Chem+174–Lecture+12a..
... a p-bond, yet it binds to some metal centers as intact molecule (meaning it does not perform an oxidative addition!) The s-bond of the H2 molecule is the electron donor in this bond (red bond), while the s*-orbital acts as an acceptor for the back-bonding (blue bond) In order to maximize the overlap ...
... a p-bond, yet it binds to some metal centers as intact molecule (meaning it does not perform an oxidative addition!) The s-bond of the H2 molecule is the electron donor in this bond (red bond), while the s*-orbital acts as an acceptor for the back-bonding (blue bond) In order to maximize the overlap ...
Protein Structure and Function
... Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) belong to the superfamily of proteins containing a heme cofactor and, therefore, are hemoproteins. CYPs use a variety of small and large molecules as substrates in enzymatic reactions. Often, they form part of multi-component electron transfer chains, called P450-containing s ...
... Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) belong to the superfamily of proteins containing a heme cofactor and, therefore, are hemoproteins. CYPs use a variety of small and large molecules as substrates in enzymatic reactions. Often, they form part of multi-component electron transfer chains, called P450-containing s ...
lecture 5
... - slow because it involves rotation about a partial double-bond (t1/2 between 10-100 sec at 25ºC) - cis-trans equilibria more common in flexible regions of native proteins (e.g., coils) OR: during protein folding ...
... - slow because it involves rotation about a partial double-bond (t1/2 between 10-100 sec at 25ºC) - cis-trans equilibria more common in flexible regions of native proteins (e.g., coils) OR: during protein folding ...
Lipids, Carbohydrates, and Proteins!
... Humans can make 12 amino acids How do they get the others? Must ingest remaining 8 amino acids ...
... Humans can make 12 amino acids How do they get the others? Must ingest remaining 8 amino acids ...
Protein Basics
... • Used computer models of small polypeptides to systematically vary φ and ψ with the objective of finding stable conformations • For each conformation, the structure was examined for close contacts between atoms • Atoms were treated as hard spheres with dimensions corresponding to their van der Waal ...
... • Used computer models of small polypeptides to systematically vary φ and ψ with the objective of finding stable conformations • For each conformation, the structure was examined for close contacts between atoms • Atoms were treated as hard spheres with dimensions corresponding to their van der Waal ...
Intro to Chemical Equations note
... HALOGEN HON: When any halogen (Group 17), hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen are by themselves in an equation, they are shown as DIATOMIC ELEMENTS. H2 O2 N2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 ...
... HALOGEN HON: When any halogen (Group 17), hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen are by themselves in an equation, they are shown as DIATOMIC ELEMENTS. H2 O2 N2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 ...
3 MoleculesCells
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
coordination chemistry notes
... Energy would be weak. Thus, it can be extrapolated as a covalent factor, so polarizing power and polarizability of the electrons becomes important. Thus soft transition metal acids with dn electrons where n >= 6 show soft-soft interactions (particularly d10). The polarisation effects here resemble F ...
... Energy would be weak. Thus, it can be extrapolated as a covalent factor, so polarizing power and polarizability of the electrons becomes important. Thus soft transition metal acids with dn electrons where n >= 6 show soft-soft interactions (particularly d10). The polarisation effects here resemble F ...
pH - Bio-Link
... equilibrium by adding a compound that can dissociate in water to change the concentration of either H+ or OH- ions. An acid is a compound that can release H+ ions in solution. Bases are compounds that can accept H+ ions. In practical terms, a lower pH means a higher H+ concentration, or greater aci ...
... equilibrium by adding a compound that can dissociate in water to change the concentration of either H+ or OH- ions. An acid is a compound that can release H+ ions in solution. Bases are compounds that can accept H+ ions. In practical terms, a lower pH means a higher H+ concentration, or greater aci ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 16. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors participate. ...
... 16. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors participate. ...
Biological Molecules
... molecules eg. Starch and Glycogen have compact, coiled and branched molecules, making them ideal stores of energy ...
... molecules eg. Starch and Glycogen have compact, coiled and branched molecules, making them ideal stores of energy ...
Metabolism: the chemical reactions of a cell
... is not consumed in the reaction, but can be re-used. Enzymes are biological catalysts; 99.99% of them are proteins. Enzymes are very specific; a different one is required for each type of chemical reaction. Because the 3-D shape of an enzyme is critical for its function, anything that alters that (h ...
... is not consumed in the reaction, but can be re-used. Enzymes are biological catalysts; 99.99% of them are proteins. Enzymes are very specific; a different one is required for each type of chemical reaction. Because the 3-D shape of an enzyme is critical for its function, anything that alters that (h ...
221_exam_2_2003
... In the first section of this class we discussed stromatolites which are fossilized microbial mat communities. The microbial mats consisted of layers of different prokaryotic phototrophs. Based on what you have learned about the properties of the different kinds of phototrophs in this section of the ...
... In the first section of this class we discussed stromatolites which are fossilized microbial mat communities. The microbial mats consisted of layers of different prokaryotic phototrophs. Based on what you have learned about the properties of the different kinds of phototrophs in this section of the ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... • Glycine, NH2CH2COOH, the simplest of all naturally occurring amino acids, has a melting point of 292 °C. The pKa of the acid group is 2.35 and the pKa associated with the amino group is 9.78. Draw a Lewis structure that indicates the charges on the molecule at the physiological pH of 7.4. ...
... • Glycine, NH2CH2COOH, the simplest of all naturally occurring amino acids, has a melting point of 292 °C. The pKa of the acid group is 2.35 and the pKa associated with the amino group is 9.78. Draw a Lewis structure that indicates the charges on the molecule at the physiological pH of 7.4. ...
Predicting Products online assistance #3
... 3. single replacement - an element replaces another in a compound. 4. double replacement - the elements in two compounds switch partners to form two new compounds. Writing Balanced Equations A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different sub ...
... 3. single replacement - an element replaces another in a compound. 4. double replacement - the elements in two compounds switch partners to form two new compounds. Writing Balanced Equations A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different sub ...
The Chemical Basis for Life (Bio.A.2)
... • Adhesion – H bonds allow water molecules to stick to other, polar molecules – Capillary action (ex. straws) ...
... • Adhesion – H bonds allow water molecules to stick to other, polar molecules – Capillary action (ex. straws) ...
Notes
... C. Element – matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances via chemical reaction 1. there are 92 naturally-occurring elements 2. cannot be changed into a different element or destroyed via chemical reactions 3. about 25 elements are essential for life A) 4 of these make up 96% of living ...
... C. Element – matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances via chemical reaction 1. there are 92 naturally-occurring elements 2. cannot be changed into a different element or destroyed via chemical reactions 3. about 25 elements are essential for life A) 4 of these make up 96% of living ...
File
... • Polysaccharides • Three or more monosaccharide's join to form large macromolecules such as starches, cellulose, chitin & glycogen. These are complex carbohydrates ...
... • Polysaccharides • Three or more monosaccharide's join to form large macromolecules such as starches, cellulose, chitin & glycogen. These are complex carbohydrates ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 22. Describe the process of translation.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
... 22. Describe the process of translation.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
Photosynthesis: dark reactions
... and used to make amino acids • G-3-P (glyceraldehyde 3-P) is used to make fructose with is in turn used to make other sugars and starch • some fructose is converted into glucose; molecular of glucose are smaller and store more energy than ATP • fructose and glucose are used to make sucrose which is ...
... and used to make amino acids • G-3-P (glyceraldehyde 3-P) is used to make fructose with is in turn used to make other sugars and starch • some fructose is converted into glucose; molecular of glucose are smaller and store more energy than ATP • fructose and glucose are used to make sucrose which is ...
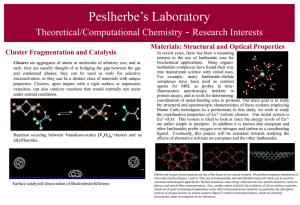
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... interest in the use of lanthanide ions for biochemical applications. Many organolanthanide complexes have found their way into mainstream science with varied uses. For example, many lanthanide-chelate complexes have been used as contrast agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, ma ...
... interest in the use of lanthanide ions for biochemical applications. Many organolanthanide complexes have found their way into mainstream science with varied uses. For example, many lanthanide-chelate complexes have been used as contrast agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, ma ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16. What do you understand by oxidative phosphorylation? Mention the role of subunits involved in complex V 17. Explain the process of glycogenolysis in detail. 18. Elaborate on the process of translation elongation. 19. What are the possible inborn errors of amino acid metabolism? Explain phenyl ke ...
... 16. What do you understand by oxidative phosphorylation? Mention the role of subunits involved in complex V 17. Explain the process of glycogenolysis in detail. 18. Elaborate on the process of translation elongation. 19. What are the possible inborn errors of amino acid metabolism? Explain phenyl ke ...
CHE-09 Biochemistry
... How do competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors alter an enzyme activity? ...
... How do competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors alter an enzyme activity? ...
How Enzymes Work
... some cases by shielding the had persistent structure and that catalytic site from contact with Elucidating the active site. In the crystal structure of a lysozyme mutant bound to destruction of that structure could a synthetic sugar substrate, the sugar ring in the active site is distorted, and the ...
... some cases by shielding the had persistent structure and that catalytic site from contact with Elucidating the active site. In the crystal structure of a lysozyme mutant bound to destruction of that structure could a synthetic sugar substrate, the sugar ring in the active site is distorted, and the ...
Default Normal Template - Philadelphia University Jordan
... 1 A mutation results in a single amino acid substitution of a protein. One technique that is more likely to be useful in differentiating between the normal and the mutant forms of the enzyme is a. Denatured SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. b. Native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. c. Gel ...
... 1 A mutation results in a single amino acid substitution of a protein. One technique that is more likely to be useful in differentiating between the normal and the mutant forms of the enzyme is a. Denatured SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. b. Native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. c. Gel ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.