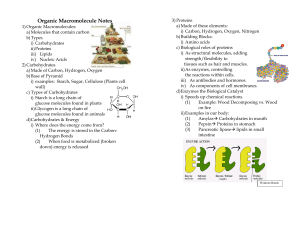
3. Proteins
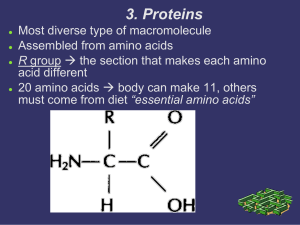
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... 1. Carbon forms bonds easily because it has 4 valence electrons. 2. Carbon atoms can bond to other carbon atoms, forming chains that are almost unlimited in length. 3. All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorous (P). ...
... 1. Carbon forms bonds easily because it has 4 valence electrons. 2. Carbon atoms can bond to other carbon atoms, forming chains that are almost unlimited in length. 3. All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorous (P). ...
Quiz Chapter 5 Organic Molecules
... Directions: Each group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of numbered phrases or sentences. For each numbered phrase or sentence, select the one heading that is most closely related to it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each heading may be used ...
... Directions: Each group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of numbered phrases or sentences. For each numbered phrase or sentence, select the one heading that is most closely related to it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each heading may be used ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
Amino acid metabolism III. Brake down of amino acids
... Mixed function oxidases: catalyze simultaneous hydroxylation of a substrate by an oxygen atom of O2 and reduction of the other oxygen atom to H2O ...
... Mixed function oxidases: catalyze simultaneous hydroxylation of a substrate by an oxygen atom of O2 and reduction of the other oxygen atom to H2O ...
Organic Macromolecule Notes
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
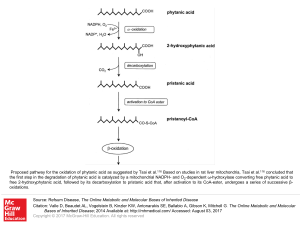
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
CH2 - SCF Faculty Site Homepage
... b. A patient in a coma is brought to the emergency room. A blood test shows that he has severe hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood glucose) and acidosis. Treatment is begun immediately to increase both blood sugar and pH. 1) Why is a normal level of blood glucose important? __________________________ ...
... b. A patient in a coma is brought to the emergency room. A blood test shows that he has severe hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood glucose) and acidosis. Treatment is begun immediately to increase both blood sugar and pH. 1) Why is a normal level of blood glucose important? __________________________ ...
Sample exam
... 14. Which molecules drawn above would you attribute the property of amphipathic. 15. Which processes below consume more energy than they produce? (consume ATP, NADPH etc ) Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis Citric acid cycle Cholesterol synthesis Pentose phosphate pathway Fatty acid oxidation Fatty acid bio ...
... 14. Which molecules drawn above would you attribute the property of amphipathic. 15. Which processes below consume more energy than they produce? (consume ATP, NADPH etc ) Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis Citric acid cycle Cholesterol synthesis Pentose phosphate pathway Fatty acid oxidation Fatty acid bio ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 9. What kind of molecules will result when a protein is completely hydrolyzed? A mixture of various amino acids will result. 10. What makes different kinds of proteins unique? The sequence of amino acids (primary structure) 11. Explain how a protein’s shape is determined. Some of the side chains for ...
... 9. What kind of molecules will result when a protein is completely hydrolyzed? A mixture of various amino acids will result. 10. What makes different kinds of proteins unique? The sequence of amino acids (primary structure) 11. Explain how a protein’s shape is determined. Some of the side chains for ...
Chapter 2: Biochemistry
... temperature are referred to as oils. If all the carbonto-carbon bonds are single bonds, that fat is said to be saturated. If one or more pairs of carbon are joined by a double or even triple bond, they are said to be unsaturated fats. If a fat just has one unsaturated bond, it is known as monounsatu ...
... temperature are referred to as oils. If all the carbonto-carbon bonds are single bonds, that fat is said to be saturated. If one or more pairs of carbon are joined by a double or even triple bond, they are said to be unsaturated fats. If a fat just has one unsaturated bond, it is known as monounsatu ...
Proteins, Lipids, and Carbs!!!
... The protein has become renatured The protein has become denatured The protein has reached its highest level of organization A None of the above ...
... The protein has become renatured The protein has become denatured The protein has reached its highest level of organization A None of the above ...
Chemistry of lipids Lipids are defined as a group of naturally
... 4. Building materials. Breakdown products of fats can be utilized for building biologically active materials like cholesterol, which in turn can be utilized for synthesis of certain hormones. 5. Lipids supply the essential fatty acids which cannot be synthesized in the body. 6. The nervous system is ...
... 4. Building materials. Breakdown products of fats can be utilized for building biologically active materials like cholesterol, which in turn can be utilized for synthesis of certain hormones. 5. Lipids supply the essential fatty acids which cannot be synthesized in the body. 6. The nervous system is ...
Lecture on Lipids
... chains of carbon atoms an acid group at one end and hydrogen atoms attached all along their length If not attached with other molecule--free fatty acid When metabolized yield ATP Heart and muscle---prefer fatty acid for fuel Without double bond---saturated With double bond---unsaturated ...
... chains of carbon atoms an acid group at one end and hydrogen atoms attached all along their length If not attached with other molecule--free fatty acid When metabolized yield ATP Heart and muscle---prefer fatty acid for fuel Without double bond---saturated With double bond---unsaturated ...
Chemistry of Life
... Unsaturated fatty acids have some single Covalent bonds but have double covalent bonds as well, like Linoleic acid Plant oils ...
... Unsaturated fatty acids have some single Covalent bonds but have double covalent bonds as well, like Linoleic acid Plant oils ...
Slide 1
... Ketone Bodies • Liver mitochondria can convert acetyl CoA derived from the oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies which are: 1- Acetoacetate 2- 3-hydroxybutyrate (or b-hydroxybutyrate) 3- Acetone (nonmetabolized side product) • Acetoacetate & 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesized in the liver are transp ...
... Ketone Bodies • Liver mitochondria can convert acetyl CoA derived from the oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies which are: 1- Acetoacetate 2- 3-hydroxybutyrate (or b-hydroxybutyrate) 3- Acetone (nonmetabolized side product) • Acetoacetate & 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesized in the liver are transp ...
Lipids Metabolism - GIT
... Ketone Bodies • Liver mitochondria can convert acetyl CoA derived from the oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies which are: 1- Acetoacetate 2- 3-hydroxybutyrate (or b-hydroxybutyrate) 3- Acetone (nonmetabolized side product) • Acetoacetate & 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesized in the liver are transp ...
... Ketone Bodies • Liver mitochondria can convert acetyl CoA derived from the oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies which are: 1- Acetoacetate 2- 3-hydroxybutyrate (or b-hydroxybutyrate) 3- Acetone (nonmetabolized side product) • Acetoacetate & 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesized in the liver are transp ...
Key: Biomolecule Study Guide 1) In animals, excess carbohydrates
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
Carbon Compounds in Cells
... storage, and transport agents (hormones, antibodies, and structural material) • Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins (peptide bonds) – Amino acids coil into a 3D structure – Heat can denatured proteins causing a change in shape and the ability to work properly ...
... storage, and transport agents (hormones, antibodies, and structural material) • Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins (peptide bonds) – Amino acids coil into a 3D structure – Heat can denatured proteins causing a change in shape and the ability to work properly ...
macromolecule packet
... Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms The most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds ar ...
... Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms The most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds ar ...
3.1 The Molecules of Life--From Structure to Function A. What Is An
... A. Lipids are greasy or oily compounds with little tendency to dissolve in water. 1. They can be broken down by hydrolysis reactions. ...
... A. Lipids are greasy or oily compounds with little tendency to dissolve in water. 1. They can be broken down by hydrolysis reactions. ...
Lipids
... • There are different types of fatty acids in one molecule of triglyceride. • Regardless of the degree saturation, all lipid have essentially the same number of calories per unit weight. The American Heart Association has set guidelines for triglyceride levels in blood: ...
... • There are different types of fatty acids in one molecule of triglyceride. • Regardless of the degree saturation, all lipid have essentially the same number of calories per unit weight. The American Heart Association has set guidelines for triglyceride levels in blood: ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.