* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Four Types of Organic Molecules
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
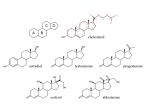
Four Types of Organic Molecules Importance of Carbon Although cells are 70-95% water, the rest are composed mainly of ______________________________. _____________________, ________________________, ________________________, and other molecules are compounds of carbon bonded to other elements. Carbon often bonds to H, O, N, S, and P in organic compounds. Properties of Carbon Has _________________________________________; can form covalent bonds with ____________ other atoms Carbon can form _______________________, _______________________, or_________________ bonds with other atoms. Carbon chains form the ___________________________ of most organic molecules. Chains can be ____________________, ______________________, or arranged in closed ___________. Hydrocarbons contain _______________________________________ only, and are hydrophobic. H—C and C—C bonds are nonpolar. Hydrocarbons make up fossil fuels, and parts of cellular organic molecules such as fats and phospholipids. Organic Molecules are made by cells and contain carbon 4 types of Organic Molecules 1. ______________________________________- used as fuel and building material 2. ______________________________________-energy storage 3. ______________________________________-structure, movement, enzymes 4. ______________________________________-store and transmit hereditary information. They are _________________________because of their large size. The largest macromolecules are called ____________________ created by linking smaller subunits called ___________________. Dehydration Monomers are ______________together to form polymers through ___________ reactions, which _____________ _______________. This process is called dehydration because water is removed Monomers are linked together by ________________ ________________. Hydrolysis Polymers are ____________ apart by_____________, the ____________of __________. Hydro means water and lysis means to rupture or break apart. You break apart molecules by adding water. Breaks _________________ ____________________ between monomers. Hydrocarbons ____________________ are compounds made of only __________ and ____________. Fill in this chart: Found in a variety of structures. 1. 2. 3. 4. Functional group: Compounds containing functional groups are __________________(water-__________) There are 6 Functional groups 1.______________ group - a hydrogen bonded to an oxygen 2.______________ group - a carbon linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom 3.______________ group - a carbon double-bonded to both an oxygen and a hydroxyl group 4.______________ group - a nitrogen bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton 5.______________ group - a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms 6.______________ group - a carbon bonded to three hydrogens. Types of Organic Molecules 1. Carbohydrates (monomer = monosaccharide) • Function: used for ______________________, but some of them are used for structure • All carbs are in a _________________________ ratio of C:H:O • The common name for carbohydrates is “__________________________” • Most carbohydrates (but not all) end in the letters “________”. • Carbohydrates occur in the form of 1 (mono), 2 (di), or more (poly) rings There are 3 different types of carbohydrates: 1. 2. 3. 3 different types of carbohydrates: 1. ________________________________________ – simple (one) ring sugars Usage: give energy ____________________ because they can be _________ _____________________________ easily by the body. Even so, this energy does ________________________________________ because it is used up very quickly. Types: a. _____________________ – 6 carbon sugar found in blood b. _____________________ – 6 carbon sugar found in fruit c. _____________________ – 6 carbon sugar found in peas 2. _____________________________– 2 ring sugar Made by joining 2 _____________________________________ by process of dehydration Usage: give energy that lasts a little longer than ____________________________ because the ___________________________________________ (a covalent bond between two monosaccharides) must be broken before the sugar can be used for energy. Examples _________________________ = table sugar (made by Glucose + fructose) _________________________= milk sugar (made by Glucose + galactose) _________________________ = malt sugar (made by glucose + glucose) 3. Polysaccharides – _____________________________ sugar (repeating units of monosaccharides) Usage: energy storage and as structural components. Examples: Energy _________________ (plants produce for a storage molecule.) _________________ (storage molecule in muscle and liver cells.) Structural (only 2 carbs we’ll talk about that aren’t used for energy) __________________ (plants produce for cell wall construction.) indigestible because we lack enzymes to break it down. __________________ (used by insects and crustaceans to build an exoskeleton.) 2. Protein - Made of a long chain of _____________ ____________linked by __________________ reactions Amino acids (monomer for protein) Have an ________________ group and a _____________________ group. Also they have a chemical group symbolized by the letter _________. –Dehydration reaction links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid. The covalent linkage resulting is called a __________________ ____________. - Peptide bonds Peptide bonds are _________________________________ formed by a condensation reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Has polarity with an __________________________ one end (N-terminus) and a ____________ ____________________________ on the other (C-terminus). Has a backbone of repeating N-C-C-N-C-C Polypeptide chains range in length from a few monomers to more than a thousand, and a unique linear sequence of amino acids. The ___ ______________determines if the amino acid is hydrophobic (hates water) or hydrophilic (loves water). A protein’s specific ________________ determines its ___________________. A __________________ chain contains hundreds or thousands of ___________ _________ linked by ____________ ___________. –The amino acid _________________ causes the polypeptide to assume a particular _____________, the shape of a protein determines its specific __________________. Amino Acid sequence = shape = function! Proteins have many functions 1. __________________________ (support) _______________ for hair and nails & ________________ for ligaments, tendons, skin 2. _____________________________ Found in muscle cells, enables them to move 3. _______________________ – Proteins that promote chemical conversions, as well as speed up reactions Example: _______________ is an enzyme in saliva that breaks starch into glucose monomers. 4. ______________________ across cell membranes Ex. ______________________ 5. ______________________ from infection Ex. __________________ 6._____________ __________ Ex. __________________ 7. ________________ Source of food for developing embryos. Ex. Albumin (egg whites) Experiences heat coagulation (denaturation) Protein in seeds 8. ______________________ Built in cell membrane. Transmits signals to the inside of the cell A protein can have four levels of structure 1. The _______________________________ of a protein is its unique amino acid sequence 2. Protein ____________________________ results from coiling or folding of the polypeptide held by hydrogen bonds. – Coiling = ___________________________________ structure – Folding = ___________________________________ structure 3. The overall three-dimensional shape of a protein is called its ____________________________ _________________________ – results from interactions between the R groups of the amino acids 4. Two or more polypeptide chains (subunits) associate providing __________________________ ________________________ Label each level on this diagram Denature Protein structure is key to their function ________________________ – a protein ______________________________________ (and consequently its ___________________________) when it is taken out of its natural range for factors such as temperature, pH, or salinity 3. Nucleic Acids (monomer = nucleotide) Function: _________________________ material and instructions for making ________________ Two types: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Nucleotides - _____________________ are the building blocks of _________________ __________. Have 3 parts: 1. ___________________________________ 2. ___________________________________ 3. ___________________________________ 4 base pairs There are ___ base pairs: Nitrogenous bases are __________________ (A) ___________________(T) __________________ (C) __________________ (G) RNA also has A, C, and G, but instead of T, it has ___________________ (U) Double Helix Two DNA strands wrap around each other to form a _____________ ____________. –The two strands are connected by a _________________ ____________between the base pairs. –____ pairs with ____ –____ pairs with ____ *U pairs with _________ RNA is usually a ___________ strand ________________ are enough ___________________ to code for the sequence of amino acids for ______________________________________ (primary structure of proteins). Genes do not use DNA to code directly. Genes use an intermediary (RNA). The DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into the amino acid sequence. Flow of information: _____________ ____________ ____________________ 4. Lipids Functions: _____________________________- fats store twice as many calories/gram as carbs. Protection of vital organs and insulation in humans and other mammals. ____________________________ make up cell membranes. _____________________ are often in cell membranes (cholesterol) and make up some hormones (estrogen and testosterone) Monomer: No single monomer for lipids (each type of lipid has its own monomers) Lipids are _________________________________ – Will not mix with water Types of lipids: 1. Fats Fats can be Saturated or Unsaturated. Saturated – * * * Unsaturated – * * * 2. _____________________________ - Form cell membranes 3. _________________________ - cell messengers examples: 4. ___________________________ - protection and waterproofing