Bio Chap 2 Biomolecules
... Control rates of reaction - enzymes Transport substances in & out of the cell - hormones, channel proteins ...
... Control rates of reaction - enzymes Transport substances in & out of the cell - hormones, channel proteins ...
Biomolecules
... it to form up to four covalent bonds • Hydrocarbons consist only of C and H – Propane CH8 ...
... it to form up to four covalent bonds • Hydrocarbons consist only of C and H – Propane CH8 ...
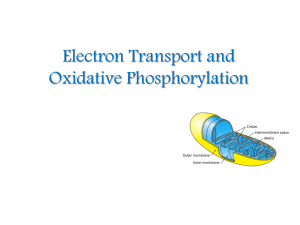
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
... molecules. because each contains a pair of electrons having a high transfer potential. ...
... molecules. because each contains a pair of electrons having a high transfer potential. ...
(1) Identify the secondary structure described in each of the
... stable protein consisting of a triple helix – three polypeptide chains wound around each other. When gelatin is mixed with hot water, the triple helix structure unwinds and the chains separate becoming random coils that dissolve in the water. As the dissolved gelatin mixture cools, the collagen form ...
... stable protein consisting of a triple helix – three polypeptide chains wound around each other. When gelatin is mixed with hot water, the triple helix structure unwinds and the chains separate becoming random coils that dissolve in the water. As the dissolved gelatin mixture cools, the collagen form ...
Chapter 3 Chemistry of Life Modern Biology Textbook Holt
... • Polysaccharides • Three or more monosaccharide's join to form large macromolecules such as starches, cellulose, chitin & glycogen. These are complex carbohydrates ...
... • Polysaccharides • Three or more monosaccharide's join to form large macromolecules such as starches, cellulose, chitin & glycogen. These are complex carbohydrates ...
CHEM 220 Problem Set 3
... 4) What is the purpose of the sulfuric acid in these reactions? 5) What is the difference between “regular” glass and Pyrex or Kimax? 6) Describe (using sketches) Zone Purification of Si cylinders. 7) Write out the synthesis, including mechanism, of the amides of the following ...
... 4) What is the purpose of the sulfuric acid in these reactions? 5) What is the difference between “regular” glass and Pyrex or Kimax? 6) Describe (using sketches) Zone Purification of Si cylinders. 7) Write out the synthesis, including mechanism, of the amides of the following ...
Organic Polymers Synthetic and Natural
... Where R is the resistance, I the current and V the voltage present in the material. The conduc'vity depends on the number of charge carriers (number of electrons) in the material and their mobility.I ...
... Where R is the resistance, I the current and V the voltage present in the material. The conduc'vity depends on the number of charge carriers (number of electrons) in the material and their mobility.I ...
Broomfield High School
... 1. Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form molecules that are large, complex and diverse. Why? a. It has four valence electrons. b. It can form up to 4 covalent bonds. c. These can be single, double, or triple covalent bonds. d. It can form large molecules. e. These molecules can be chains, r ...
... 1. Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form molecules that are large, complex and diverse. Why? a. It has four valence electrons. b. It can form up to 4 covalent bonds. c. These can be single, double, or triple covalent bonds. d. It can form large molecules. e. These molecules can be chains, r ...
Rxn Pred students
... non-spontaneous redox reaction is brought about by the passage of current under sufficient external electrical potential. The devices in which electrolysis reactions occur are called electrolytic cells. ...
... non-spontaneous redox reaction is brought about by the passage of current under sufficient external electrical potential. The devices in which electrolysis reactions occur are called electrolytic cells. ...
Template to create a scientific poster
... HSPA1A is the major heat-inducible Hsp70 in humans and is a key player in several signaling pathways that regulate protein homeostasis, cell survival. This protein has been associated with a variety of human conditions including breast and ovarian cancer, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Th ...
... HSPA1A is the major heat-inducible Hsp70 in humans and is a key player in several signaling pathways that regulate protein homeostasis, cell survival. This protein has been associated with a variety of human conditions including breast and ovarian cancer, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Th ...
TM shape and colour
... • For each of the following complexes, give the charge on the central metal ion and its coordination number and its name ...
... • For each of the following complexes, give the charge on the central metal ion and its coordination number and its name ...
Chapter 3 Notes Set 7
... 5. ___________ at least one more time from the beginning with a fresh sample of protein, but choose a ____________________. Need this to put fragments in the proper order. 6. To finish the complete sequence, the location of S-S bonds must be determined. use ______________________________________ - ...
... 5. ___________ at least one more time from the beginning with a fresh sample of protein, but choose a ____________________. Need this to put fragments in the proper order. 6. To finish the complete sequence, the location of S-S bonds must be determined. use ______________________________________ - ...
The Study of Life
... Each protein has a specific role, ex : 1. Control the rate of reactions & regulate cell processes. 2. Form bones, muscles, & hormones. 3. Transport substances in or out of cells & fight disease : antibodies. Enzymes – proteins that help control chemical reactions. Can speed up reactions, ex : ...
... Each protein has a specific role, ex : 1. Control the rate of reactions & regulate cell processes. 2. Form bones, muscles, & hormones. 3. Transport substances in or out of cells & fight disease : antibodies. Enzymes – proteins that help control chemical reactions. Can speed up reactions, ex : ...
24_Test - Ventura College
... Which of the following is not true of metal-ion catalysis? A. It can make a reaction center more susceptible to ...
... Which of the following is not true of metal-ion catalysis? A. It can make a reaction center more susceptible to ...
Metabolism: the chemical reactions of a cell
... is not consumed in the reaction, but can be re-used. Enzymes are biological catalysts; 99.99% of them are proteins. Enzymes are very specific; a different one is required for each type of chemical reaction. Because the 3-D shape of an enzyme is critical for its function, anything that alters that (h ...
... is not consumed in the reaction, but can be re-used. Enzymes are biological catalysts; 99.99% of them are proteins. Enzymes are very specific; a different one is required for each type of chemical reaction. Because the 3-D shape of an enzyme is critical for its function, anything that alters that (h ...
File
... Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process and is provided by the pe ...
... Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process and is provided by the pe ...
Lecture 6
... • Define metabolism, and describe the fundamental differences between anabolism and catabolism. • Identify the role of ATP as an intermediate between catabolism and anabolism. • Identify the components of an enzyme. • Describe the mechanism of enzymatic action. • List the factors that influence enzy ...
... • Define metabolism, and describe the fundamental differences between anabolism and catabolism. • Identify the role of ATP as an intermediate between catabolism and anabolism. • Identify the components of an enzyme. • Describe the mechanism of enzymatic action. • List the factors that influence enzy ...
Document
... range of 1–2 eV, being lowerfor a tetrahedral ligand field than for an octahedral field. Hence absorption of light, associated with electronic transitions between the lower and upper d levels, generally occurs in the visible or near IR regions of the spectrum. The situation is actually a little more ...
... range of 1–2 eV, being lowerfor a tetrahedral ligand field than for an octahedral field. Hence absorption of light, associated with electronic transitions between the lower and upper d levels, generally occurs in the visible or near IR regions of the spectrum. The situation is actually a little more ...
A Review of High School Chemistry
... now manipulate all manner of unit factors to solve problems involving amounts of chemical materials, and while there was some modest requirement that you understand the nature of the substances involved in the problems, you might just as well have applied the techniques you learned to solve problems ...
... now manipulate all manner of unit factors to solve problems involving amounts of chemical materials, and while there was some modest requirement that you understand the nature of the substances involved in the problems, you might just as well have applied the techniques you learned to solve problems ...
Chapter 3 Biological Molecules
... Inorganic refers to carbon dioxide and all molecules without carbon ...
... Inorganic refers to carbon dioxide and all molecules without carbon ...
2.6 Natural Polymers
... Nucleotides Have Three Parts 3) A phosphoric acid molecule (phosphate group) ...
... Nucleotides Have Three Parts 3) A phosphoric acid molecule (phosphate group) ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.