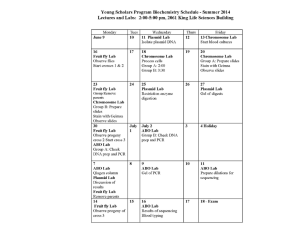
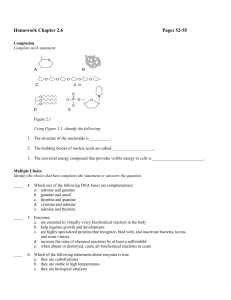
Assignment 5 Bioenergy/ Photosynthesis
... replace the electrons lost from the first pigment system (PSII). Remember PSII gave its electrons to the second pigment system (PSI). The H+ ion moves across the thylakoid membrane where the cytochrome complexes are embedded to cause a build-up of potential energy. This gradient energy is allowed to ...
... replace the electrons lost from the first pigment system (PSII). Remember PSII gave its electrons to the second pigment system (PSI). The H+ ion moves across the thylakoid membrane where the cytochrome complexes are embedded to cause a build-up of potential energy. This gradient energy is allowed to ...
Metabolism Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions within an
... α- mucoitin polysulphuric acid inhibits the formation of thrombin from prothrombin. It's usually available as the Na, NH4 and Li salts. 2- ………………………………………………………………..it precipitates calcium ions which are essential for clotting mechanism. Its dipotasium and dilithium salts are most often used. 3- ……… ...
... α- mucoitin polysulphuric acid inhibits the formation of thrombin from prothrombin. It's usually available as the Na, NH4 and Li salts. 2- ………………………………………………………………..it precipitates calcium ions which are essential for clotting mechanism. Its dipotasium and dilithium salts are most often used. 3- ……… ...
Chemical equations must be balanced.
... This equation is not balanced. There is one C on each side of the equation, so C is balanced. However, on the left side, H has a subscript of 4, which means there are four hydrogen atoms. On the right side, H has a subscript of 2, which means there are two hydrogen atoms. Also, there are two oxygen ...
... This equation is not balanced. There is one C on each side of the equation, so C is balanced. However, on the left side, H has a subscript of 4, which means there are four hydrogen atoms. On the right side, H has a subscript of 2, which means there are two hydrogen atoms. Also, there are two oxygen ...
enzymes are proteins
... • Law: A law that generalizes a body of observations. At the time it is made, no exceptions have been found to a law. It explains things but does not describe them; serves as the basis of scientific principles. (Ex: Law of Gravity, Newton’s Laws of motion). • Theory: A proposed explanation for obser ...
... • Law: A law that generalizes a body of observations. At the time it is made, no exceptions have been found to a law. It explains things but does not describe them; serves as the basis of scientific principles. (Ex: Law of Gravity, Newton’s Laws of motion). • Theory: A proposed explanation for obser ...
Chapter 3
... 3. since carbon can form up to 4 single bonds, there are a wide variety of compounds it can form 4. chemists group organic compounds into classes with similar characteristics to make their study easier ...
... 3. since carbon can form up to 4 single bonds, there are a wide variety of compounds it can form 4. chemists group organic compounds into classes with similar characteristics to make their study easier ...
Coordination Complexes
... Metals with high charge are more likely to be low spin with large d splittings. The ligands can be arranged in a series called the spectrochemical series. At one end of the series the “strong field” ligands usually give large d splittings and low spin complexes, at the other end of the series, the “ ...
... Metals with high charge are more likely to be low spin with large d splittings. The ligands can be arranged in a series called the spectrochemical series. At one end of the series the “strong field” ligands usually give large d splittings and low spin complexes, at the other end of the series, the “ ...
Protein
... Protein is made of chains of substances called amino acids: a type of organic acid. – Organic acids are molecules that contain a carboxyl group (COOH). – They also contain an amine group: two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of nitrogen (-NH2). ...
... Protein is made of chains of substances called amino acids: a type of organic acid. – Organic acids are molecules that contain a carboxyl group (COOH). – They also contain an amine group: two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of nitrogen (-NH2). ...
nucleic acids
... • Using the example of Kool-Aid and water, identify the solute and solvent. • T/F Water is polar. This means it has an uneven distribution of electrons. • In water, acids release excess _______ ions. In water, bases release excess _______ ions. ...
... • Using the example of Kool-Aid and water, identify the solute and solvent. • T/F Water is polar. This means it has an uneven distribution of electrons. • In water, acids release excess _______ ions. In water, bases release excess _______ ions. ...
Nitrogen Anabolism
... Haber-Bosch Cycle N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 500oC, 300 ATM •Ammonia was first made on an industrial scale in 1913. •Critical for the German munitions effort. •Later, principally used to make fertilizer, allowing more efficient food production. •Nearly 80% of the nitrogen found in human tissues originated ...
... Haber-Bosch Cycle N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 500oC, 300 ATM •Ammonia was first made on an industrial scale in 1913. •Critical for the German munitions effort. •Later, principally used to make fertilizer, allowing more efficient food production. •Nearly 80% of the nitrogen found in human tissues originated ...
Ch6PROTEIN
... when conditions are acidic, and donating hydrogen ions when conditions are alkaline • Otherwise, the resulting conditions of acidosis or alkalosis could lead to coma or death Transport Functions • Lipoproteins • Albumin transports a variety of nutrients such as calcium, zinc, and Vitamin B6 • Transf ...
... when conditions are acidic, and donating hydrogen ions when conditions are alkaline • Otherwise, the resulting conditions of acidosis or alkalosis could lead to coma or death Transport Functions • Lipoproteins • Albumin transports a variety of nutrients such as calcium, zinc, and Vitamin B6 • Transf ...
DISULFIDE GROUPS Disulfide bonds in proteins are
... Haber (1961) for the reduction and reoxidation of pancreatic ribonuclease. Reduction. In a typical experiment, 350 mg of ribonuclease were dissolved in 10 ml of a freshly prepared 8 M solution of recrystallized urea, adjusted to pH 8.6 with 5% methylamine. Mercaptoethanol was added at a level of 1 µ ...
... Haber (1961) for the reduction and reoxidation of pancreatic ribonuclease. Reduction. In a typical experiment, 350 mg of ribonuclease were dissolved in 10 ml of a freshly prepared 8 M solution of recrystallized urea, adjusted to pH 8.6 with 5% methylamine. Mercaptoethanol was added at a level of 1 µ ...
Exam II Review: - Texas Tech University
... 1. Protein folding occurs as it is being synthesized. 2. Protein is facilitated by chaperone proteins that prevent interaction of protein with other molecules. a. HSP70 and HSP60 use ATP to bind and unbind folding protein. b. Protein folding errors cause diseases. c. Ubiquitin and proteosomes funct ...
... 1. Protein folding occurs as it is being synthesized. 2. Protein is facilitated by chaperone proteins that prevent interaction of protein with other molecules. a. HSP70 and HSP60 use ATP to bind and unbind folding protein. b. Protein folding errors cause diseases. c. Ubiquitin and proteosomes funct ...
COMPLEXING ABILITY OF REE IMMOBILIZED IN A POLYMER
... too. Ionic conductors based on polymeric materials have several advantages over existing and currently used by solid electrolytes, such as silver iodide. The action nonmetalocene organometallic derivatives of rare earth metals in the catalysis of unsaturated substrates’ transformations are considere ...
... too. Ionic conductors based on polymeric materials have several advantages over existing and currently used by solid electrolytes, such as silver iodide. The action nonmetalocene organometallic derivatives of rare earth metals in the catalysis of unsaturated substrates’ transformations are considere ...
Biochemistry PPT - Madison County Schools
... Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds with other atoms. ...
... Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds with other atoms. ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... start the process 30 molecules of NADH are produced 6 molecules of FADH2 are produced 18 molecules of ATP are produced via substrate phosphorylation (12 in glycolysis and 6 in Krebs) 18 molecules of water are produced in ETS 18 molecules of CO2 are released from the process ...
... start the process 30 molecules of NADH are produced 6 molecules of FADH2 are produced 18 molecules of ATP are produced via substrate phosphorylation (12 in glycolysis and 6 in Krebs) 18 molecules of water are produced in ETS 18 molecules of CO2 are released from the process ...
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
... • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.