Fatty acids with
... Palmitoyl-CoA *Inhibits Ac-CoA carboxylase *Inhibits translocation of citrate from mitochondria to cytosol *Inhibits glucose 6-P dehydrogenase NADPH ...
... Palmitoyl-CoA *Inhibits Ac-CoA carboxylase *Inhibits translocation of citrate from mitochondria to cytosol *Inhibits glucose 6-P dehydrogenase NADPH ...
Lipid metabolism
... Citrate is an allosteric stimulator and palmitoyl-CoA inhibits this enzyme. Hormonal regulation: glucagon and epinephrine - inhibition insulin - stimulation ...
... Citrate is an allosteric stimulator and palmitoyl-CoA inhibits this enzyme. Hormonal regulation: glucagon and epinephrine - inhibition insulin - stimulation ...
citric acid cycle
... pyruvate through the citric acid cycle. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is allosterically inhibited at high [ATP]/[ADP], [NADH]/[NAD+], and [acetyl-CoA]/[CoA] rations, all of which indicate the energy-sufficent metabolic state. When these rations decrease, allosteric activation of pyruvate oxidat ...
... pyruvate through the citric acid cycle. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is allosterically inhibited at high [ATP]/[ADP], [NADH]/[NAD+], and [acetyl-CoA]/[CoA] rations, all of which indicate the energy-sufficent metabolic state. When these rations decrease, allosteric activation of pyruvate oxidat ...
Document
... Monomer: nucleotide (made of 3 parts) a. 5 carbon sugar b. Phosphate group c. Nitrogen base ...
... Monomer: nucleotide (made of 3 parts) a. 5 carbon sugar b. Phosphate group c. Nitrogen base ...
IV. Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
... 16.18) and denotes the position of the last double bond relative to the terminal methyl group. ...
... 16.18) and denotes the position of the last double bond relative to the terminal methyl group. ...
File
... A fatty acid with an odd number of carbons will enter the citric acid cycle as acetylCoA and: A. α-ketoglutarate B. Malate C. Succinyl-CoA D. Citrate E. Butyrate Which of the following statements apply to the β-oxidation of fatty acids? A. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. B ...
... A fatty acid with an odd number of carbons will enter the citric acid cycle as acetylCoA and: A. α-ketoglutarate B. Malate C. Succinyl-CoA D. Citrate E. Butyrate Which of the following statements apply to the β-oxidation of fatty acids? A. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. B ...
No Slide Title
... A fatty acid with an odd number of carbons will enter the citric acid cycle as acetylCoA and: A. α-ketoglutarate B. Malate C. Succinyl-CoA D. Citrate E. Butyrate Which of the following statements apply to the β-oxidation of fatty acids? A. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. B ...
... A fatty acid with an odd number of carbons will enter the citric acid cycle as acetylCoA and: A. α-ketoglutarate B. Malate C. Succinyl-CoA D. Citrate E. Butyrate Which of the following statements apply to the β-oxidation of fatty acids? A. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. B ...
The Four major Groups of
... and Ketoses • Carbohydrates have the atomic ratio C:H2O. • They are composed of many monosaccharide (monomers) chemically combined through dehydration synthesis into polysaccharides (polymers). • Glucose C6H12O6 is made by plants and is the most common monosaccharide. • Serve as energy sources for p ...
... and Ketoses • Carbohydrates have the atomic ratio C:H2O. • They are composed of many monosaccharide (monomers) chemically combined through dehydration synthesis into polysaccharides (polymers). • Glucose C6H12O6 is made by plants and is the most common monosaccharide. • Serve as energy sources for p ...
2008 VFA Absorption
... – Acetate and B(OH)butyrate contribute equally to the first 4 carbons – Must be converted to acetyl CoA for additional C • Lactate – 5 – 10% of the fatty acids in milk – Inversely related to the amount of acetate available » Controlled by pyruvate dehydrogenase – Additional uses of lactate » Glycero ...
... – Acetate and B(OH)butyrate contribute equally to the first 4 carbons – Must be converted to acetyl CoA for additional C • Lactate – 5 – 10% of the fatty acids in milk – Inversely related to the amount of acetate available » Controlled by pyruvate dehydrogenase – Additional uses of lactate » Glycero ...
Fats and Lipids
... molecules fatty acids (salt form) • It is also the term used to prepare soap • The soap formed in the reaction is known as ‘crude soap’ • Most soaps used now are detergents ...
... molecules fatty acids (salt form) • It is also the term used to prepare soap • The soap formed in the reaction is known as ‘crude soap’ • Most soaps used now are detergents ...
Biological Macromolecules
... 2. Understand how carbohydrates are used in plants and animals as energy storage molecules. 3. Understand how carbohydrates are used in plants and animals as structural molecules. 4. Identify biological molecules that contain pentoses ...
... 2. Understand how carbohydrates are used in plants and animals as energy storage molecules. 3. Understand how carbohydrates are used in plants and animals as structural molecules. 4. Identify biological molecules that contain pentoses ...
Chemistry Option B: Human Biochemistry
... the nucleotides condense/form a phosphodiester bond; between the C3 of the sugar and a neighbouring phosphate group; bases form a part of nucleotide in DNA by bases are covalently bonded to deoxyribose/pentose sugar; bond via a condensation reaction with the sugar / N from the thymine bonds ...
... the nucleotides condense/form a phosphodiester bond; between the C3 of the sugar and a neighbouring phosphate group; bases form a part of nucleotide in DNA by bases are covalently bonded to deoxyribose/pentose sugar; bond via a condensation reaction with the sugar / N from the thymine bonds ...
Carbon Compounds
... I. Chemistry of Carbon A. Organic Chemistry – study of carbon compounds 1. All organic compounds contain carbon! 2. Examples: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) ...
... I. Chemistry of Carbon A. Organic Chemistry – study of carbon compounds 1. All organic compounds contain carbon! 2. Examples: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) ...
Fats - MBBS Students Club
... the liquid state. b. Waxes: Esters of fatty acids with higher molecular ...
... the liquid state. b. Waxes: Esters of fatty acids with higher molecular ...
Biochemistry Test Review KEY
... 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describe the active site of an enzyme. It is a small port in an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction 16. Enzymes are what type ...
... 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describe the active site of an enzyme. It is a small port in an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction 16. Enzymes are what type ...
BIO 101 Exam 2 Practice Quiz Name
... 5. Which of the following is not a macromolecule? a. Proteins b. Nucleic Acids ...
... 5. Which of the following is not a macromolecule? a. Proteins b. Nucleic Acids ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids annd proteins
... between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
... between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
Introduction and Chemistry (Ch1 2)
... -Your genetic code -Provide the directions for building proteins • DNA is a double stranded molecule that resides in the cell nucleus • RNA is single stranded molecule that is found mainly outside of the nucleus, usually serving as a ‘copy’ of DNA ...
... -Your genetic code -Provide the directions for building proteins • DNA is a double stranded molecule that resides in the cell nucleus • RNA is single stranded molecule that is found mainly outside of the nucleus, usually serving as a ‘copy’ of DNA ...
The_Light_Independent_Reactions
... (Calvin cycle) to produce triose phosphate (TP) – referring also to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP). • Explain the role of carbon dioxide in the lightindependent stage. • State that TP (and GP) can be used to make carbohydrates ...
... (Calvin cycle) to produce triose phosphate (TP) – referring also to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP). • Explain the role of carbon dioxide in the lightindependent stage. • State that TP (and GP) can be used to make carbohydrates ...
8.07 Fatty Acid Biosynthesis And Oxidation
... widely held as the enzyme required for the temperature-dependent regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis.5–7 In M. tuberculosis, KasA and KasB have overlapping substrate specificity with KasB possibly being responsible for the synthesis of very long-chain fatty acids (C54). Both KasA and KasB are impo ...
... widely held as the enzyme required for the temperature-dependent regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis.5–7 In M. tuberculosis, KasA and KasB have overlapping substrate specificity with KasB possibly being responsible for the synthesis of very long-chain fatty acids (C54). Both KasA and KasB are impo ...
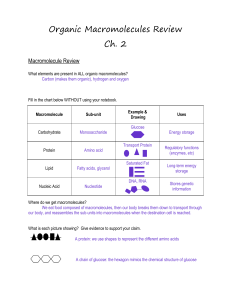
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... Where do we get macromolecules? We eat food composed of macromolecules, then our body breaks them down to transport through our body, and reassembles the sub-units into macromolecules when the destination cell is reached. What is each picture showing? Give evidence to support your claim. A protein: ...
... Where do we get macromolecules? We eat food composed of macromolecules, then our body breaks them down to transport through our body, and reassembles the sub-units into macromolecules when the destination cell is reached. What is each picture showing? Give evidence to support your claim. A protein: ...
Review 3
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
Exam 4, 2015 - Biochemistry at CSU, Stanislaus
... C. The gluconeogenesis pathway is the glycolysis pathway running in the opposite direction. D. Plants do not undergo gluconeogenesis. E. None of these 7. Rapidly dividing cells have a high need for nucleotide precursors, which are provided by A. the Cori cycle. D. gluconeogenesis. B. the pentose pho ...
... C. The gluconeogenesis pathway is the glycolysis pathway running in the opposite direction. D. Plants do not undergo gluconeogenesis. E. None of these 7. Rapidly dividing cells have a high need for nucleotide precursors, which are provided by A. the Cori cycle. D. gluconeogenesis. B. the pentose pho ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.