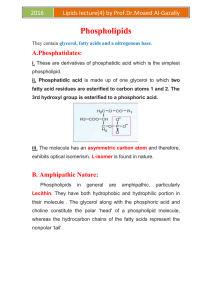
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
... In the layer of cells of the villi lining the wall of the small intestine, fatty acids and glycerol join together to make , which are made into a package that can travel in the watery lymph (then blood) because it has emulsifiers and protein. The package is a combination of: a. TGs from food, b. Pro ...
... In the layer of cells of the villi lining the wall of the small intestine, fatty acids and glycerol join together to make , which are made into a package that can travel in the watery lymph (then blood) because it has emulsifiers and protein. The package is a combination of: a. TGs from food, b. Pro ...
Rebecca Landerman Advanced Nutrition Science 1: 81944
... Triglycerides, also called triacylglycerols, are molecules consisting of three fatty acids attached to a three carbon glycerol backbone, as represented by the prefix “tri” and are the most common fat found in food (1). Fatty acids are long chains of carbon atoms bound to each other as well as to hyd ...
... Triglycerides, also called triacylglycerols, are molecules consisting of three fatty acids attached to a three carbon glycerol backbone, as represented by the prefix “tri” and are the most common fat found in food (1). Fatty acids are long chains of carbon atoms bound to each other as well as to hyd ...
Lipids • Triglycerides –Fats and oils • Phospholipids
... • Degree of unsaturation revisited –Hydrogenation –Cis vs. trans-fatty acids •Trans fat occurs naturally in meat and dairy foods – Conjugated linoleic in milk » Possibly positive for heart health ...
... • Degree of unsaturation revisited –Hydrogenation –Cis vs. trans-fatty acids •Trans fat occurs naturally in meat and dairy foods – Conjugated linoleic in milk » Possibly positive for heart health ...
PowerPoint Rubric: Biochemistry worksheet
... (a few exceptions: CO2, CO) Organic compounds- do contain carbon: C6H12O6 ...
... (a few exceptions: CO2, CO) Organic compounds- do contain carbon: C6H12O6 ...
4 – 2 Chemical Compounds in Living Things
... o Ex: glucose, fructose, galactose o All have the formula C6H12O6; different in the arrangement of atoms; called isomers Disaccharide - 2 sugar molecules bonded together o Ex: sucrose (table sugar – glucose & fructose bonded together) Polysaccharide – many sugar molecules hooked together in a ch ...
... o Ex: glucose, fructose, galactose o All have the formula C6H12O6; different in the arrangement of atoms; called isomers Disaccharide - 2 sugar molecules bonded together o Ex: sucrose (table sugar – glucose & fructose bonded together) Polysaccharide – many sugar molecules hooked together in a ch ...
MASTERY 2.01 ______ 2.04 ______ Biology I Name: Unit 2
... B. Specific proteins called enzymes break down carbohydrates to release quick energy. C. Antibodies are proteins that protect the body from harmful substances, such as carbohydrates. D. Proteins produce all of the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen make up a carbohydrate. ...
... B. Specific proteins called enzymes break down carbohydrates to release quick energy. C. Antibodies are proteins that protect the body from harmful substances, such as carbohydrates. D. Proteins produce all of the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen make up a carbohydrate. ...
Lipids lecture(4) by Prof.Dr.Moaed Al
... They are found in large quantities in nervous system. Different sphingomyelins may be formed depending on the fatty acid attached. Common fatty acids found are—lignoceric (24 C), nervonic (24 C, one double bond) and cervonic (22 C, 6 double bonds) acids .Because of its amphipathic nature sphingomyel ...
... They are found in large quantities in nervous system. Different sphingomyelins may be formed depending on the fatty acid attached. Common fatty acids found are—lignoceric (24 C), nervonic (24 C, one double bond) and cervonic (22 C, 6 double bonds) acids .Because of its amphipathic nature sphingomyel ...
Document
... • This reaction is catalyzed by NO synthase, which is found in many tissues and cell types. ...
... • This reaction is catalyzed by NO synthase, which is found in many tissues and cell types. ...
Outline06 Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... - fatty acids are broken down into 2C units → acetyl CoA → Krebs Cycle → CO2 + H2O - high energy yield: >100 ATP per fatty acid > 2X more energy yield per gram than carbohydrates 2. Lipid Synthesis - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to ...
... - fatty acids are broken down into 2C units → acetyl CoA → Krebs Cycle → CO2 + H2O - high energy yield: >100 ATP per fatty acid > 2X more energy yield per gram than carbohydrates 2. Lipid Synthesis - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to ...
chapter3_part1
... The function of organic molecules in biological systems begins with their structure The building blocks of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids bond together in different arrangements to form different kinds of ...
... The function of organic molecules in biological systems begins with their structure The building blocks of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids bond together in different arrangements to form different kinds of ...
Lecture 36
... in the intestine to generated freey fatty acids and monoacylglycerols. After passing through the membrane of mucosal cells that line the intestine, enzymes catalyze the formation of triglycerides which are then packaged into large lipid rich particles called chylomicrons. We will look at this in mor ...
... in the intestine to generated freey fatty acids and monoacylglycerols. After passing through the membrane of mucosal cells that line the intestine, enzymes catalyze the formation of triglycerides which are then packaged into large lipid rich particles called chylomicrons. We will look at this in mor ...
LECTURES 1,2 Membranes, lipids and phospholipases.ppt
... • It ‘fills the gaps’ and stabilizes the bilayer • It stiffens the bilayer ∴ decreases fluidity & permeability ...
... • It ‘fills the gaps’ and stabilizes the bilayer • It stiffens the bilayer ∴ decreases fluidity & permeability ...
LIPIDS
... • Phosholipids are the major component of cell membranes • Fatty acids, choline, as well as other substances are bound in the phospholipid layer ...
... • Phosholipids are the major component of cell membranes • Fatty acids, choline, as well as other substances are bound in the phospholipid layer ...
Amino Acids
... and transport into the blood, so lots of them may indicate a cholesterol problem, so these complexes are called “bad cholesterol”. High-density lipoproteins tend to transport cholesterol back into the liver for storage, so tend to be called “good cholesterol”. It’s all the same cholesterol…. ...
... and transport into the blood, so lots of them may indicate a cholesterol problem, so these complexes are called “bad cholesterol”. High-density lipoproteins tend to transport cholesterol back into the liver for storage, so tend to be called “good cholesterol”. It’s all the same cholesterol…. ...
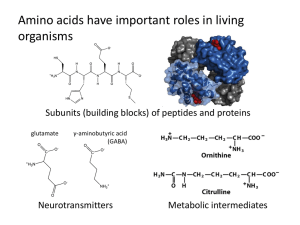
Amino acids have many roles in living organisms
... Vertical bonds point away from viewer (dashed wedges) ...
... Vertical bonds point away from viewer (dashed wedges) ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Phosphate with the unlabeled P (i) Name the first glycolysis metabolite to which the phosphate can be traced 1,3-BPG (ii) Name the enzyme which catalyzed the phosphorylation (along with another reaction) GAP-dehydrogenase (iii) Identify the source of the phosphate with the unlabeled P enzyme bound p ...
... Phosphate with the unlabeled P (i) Name the first glycolysis metabolite to which the phosphate can be traced 1,3-BPG (ii) Name the enzyme which catalyzed the phosphorylation (along with another reaction) GAP-dehydrogenase (iii) Identify the source of the phosphate with the unlabeled P enzyme bound p ...
LIPIDS
... • In adipocytes, glycerol 3-phosphate can be formed by the reduction of dihydroxyacetone phosphate catalyzed by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase • In liver, glycerol kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of glycerol to form glycerol 3-phosphate. ...
... • In adipocytes, glycerol 3-phosphate can be formed by the reduction of dihydroxyacetone phosphate catalyzed by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase • In liver, glycerol kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of glycerol to form glycerol 3-phosphate. ...
Slide 1
... • Macromolecules - larger molecules made from smaller ones. • 4 major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • 3 of these are polymers because they are made from individual building blocks called monomers. ...
... • Macromolecules - larger molecules made from smaller ones. • 4 major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • 3 of these are polymers because they are made from individual building blocks called monomers. ...
Organic Molecules
... • A glycerol and two fatty acids • A phosphate group takes the place of the third fatty acid • Glycerol is hydrophobic • Phosphate is hydrophyllic ...
... • A glycerol and two fatty acids • A phosphate group takes the place of the third fatty acid • Glycerol is hydrophobic • Phosphate is hydrophyllic ...
Biochemistry Practice Questions
... 20. Which type of organic compound has molecules that include both an amino group and a carboxyl group? a. Alcohols b. Proteins c. Carbohydrates d. Lipids 21.Two side groups which are characteristic of all amino acids are a. –OH and –COOH b. –CH3 and –OH c. –NH2 and –COOH d. –NH2 and –CH2OH 22. Wha ...
... 20. Which type of organic compound has molecules that include both an amino group and a carboxyl group? a. Alcohols b. Proteins c. Carbohydrates d. Lipids 21.Two side groups which are characteristic of all amino acids are a. –OH and –COOH b. –CH3 and –OH c. –NH2 and –COOH d. –NH2 and –CH2OH 22. Wha ...
1 - TechnionMed
... 17) Which of the following is the most accurate description of phosphofructokinase-1? a. This enzyme uses fructose-6-phosphate as a substrate and converts it to fructose-2,6-biphosphate b. This enzyme is inhibited by ATP, citrate and fructose-2,6-biphosphate c. This enzyme catalyzes a fully reversib ...
... 17) Which of the following is the most accurate description of phosphofructokinase-1? a. This enzyme uses fructose-6-phosphate as a substrate and converts it to fructose-2,6-biphosphate b. This enzyme is inhibited by ATP, citrate and fructose-2,6-biphosphate c. This enzyme catalyzes a fully reversib ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.