Physiology
... protoporphyrin 1x, which then combine with iron to form heme molecule. Finally, each heme molecule combine with long polypeptide chain, called globin, synthesized by the ribosomes, forming a subunit called Hb chain. Each chain has a molecular weight about 16.000, four of them turn, bind together loo ...
... protoporphyrin 1x, which then combine with iron to form heme molecule. Finally, each heme molecule combine with long polypeptide chain, called globin, synthesized by the ribosomes, forming a subunit called Hb chain. Each chain has a molecular weight about 16.000, four of them turn, bind together loo ...
Unit 3 Review Sheet – Biochemistry
... What are the characteristics of water that make it important to life? Polar, high heat capacity, resists temperature change, abililty to bond and attract other molecules (cohesion and adhesion), ice is less dense than liquid water, universal solvent, most abundant compound in living things What does ...
... What are the characteristics of water that make it important to life? Polar, high heat capacity, resists temperature change, abililty to bond and attract other molecules (cohesion and adhesion), ice is less dense than liquid water, universal solvent, most abundant compound in living things What does ...
Name
... structure. What part of the enzyme is involved in catalytic activity? A Binding pocket C Active site _ B Pleated sheet D Quaternary structure 27. Which of the following molecules is most abundant in the cells of the human body? A Amino acids C Lipids B Nucleotides D Water _ 28. Enzymes only work wit ...
... structure. What part of the enzyme is involved in catalytic activity? A Binding pocket C Active site _ B Pleated sheet D Quaternary structure 27. Which of the following molecules is most abundant in the cells of the human body? A Amino acids C Lipids B Nucleotides D Water _ 28. Enzymes only work wit ...
Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
... The golden-orange compound is CoCl3*6NH3 while the purple compound only has 5 ammonia molecules in the coordinated compound. As shown in the ball-and-stick model, the chlorides serve as counter ions to the cobalt/ammonia coordiation complex in the orange compound, while one of the ammonia molecules ...
... The golden-orange compound is CoCl3*6NH3 while the purple compound only has 5 ammonia molecules in the coordinated compound. As shown in the ball-and-stick model, the chlorides serve as counter ions to the cobalt/ammonia coordiation complex in the orange compound, while one of the ammonia molecules ...
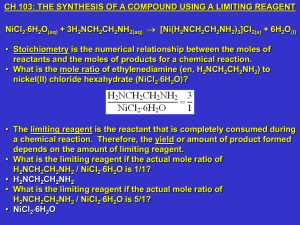
Week #10: The Synthesis of a Compound using a Limiting Reagent
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
Document
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
... cation bonded (or coordinated) to 1 or more groups of atoms. These groups of atoms are called ligands. • Coordination number is the number of ligand atoms that bond to the central metal of a complex ion. • What is the metal atom in this complex ion? • Ni2+ • What is the ligand? ...
Chapter 6: Biochemistry
... A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers ...
... A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers ...
Unit 7 Review
... What set of coefficients will balance this equation? NH4OH + H3PO4 (NH4)3PO4 + H2O ...
... What set of coefficients will balance this equation? NH4OH + H3PO4 (NH4)3PO4 + H2O ...
Biopolymers Modulation of nucleic acids, carbohydrates and
... the activity of the ribozymes, it is not surprising that such displacement often results in inhibition of ribozyme activity. In vitro selected RNA aptamers with affinities for neomycin B show similar structural folds that, however, do not necessarily require sequence homology. These studies underlin ...
... the activity of the ribozymes, it is not surprising that such displacement often results in inhibition of ribozyme activity. In vitro selected RNA aptamers with affinities for neomycin B show similar structural folds that, however, do not necessarily require sequence homology. These studies underlin ...
Transition Metals
... cations as needed to produce a neutral compound). [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 [Fe(en)2(NO2)2]2SO4 Secondary valence: refers to the ability of a metal ion to bind to Lewis base (ligand) to form complex ions. This is known as coordination number (# of bonds formed between the metal ion and the ligands) Primary va ...
... cations as needed to produce a neutral compound). [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 [Fe(en)2(NO2)2]2SO4 Secondary valence: refers to the ability of a metal ion to bind to Lewis base (ligand) to form complex ions. This is known as coordination number (# of bonds formed between the metal ion and the ligands) Primary va ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.