powerpoint
... chains of insulin (21 aa) • All of the molecules of a given protein have the same sequence • Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: - direct amino acid sequencing - indirect sequencing of the encoding gene (DNA) ...
... chains of insulin (21 aa) • All of the molecules of a given protein have the same sequence • Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: - direct amino acid sequencing - indirect sequencing of the encoding gene (DNA) ...
Lipids - Cloudfront.net
... If all the Amino Acids were the same…how come we have 20 different types? The Variable group is the difference for each amino acid (kind of like a fingerprint) ...
... If all the Amino Acids were the same…how come we have 20 different types? The Variable group is the difference for each amino acid (kind of like a fingerprint) ...
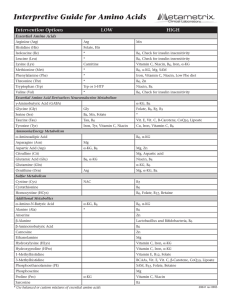
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... Glutamine Low - deficient intake or absorption of essential amino acids (glutamine is derived fiom histidine). Check overall amino acid level of diet. High - marker of vitamin B6 deficiency. Ammonia accumulation suspected, if low or low normal glutamic acid. Extra α-KG needed to combine with ammonia an ...
... Glutamine Low - deficient intake or absorption of essential amino acids (glutamine is derived fiom histidine). Check overall amino acid level of diet. High - marker of vitamin B6 deficiency. Ammonia accumulation suspected, if low or low normal glutamic acid. Extra α-KG needed to combine with ammonia an ...
print last name first name
... 3. ATP is available for use to make a dipeptide from two component amino acids. Δ G0 for the hydrolysis of ATP is –8 kcal/mol, and Δ G0 for the formation of the dipeptide is +0.5 kcal/mol. a. What is the net Δ G0 for this reaction? ___________________________ b. For a reaction at equilibrium, show t ...
... 3. ATP is available for use to make a dipeptide from two component amino acids. Δ G0 for the hydrolysis of ATP is –8 kcal/mol, and Δ G0 for the formation of the dipeptide is +0.5 kcal/mol. a. What is the net Δ G0 for this reaction? ___________________________ b. For a reaction at equilibrium, show t ...
Test 1 Notecards
... Response to Stimulus, Genetic Material, Homeostasis, cells, growth and development pH: acids = 0-6, neutral = 7, base = 8-14; buffer helps to maintain homeostasis Organic compounds: contain carbon; include lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lipids: made of glycerol and fatty acids; ...
... Response to Stimulus, Genetic Material, Homeostasis, cells, growth and development pH: acids = 0-6, neutral = 7, base = 8-14; buffer helps to maintain homeostasis Organic compounds: contain carbon; include lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lipids: made of glycerol and fatty acids; ...
H - Bioinf!
... Protein stability and denaturation The native structure of proteins can be broken up, by heating or by high concentrations of certain chemicals such as urea (DENATURATION) Denaturation destroys the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures but leaves the polypeptide chain intact. The stability ...
... Protein stability and denaturation The native structure of proteins can be broken up, by heating or by high concentrations of certain chemicals such as urea (DENATURATION) Denaturation destroys the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures but leaves the polypeptide chain intact. The stability ...
Multiple Choice Questions
... d. region of the peptide bond that contributes to a Ramachandran plot e. theoretical space between -180 and +180 degrees that can be occupied by the φ and ψ angles in the peptide bond 17. The major reason that antiparallel β-stranded protein structures are more stable than parallel β-stranded struct ...
... d. region of the peptide bond that contributes to a Ramachandran plot e. theoretical space between -180 and +180 degrees that can be occupied by the φ and ψ angles in the peptide bond 17. The major reason that antiparallel β-stranded protein structures are more stable than parallel β-stranded struct ...
Chemdraw B&W - Pennsylvania State University
... Alanine A, Ala Arginine R, Arg Asparagine N, Asn Aspartic acid D, Asp Cysteine C, Cys Glutamine Q, Gln Glutamic Acid E, Glu Glycine G, Gly Histidine H, His Isoleucine I, Ile ...
... Alanine A, Ala Arginine R, Arg Asparagine N, Asn Aspartic acid D, Asp Cysteine C, Cys Glutamine Q, Gln Glutamic Acid E, Glu Glycine G, Gly Histidine H, His Isoleucine I, Ile ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-central dogma
... words (triplets), called codons. - Each word stands for one amino acid. - During translation are linked together to form a chain which will later be folded into a protein. ...
... words (triplets), called codons. - Each word stands for one amino acid. - During translation are linked together to form a chain which will later be folded into a protein. ...
chapter 5 the structure & function of macromolecules
... •Defense against foreign substances •Enzymes – speed up chemical reactions ...
... •Defense against foreign substances •Enzymes – speed up chemical reactions ...
Lab 9
... How does one recognize a gene and what are the implications for the production of protein? Proteins contain combinations of up to 20 amino acids, which are based on the codes in the RNA transcribed from a DNA sequence. One gets to the RNA sequence by exchanging every T (thymine) for a U (uracil). Di ...
... How does one recognize a gene and what are the implications for the production of protein? Proteins contain combinations of up to 20 amino acids, which are based on the codes in the RNA transcribed from a DNA sequence. One gets to the RNA sequence by exchanging every T (thymine) for a U (uracil). Di ...
Chapter 3: Biochemistry
... Most lipids contain fatty acids, unbranched carbon molecules that have a hydrophilic end (head) and a hydrophobic end (tail) ...
... Most lipids contain fatty acids, unbranched carbon molecules that have a hydrophilic end (head) and a hydrophobic end (tail) ...
Assignment: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... 14. In an amino analysis, a large protein is broken down into overlapping fragments by using specific enzymes. Why must the sequences be overlapping? With overlapping fragments the segments can be fitted together because fragments that fit together have common sequences at their ends. if the segmen ...
... 14. In an amino analysis, a large protein is broken down into overlapping fragments by using specific enzymes. Why must the sequences be overlapping? With overlapping fragments the segments can be fitted together because fragments that fit together have common sequences at their ends. if the segmen ...
Chapter 22-23 - Bakersfield College
... Transferases: transfer a group between two compounds. Hydrolases: hydrolysis reactions. Lyases: add or remove groups involving a double bond without hydrolysis. Isomerases: rearrange atoms in a molecule to form a isomer. Ligases: form bonds between molecules. ...
... Transferases: transfer a group between two compounds. Hydrolases: hydrolysis reactions. Lyases: add or remove groups involving a double bond without hydrolysis. Isomerases: rearrange atoms in a molecule to form a isomer. Ligases: form bonds between molecules. ...
Organic Chemistry I. Organic compounds
... A. These are the four most common elements. B. Arrangement of letters in rule tell us the number of bonds the atom needs in order to be stable: 1. Hydrogen needs to form one chemical bond. 2. Oxygen needs to form two chemical bonds. 3. Nitrogen needs to form three chemical bonds. 4. Carbon needs to ...
... A. These are the four most common elements. B. Arrangement of letters in rule tell us the number of bonds the atom needs in order to be stable: 1. Hydrogen needs to form one chemical bond. 2. Oxygen needs to form two chemical bonds. 3. Nitrogen needs to form three chemical bonds. 4. Carbon needs to ...
Molecular Biology Final Exam (Set A)
... complementary, anti-parallel strand. This means that DNA has a very regular structure, typically a Watson-Crick double helix, regardless of its sequence. In contrast, RNA is almost always single-stranded. As an elongated single strand, its nitrogenous bases would be exposed to the water solvent. Thi ...
... complementary, anti-parallel strand. This means that DNA has a very regular structure, typically a Watson-Crick double helix, regardless of its sequence. In contrast, RNA is almost always single-stranded. As an elongated single strand, its nitrogenous bases would be exposed to the water solvent. Thi ...