Example Problem Set for CHEM106 Section 002 Test 2
... monoprotic acid (Ka = 1.7 x10-5) what would the pH be in the final 100 mL solution? 17) Draw the chemical structure of the following compounds: a) b) c) d) ...
... monoprotic acid (Ka = 1.7 x10-5) what would the pH be in the final 100 mL solution? 17) Draw the chemical structure of the following compounds: a) b) c) d) ...
Biochemistry of Sulfur
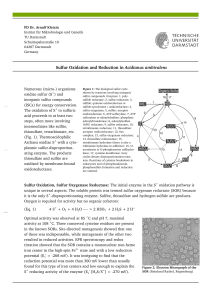
... The predicted orientation and the molecular composition of the Ac. ambivalens SR deduced from the biochemical results and the sequence analysis are similar to the W. succinogenes PSR (Fig. 7). Both enzymes consist of homologous catalytic and electron transfer subunits (SreA/PsrA and SreB/PsrB, resp ...
... The predicted orientation and the molecular composition of the Ac. ambivalens SR deduced from the biochemical results and the sequence analysis are similar to the W. succinogenes PSR (Fig. 7). Both enzymes consist of homologous catalytic and electron transfer subunits (SreA/PsrA and SreB/PsrB, resp ...
Oxidation Numbers and Writing Redox Equations
... but don’t appear in the overall redox equation. The electrons, on different sides of the half equations, cancel out when the half equations are added. ...
... but don’t appear in the overall redox equation. The electrons, on different sides of the half equations, cancel out when the half equations are added. ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... the arrangement of bonded atoms or ions within a substance. • a. Two terms are used to specify the relative positions of atoms to each other in a compound. − (1) Bond length - gives the distance between the two nuclei of the atoms − (2) Bond angles tell how these atoms are oriented when you have thr ...
... the arrangement of bonded atoms or ions within a substance. • a. Two terms are used to specify the relative positions of atoms to each other in a compound. − (1) Bond length - gives the distance between the two nuclei of the atoms − (2) Bond angles tell how these atoms are oriented when you have thr ...
Understanding an Enzyme Active Site
... alpha helices and/or beta sheets (secondary structure) connected by short turns of less regular protein structure. In the space below, draw and label examples of primary, secondary and tertiary structures. ...
... alpha helices and/or beta sheets (secondary structure) connected by short turns of less regular protein structure. In the space below, draw and label examples of primary, secondary and tertiary structures. ...
Chapter 4 - Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry
... protein to change. This can be caused by changes in temperature, pH, or salt concentration. For example, acid causes milk to curdle and heat (cooking) causes egg whites to coagulate because the proteins within them denature. If the protein is not severely denatured, it may regain its normal structur ...
... protein to change. This can be caused by changes in temperature, pH, or salt concentration. For example, acid causes milk to curdle and heat (cooking) causes egg whites to coagulate because the proteins within them denature. If the protein is not severely denatured, it may regain its normal structur ...
1. Review (MC problems, due Monday) 2. - mvhs
... (a) Write equations for the decomposition of both carbonates described above. (b) It was also determined that the initial sample contained 0.0448 gram of calcium. What percent of the limestone by mass was CaCO3? (c) How many grams of the magnesium-containing product were present in the sample in (a) ...
... (a) Write equations for the decomposition of both carbonates described above. (b) It was also determined that the initial sample contained 0.0448 gram of calcium. What percent of the limestone by mass was CaCO3? (c) How many grams of the magnesium-containing product were present in the sample in (a) ...
File
... Biomolecule – large molecule found in living organisms that consists of repeating subunit. typically consists of a carbon backbone Monomer – single repeating subunit Polymer – many monomers bonded together Saturated fat – a lipid that is completely saturated in hydrogen atoms – no double bonds betwe ...
... Biomolecule – large molecule found in living organisms that consists of repeating subunit. typically consists of a carbon backbone Monomer – single repeating subunit Polymer – many monomers bonded together Saturated fat – a lipid that is completely saturated in hydrogen atoms – no double bonds betwe ...
Nadine Noelting
... superfamily. This is roughly located between amino acids 120 and 420. The mutations associated with my gene are found in this conserved domain. The family consists of nonheme, iron (II)- dependent enzymes, including phenylalanine hydroxylase, eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase, and eukaryotic tryptopha ...
... superfamily. This is roughly located between amino acids 120 and 420. The mutations associated with my gene are found in this conserved domain. The family consists of nonheme, iron (II)- dependent enzymes, including phenylalanine hydroxylase, eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase, and eukaryotic tryptopha ...
File - Mr. Holz`s Website
... put together to form polymers (dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis) a. What properties of the molecules allows for dehydration synthesis? (H and OH on each side of macromolecules) b. What happens with water for each process? ...
... put together to form polymers (dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis) a. What properties of the molecules allows for dehydration synthesis? (H and OH on each side of macromolecules) b. What happens with water for each process? ...
STUDY GUIDE
... carbohydrates, peptide bond, amino acids, glycerol, disaccharide, fatty acids, proteins, unsaturated, organic compounds, oxygen, polymerization, carbon, lipids, saturated) Living organisms are composed of a special category of molecules called ______________________. Molecules must have both _______ ...
... carbohydrates, peptide bond, amino acids, glycerol, disaccharide, fatty acids, proteins, unsaturated, organic compounds, oxygen, polymerization, carbon, lipids, saturated) Living organisms are composed of a special category of molecules called ______________________. Molecules must have both _______ ...
Carbon Isomers
... Chaperones • Once thought newly made proteins folded spontaneously • Chaperone proteins help protein fold correctly • Deficiencies in chaperone proteins implicated in certain diseases – Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disorder • In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequenc ...
... Chaperones • Once thought newly made proteins folded spontaneously • Chaperone proteins help protein fold correctly • Deficiencies in chaperone proteins implicated in certain diseases – Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disorder • In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequenc ...
The Chemistry of Life
... a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required ...
... a. All enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes b. Most are proteins c. Speed up reaction or reduce activation energy required ...
Proteins - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... Hydrocarbons – contain only C & H (ex. CH4) Most also include oxygen and some also have nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Carbon can form thousands of different compounds because it can form 4 strong covalent bonds ...
... Hydrocarbons – contain only C & H (ex. CH4) Most also include oxygen and some also have nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Carbon can form thousands of different compounds because it can form 4 strong covalent bonds ...
CHEMISTRY-1 CHAPTER 8 CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... as a model 3. Balance it Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... as a model 3. Balance it Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... __________________ and antiparallel β-sheets are when they are in __________________ orientations b. β-sheets have some __________________ properties i. They are what give silk its incredible __________________ ii. They are abundant in __________________ proteins in insects that prevent them from fr ...
... __________________ and antiparallel β-sheets are when they are in __________________ orientations b. β-sheets have some __________________ properties i. They are what give silk its incredible __________________ ii. They are abundant in __________________ proteins in insects that prevent them from fr ...
1999
... o Understanding chemical equations, what all the symbols and numbers mean and which substances are the reactants and products. Example: photosynthesis and cellular respiration o Determine if an equation is balanced: Law of Conservation of Matter o Identify the number of atoms of each element found i ...
... o Understanding chemical equations, what all the symbols and numbers mean and which substances are the reactants and products. Example: photosynthesis and cellular respiration o Determine if an equation is balanced: Law of Conservation of Matter o Identify the number of atoms of each element found i ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Nerve activates contraction
... Toxicity: easier to OD on these than on water soluble vitamins ◦ ADEK excesses are stored in your fat cells ◦ Other vitamins are excreted in the water based urine ...
... Toxicity: easier to OD on these than on water soluble vitamins ◦ ADEK excesses are stored in your fat cells ◦ Other vitamins are excreted in the water based urine ...
Changing Coordination Numbers: Nickel Complexes
... A complex ion is a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A complex or coordination compound is a compound consisting either of complex ions with other ions of opposite charge or of a neutral complex species. Ligands are the Lewis bases attached to the metal ato ...
... A complex ion is a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A complex or coordination compound is a compound consisting either of complex ions with other ions of opposite charge or of a neutral complex species. Ligands are the Lewis bases attached to the metal ato ...
Inorganic Chemistry Basics
... Plot of charge/radius ratio against the ionization energy (M to M2+) for some divalent metal ions ...
... Plot of charge/radius ratio against the ionization energy (M to M2+) for some divalent metal ions ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.