Slide 1
... •Ankyrin Repeats Domain (ARD) monomeric in solution. •Ankyrin repeats are approximately 33 amino acid residues in length consisting of two anti-parallel alpha helices separated by intervening finger loop regions. •The three-dimensional structure of TRPV2-ARD consists of 6 ankyrin repeat structure mo ...
... •Ankyrin Repeats Domain (ARD) monomeric in solution. •Ankyrin repeats are approximately 33 amino acid residues in length consisting of two anti-parallel alpha helices separated by intervening finger loop regions. •The three-dimensional structure of TRPV2-ARD consists of 6 ankyrin repeat structure mo ...
Quiz 2
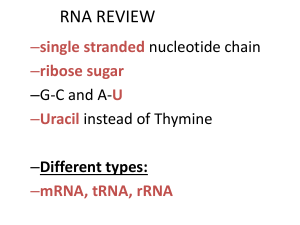
... - Base pairing through complimentary base pairing with hydrogen bonds - Adenine and Thymine – two bond - Cytosine and Guanine – Three bonds - Structure – Consensation rxn builds chain of nucelotides from a phosphodiester bond. New phosphate 5' attaches to 3' side of sugar. Grows in a 5' to 3' direct ...
... - Base pairing through complimentary base pairing with hydrogen bonds - Adenine and Thymine – two bond - Cytosine and Guanine – Three bonds - Structure – Consensation rxn builds chain of nucelotides from a phosphodiester bond. New phosphate 5' attaches to 3' side of sugar. Grows in a 5' to 3' direct ...
Test #1 Study Guide
... is equal to its atomic number Avagadro’s number indicates the amount of particles, molecules, etc. in a mole. There are always 6.022 x 10^23 particles in one mole of a substance. If you are given grams of a substance, you can find the amount of moles by multiplying the grams of substance by 1 mol/ a ...
... is equal to its atomic number Avagadro’s number indicates the amount of particles, molecules, etc. in a mole. There are always 6.022 x 10^23 particles in one mole of a substance. If you are given grams of a substance, you can find the amount of moles by multiplying the grams of substance by 1 mol/ a ...
Basic_Chemistry___Biochemistry__Ch_2__S2
... Carbon can make four bonds with many types of atoms including itself; can form large molecules Result: many different types of organic molecules each with a unique structure and therefore function ...
... Carbon can make four bonds with many types of atoms including itself; can form large molecules Result: many different types of organic molecules each with a unique structure and therefore function ...
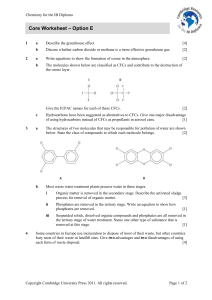
Core Worksheet – Option E - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... Suspended solids, dissolved organic compounds and phosphates are all removed in the tertiary stage of water treatment. Name one other type of substance that is removed at this stage. ...
... Suspended solids, dissolved organic compounds and phosphates are all removed in the tertiary stage of water treatment. Name one other type of substance that is removed at this stage. ...
Chapter 2: The Chemical Level of Organization
... spheres around ions and small polar molecules to keep them in solution ...
... spheres around ions and small polar molecules to keep them in solution ...
Energetics - The Practical Educator
... Amino acids • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9GzR-k7-dZ4 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qBRFIMcxZNM ...
... Amino acids • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9GzR-k7-dZ4 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qBRFIMcxZNM ...
Chapter Five: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... and Function of Macromolecules) online, pages 1-5, to complete the following questions. The reading is linked on the calendar. 1. List the four main classes of macromolecules. (Note: Nucleic Acids are not considered nutrients found in food). ...
... and Function of Macromolecules) online, pages 1-5, to complete the following questions. The reading is linked on the calendar. 1. List the four main classes of macromolecules. (Note: Nucleic Acids are not considered nutrients found in food). ...
Document
... University of Cambridge International Examinations is part of the University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES) which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. ...
... University of Cambridge International Examinations is part of the University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES) which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. ...
Microbial Metabolism Lipids and Proteins - ASAB-NUST
... Protein and Amino Acid Catabolism • The first step in amino acid use is deamination, the removal of the amino group from an amino acid. This is often accomplished by transamination. • The amino group is transferred from an amino acid to an α keto acid acceptor. • The organic acid resulting from dea ...
... Protein and Amino Acid Catabolism • The first step in amino acid use is deamination, the removal of the amino group from an amino acid. This is often accomplished by transamination. • The amino group is transferred from an amino acid to an α keto acid acceptor. • The organic acid resulting from dea ...
Document
... carboxyl group for nucleophilic attack by an amine and consequent formation of a peptide bond. This activation can be achieved in a variety of ways - see examples on pg 44. In the example of peptide synthesis presented in class the carboxyl group was activated by reaction with a carbodiimide. Anothe ...
... carboxyl group for nucleophilic attack by an amine and consequent formation of a peptide bond. This activation can be achieved in a variety of ways - see examples on pg 44. In the example of peptide synthesis presented in class the carboxyl group was activated by reaction with a carbodiimide. Anothe ...
pages 44-48
... 8. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about carbohydrates. a. Starches and sugars are examples of carbohydrates. b. Living things use them as their main source of energy. c. The monomers in sugar polymers are starch molecules. d. Plants and some animals use them for strength and rigidit ...
... 8. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about carbohydrates. a. Starches and sugars are examples of carbohydrates. b. Living things use them as their main source of energy. c. The monomers in sugar polymers are starch molecules. d. Plants and some animals use them for strength and rigidit ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Practice exam #1 – answer key September 13
... a. An atom is mostly empty space. b. Almost all of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus. c. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus are very tightly packed. d. The number of protons and neutrons is always the same in the neutral atom. e. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. 22. ...
... a. An atom is mostly empty space. b. Almost all of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus. c. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus are very tightly packed. d. The number of protons and neutrons is always the same in the neutral atom. e. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. 22. ...
13.2 Chemical Formulas
... What is a chemical formula? Chemical formulas have two important parts: chemical symbols for the elements in the compound and subscripts that tell how many atoms of each element are needed to form the compound. The chemical formula for water, H2O, tells us that a water molecule is made of the elemen ...
... What is a chemical formula? Chemical formulas have two important parts: chemical symbols for the elements in the compound and subscripts that tell how many atoms of each element are needed to form the compound. The chemical formula for water, H2O, tells us that a water molecule is made of the elemen ...
Name__________________________ Period_______ Word
... Write a balanced chemical equation, including the reaction conditions, to represent each of the following chemical reactions. (Don’t forget your diatomic molecules) 6. Mercury(II) oxide in solution when heated yields liquid mercury and oxygen gas. ...
... Write a balanced chemical equation, including the reaction conditions, to represent each of the following chemical reactions. (Don’t forget your diatomic molecules) 6. Mercury(II) oxide in solution when heated yields liquid mercury and oxygen gas. ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... Proteins (polypeptides) are large polymers that are made from monomers called amino acids. Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
... Proteins (polypeptides) are large polymers that are made from monomers called amino acids. Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
S294 Are you Ready for S294 e1i1 web029856
... form ionic bonds with other atoms by transferring bonding electrons, and so themselves become positively charged ions. The atoms of the element to which the metal transfers electrons become negatively charged ions, and the resulting molecules are electrically neutral overall. Sodium chloride (common ...
... form ionic bonds with other atoms by transferring bonding electrons, and so themselves become positively charged ions. The atoms of the element to which the metal transfers electrons become negatively charged ions, and the resulting molecules are electrically neutral overall. Sodium chloride (common ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... John Dalton (in 1805) proposes his Atomic Theory to explain the results of the quantitative studies of several scientists (including Lavoisier, Proust, and himself, among many others). Dalton’s Atomic Theory a. Elements consist of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. b. All the atoms of a given ...
... John Dalton (in 1805) proposes his Atomic Theory to explain the results of the quantitative studies of several scientists (including Lavoisier, Proust, and himself, among many others). Dalton’s Atomic Theory a. Elements consist of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. b. All the atoms of a given ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... One set of ligands may be displaced by others that form stronger co-ordinate bonds, or which are present in very high concentration – this is called ligand substitution: When copper(II) sulfate solution is treated with dilute aqueous ammonia, the solution starts blue because of the Cu(H2O)62+ ion. I ...
... One set of ligands may be displaced by others that form stronger co-ordinate bonds, or which are present in very high concentration – this is called ligand substitution: When copper(II) sulfate solution is treated with dilute aqueous ammonia, the solution starts blue because of the Cu(H2O)62+ ion. I ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... 5. On the periodic table, what are groups and periods? Groups are the columns and share similar properties, periods are rows across the table 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in ...
... 5. On the periodic table, what are groups and periods? Groups are the columns and share similar properties, periods are rows across the table 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... is stored as energy sources in animal tissues. It is more extensively branched and more water soluble. Glycogen is stored mainly in the liver and muscle cells. Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrate; it accounts for 50% or more of all the carbon in plants. Cellulose is a structural carbohydrate ...
... is stored as energy sources in animal tissues. It is more extensively branched and more water soluble. Glycogen is stored mainly in the liver and muscle cells. Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrate; it accounts for 50% or more of all the carbon in plants. Cellulose is a structural carbohydrate ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.