Chapter 3 - Proteins
... all the additional amino acids that you remember. • What are the four weak (noncovalent) interactions that determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or greatest order) when it is completely stretched out like a string an ...
... all the additional amino acids that you remember. • What are the four weak (noncovalent) interactions that determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or greatest order) when it is completely stretched out like a string an ...
Elements and their functions in biological systems
... Metal ions are often much more effective catalysts than protons because can be present in high concentrations at neutral pH, and can have charges > +1. Metal ions are therefore called „superacids”. • covalent catalysis, • mediating oxidation-reduction reactions through reversible changes in the meta ...
... Metal ions are often much more effective catalysts than protons because can be present in high concentrations at neutral pH, and can have charges > +1. Metal ions are therefore called „superacids”. • covalent catalysis, • mediating oxidation-reduction reactions through reversible changes in the meta ...
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... Lipids – elements CHO – no ratio, functions – concentrated energy 9 cal/gram Monomers: glycerol and fatty acid, structure of each Triglyceride – which monomers, how many of each Saturated and unsaturated – how different, where found o Hydrogenated and trans fat – what are they? Why important? ...
... Lipids – elements CHO – no ratio, functions – concentrated energy 9 cal/gram Monomers: glycerol and fatty acid, structure of each Triglyceride – which monomers, how many of each Saturated and unsaturated – how different, where found o Hydrogenated and trans fat – what are they? Why important? ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
... It has a numerical value of 6.02 x 1023 mol-1 Oxidation number: The difference between the number of electrons associated with an element in a compound and the element itself. Just for the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers all compounds are considered to contain ions, eg, CO2, C 4+ 2O 2- (but i ...
chap 1 + 24 review
... SO4 has -2 charge, so complex ion must have +2 charge NH3 has no charge, so Cu must also have +2 charge and oxidation number ...
... SO4 has -2 charge, so complex ion must have +2 charge NH3 has no charge, so Cu must also have +2 charge and oxidation number ...
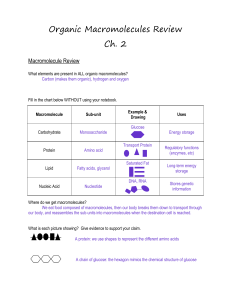
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
NUCLEIC ACIDS
... bond with another atom—N or O) and a partially negatively charged atom, such as a Nitrogen or Oxygen that is involved in a polar covalent bond with another atom. ...
... bond with another atom—N or O) and a partially negatively charged atom, such as a Nitrogen or Oxygen that is involved in a polar covalent bond with another atom. ...
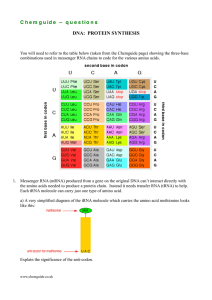
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Unit 5 - INTEC Chemistry Blog
... (i) the formation of coloured aqueous ions, and other complex ions Transition metal compounds are coloured, d orbitals are normally of similar energy but when surrounded by ligands the orbitals are split into higher and lower energy sets. absorbs light (in visible region) d-orbitals split by lig ...
... (i) the formation of coloured aqueous ions, and other complex ions Transition metal compounds are coloured, d orbitals are normally of similar energy but when surrounded by ligands the orbitals are split into higher and lower energy sets. absorbs light (in visible region) d-orbitals split by lig ...
Wheatgrass Chlorophyllcdmcoct022012
... form of poly peptides, shorter and simpler chains of amino acids which are deposited more efficiently into the bloodstream and blood tissues. Protein is essential to build and repair tissues, and is an important building block of bones, muscles, cartlidge, skin, and blood. ...
... form of poly peptides, shorter and simpler chains of amino acids which are deposited more efficiently into the bloodstream and blood tissues. Protein is essential to build and repair tissues, and is an important building block of bones, muscles, cartlidge, skin, and blood. ...
03 Complexation equilibrium
... Those that bond through electron pairs on more than one donor atom are termed polydentate ligands (“many-toothed” ligands). For example, ethylenediamine (NH2CH2CH2NH2 abbreviated en) is a bidentate ligand because it bonds to a metal using an electron pair on each of its two nitrogen atoms. ...
... Those that bond through electron pairs on more than one donor atom are termed polydentate ligands (“many-toothed” ligands). For example, ethylenediamine (NH2CH2CH2NH2 abbreviated en) is a bidentate ligand because it bonds to a metal using an electron pair on each of its two nitrogen atoms. ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation - Study in Universal Science College
... 2. -endergonic transfer of 4 protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space Complex I – k/as proton pump driven by the energy of electron transfer; where – protons move from one location (matrix which then becomes negatively charged) to the other (intermembrane space which becomes positively cha ...
... 2. -endergonic transfer of 4 protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space Complex I – k/as proton pump driven by the energy of electron transfer; where – protons move from one location (matrix which then becomes negatively charged) to the other (intermembrane space which becomes positively cha ...
chapter 2 biochemistry
... What is an enzyme? An enzyme is a special type of protein called a catalyst Catalyst: substance that speeds up a reaction because it lowers the activation energy Cells use enzymes to speed up reactions Very specific: usually only catalyzes one item called the SUBSTRATE ...
... What is an enzyme? An enzyme is a special type of protein called a catalyst Catalyst: substance that speeds up a reaction because it lowers the activation energy Cells use enzymes to speed up reactions Very specific: usually only catalyzes one item called the SUBSTRATE ...
Bonding Basics Review Worksheet
... 3. Covalent Bonds – Draw the Lewis structures for each atom, draw circles to show the electrons that are shared, and then write the bond structure and chemical formula. (A) Fluorine + Fluorine ...
... 3. Covalent Bonds – Draw the Lewis structures for each atom, draw circles to show the electrons that are shared, and then write the bond structure and chemical formula. (A) Fluorine + Fluorine ...
Chapter 2 - FacultyWeb
... AB + CD AD + CB; molecules are shuffled around to produce a new product ...
... AB + CD AD + CB; molecules are shuffled around to produce a new product ...
Four Types of Organic Molecules
... Organic Molecules are made by cells and contain carbon 4 types of Organic Molecules 1. ______________________________________- used as fuel and building material 2. ______________________________________-energy storage 3. ______________________________________-structure, movement, enzymes 4. _______ ...
... Organic Molecules are made by cells and contain carbon 4 types of Organic Molecules 1. ______________________________________- used as fuel and building material 2. ______________________________________-energy storage 3. ______________________________________-structure, movement, enzymes 4. _______ ...
Proteins
... How large are most proteins? __larger than 50 amino acids but typically hundreds of amino acids long ...
... How large are most proteins? __larger than 50 amino acids but typically hundreds of amino acids long ...
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry notes and questions for
... Ambidentate ligand: A ligand that can ligate through two different atoms, one at a time. Ex-NO2- ; SCNv) Coordination number: The no. of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded through sigma bonds only. It is commonly 4 or 6. vi) Counter ions: The ionisable groups written outside th ...
... Ambidentate ligand: A ligand that can ligate through two different atoms, one at a time. Ex-NO2- ; SCNv) Coordination number: The no. of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded through sigma bonds only. It is commonly 4 or 6. vi) Counter ions: The ionisable groups written outside th ...
Name: MACROMOLECULES Date: I. ELEMENTS AND
... inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Task: Color code the amino acid to the right ------------------> (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, and oxyge ...
... inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Task: Color code the amino acid to the right ------------------> (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, and oxyge ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.