Advanced Biology
... d) Come up with an analogy to describe ATP’s role in cells. How does this illustrate the importance of coupled reactions? 3. Take a look at the “Metabolic Pathways” poster in the science lab. It shows most of the typical metabolic reactions that happen in cells. a) There will be a quiz on this poste ...
... d) Come up with an analogy to describe ATP’s role in cells. How does this illustrate the importance of coupled reactions? 3. Take a look at the “Metabolic Pathways” poster in the science lab. It shows most of the typical metabolic reactions that happen in cells. a) There will be a quiz on this poste ...
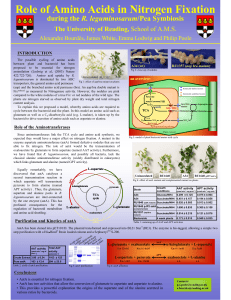
Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation
... Fixreduced as measured by Nitrogenase activity. However, the nodules are pink compared to the white nodules of a true Fix- or red nodules of the wild type. The plants are nitrogen starved as observed by plant dry weight and total nitrogen ...
... Fixreduced as measured by Nitrogenase activity. However, the nodules are pink compared to the white nodules of a true Fix- or red nodules of the wild type. The plants are nitrogen starved as observed by plant dry weight and total nitrogen ...
Slide 1 - Oceanside Moodle
... Macromolecules are the large organic molecules found in living organisms The four types of macromolecules are: 1) carbohydrates 2) lipids ...
... Macromolecules are the large organic molecules found in living organisms The four types of macromolecules are: 1) carbohydrates 2) lipids ...
Biochemistry_of_Cells abridged
... • Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
... • Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... Cell walls in plants / bacteria = cellulose & others Exoskeletons of invertebrates = chiton Many in extracellular matrix of all tissues ...
... Cell walls in plants / bacteria = cellulose & others Exoskeletons of invertebrates = chiton Many in extracellular matrix of all tissues ...
Macro-molecules short 2014
... The monomers of proteins are called amino acids Amino acids have an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end with various atoms in between The joins are formed by joining the amino group on one amino acid with the carboxyl group on another = protein synthesis ...
... The monomers of proteins are called amino acids Amino acids have an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end with various atoms in between The joins are formed by joining the amino group on one amino acid with the carboxyl group on another = protein synthesis ...
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS
... A minute round particle composed of RNA and protein that is found in the cytoplasm of living cells and serves as the site of assembly for polypeptides encoded by messenger RNA pro·tein Any of a group of complex organic macromolecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and usually sulfu ...
... A minute round particle composed of RNA and protein that is found in the cytoplasm of living cells and serves as the site of assembly for polypeptides encoded by messenger RNA pro·tein Any of a group of complex organic macromolecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and usually sulfu ...
Organic Compounds
... • Rate of reaction is determined by measuring the disappearance of substrate or the accumulation of product • Rate of reaction is the slope of the linear portion of the graph • Reaction rate is affected by pH, substrate conc., enzyme conc., temperature, and ...
... • Rate of reaction is determined by measuring the disappearance of substrate or the accumulation of product • Rate of reaction is the slope of the linear portion of the graph • Reaction rate is affected by pH, substrate conc., enzyme conc., temperature, and ...
Amino acids and peptide bonds
... processes; most typically arise from post-translational modifications to the protein, which are catalyzed by specific enzymes. Common post-translational modifications include hydroxylation, methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation. You are not responsible for knowing these amino acids, however, ...
... processes; most typically arise from post-translational modifications to the protein, which are catalyzed by specific enzymes. Common post-translational modifications include hydroxylation, methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation. You are not responsible for knowing these amino acids, however, ...
Bio 301, Biochemistry I
... a. Primase catalyzes the de novo polymerization of DNA. b. RNA polymerase II initiates RNA synthesis by elongation of a DNA primer. c. During DNA replication, every Okazaki fragment synthesized by DNA polymerase III is elongated from a separate RNA primer. d. During DNA replication, leading strands ...
... a. Primase catalyzes the de novo polymerization of DNA. b. RNA polymerase II initiates RNA synthesis by elongation of a DNA primer. c. During DNA replication, every Okazaki fragment synthesized by DNA polymerase III is elongated from a separate RNA primer. d. During DNA replication, leading strands ...
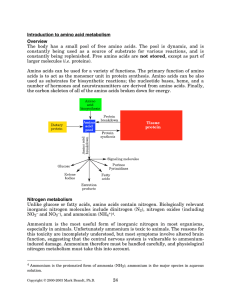
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... nitrogen by transfer of organic nitrogen from one amino acid to another. In amino acid metabolism, the most common nitrogen donor is glutamate, and the most common acceptor is a-ketoglutarate. This is logical, since glutamate is a direct link (via glutamate dehydrogenase) to inorganic ammonium. In s ...
... nitrogen by transfer of organic nitrogen from one amino acid to another. In amino acid metabolism, the most common nitrogen donor is glutamate, and the most common acceptor is a-ketoglutarate. This is logical, since glutamate is a direct link (via glutamate dehydrogenase) to inorganic ammonium. In s ...
Biodegradable Polymers – From Delivery of Drugs to Tissue
... Institute of Drug Research, School of Pharmacy- Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel ...
... Institute of Drug Research, School of Pharmacy- Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel ...
Nucleic Acid metabolism De Novo Synthesis of Purine
... • Since pyrimidine molecules are simpler than purines, so is their synthesis simpler but is still from readily available components. Glutamine's amide nitrogen and carbon dioxide provide atoms 2 and 3 or the pyrimidine ring. They do so, however, after first being converted to carbamoyl phosphate. Th ...
... • Since pyrimidine molecules are simpler than purines, so is their synthesis simpler but is still from readily available components. Glutamine's amide nitrogen and carbon dioxide provide atoms 2 and 3 or the pyrimidine ring. They do so, however, after first being converted to carbamoyl phosphate. Th ...
Jan. 28
... – Aqueous residue showed that 10 -15% of carbon had been converted to organic compounds (including amino acids) – Glycine (R=H) was found to be most abundant (least C-C bond forming reactions needed) – 12 of the other proteinogenic amino acids (20 in modern cells) were formed: – These were amino a ...
... – Aqueous residue showed that 10 -15% of carbon had been converted to organic compounds (including amino acids) – Glycine (R=H) was found to be most abundant (least C-C bond forming reactions needed) – 12 of the other proteinogenic amino acids (20 in modern cells) were formed: – These were amino a ...
Revised Chapter 4 and 5
... • Genetic material that stores information for its own replication and for the sequence of amino acids in proteins. ...
... • Genetic material that stores information for its own replication and for the sequence of amino acids in proteins. ...
1. Products of Amino Acid Transamination Name
... equilibrium constant of about 1.0. Phenyllactate is formed from phenylpyruvate by reduction (see Fig. 18–25). This pathway is of importance only when phenylalanine hydroxylase is defective. (d) The normal catabolic pathway of phenylalanine is through tyrosine, a precursor of melanin, the dark pigmen ...
... equilibrium constant of about 1.0. Phenyllactate is formed from phenylpyruvate by reduction (see Fig. 18–25). This pathway is of importance only when phenylalanine hydroxylase is defective. (d) The normal catabolic pathway of phenylalanine is through tyrosine, a precursor of melanin, the dark pigmen ...
Carbon Compounds in Cells
... • Carbon can share pairs of electrons with as many as four other atoms to form organic molecules of several configuration • Much of H and O is linked to form water ...
... • Carbon can share pairs of electrons with as many as four other atoms to form organic molecules of several configuration • Much of H and O is linked to form water ...
Molecules of life 2.4 - Madison County Schools
... A. Proteins make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight (referred to as biomass). B. Proteins are not used for energy unless there are no lipids or carbohydrates available. Proteins and enzymes are the “work horses” of a cell. They carry out numerous functions within cells. Proteins basicall ...
... A. Proteins make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight (referred to as biomass). B. Proteins are not used for energy unless there are no lipids or carbohydrates available. Proteins and enzymes are the “work horses” of a cell. They carry out numerous functions within cells. Proteins basicall ...
02 DNA and RNA and protein synthesis
... of amino acids. Once this happens, that tRNA leaves and the one with the chain moves to its place. ...
... of amino acids. Once this happens, that tRNA leaves and the one with the chain moves to its place. ...
see examples of typical exams - IQ-USP
... 6) The stability of body mass and overall appearance of an individual hides large daily fluctuations of metabolism. For example, food intake subjects the organism to opposing situations: the abundance and lack of nutrients. The adjustment of our metabolism to different metabolic conditions occurs by ...
... 6) The stability of body mass and overall appearance of an individual hides large daily fluctuations of metabolism. For example, food intake subjects the organism to opposing situations: the abundance and lack of nutrients. The adjustment of our metabolism to different metabolic conditions occurs by ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... monomers because we are making _____________________. Now that we have the place to build the protein and the copied instructions on how to make the protein, the parts (amino acids) need to be brought over to the workbench and placed in the correct order. The job of ______ is to transfer these amino ...
... monomers because we are making _____________________. Now that we have the place to build the protein and the copied instructions on how to make the protein, the parts (amino acids) need to be brought over to the workbench and placed in the correct order. The job of ______ is to transfer these amino ...
fatty acid synthesis
... mammalian cells cannot introduce double bonds more than 9 carbons from carboxyl end. Therefore, linoleate (18:29,12) and -linoleate (18:39,12,15), essential fatty acids, must be obtained from plants. These can however be elongated and additional double bonds added. See fig 16-7 for synthesis of ...
... mammalian cells cannot introduce double bonds more than 9 carbons from carboxyl end. Therefore, linoleate (18:29,12) and -linoleate (18:39,12,15), essential fatty acids, must be obtained from plants. These can however be elongated and additional double bonds added. See fig 16-7 for synthesis of ...
The role of the C-terminal tail of the ribosomal protein S13 in protein
... he ibosome is a large molecular machine that plays an important role in the expression of genetic information. The information in genomic DNA is carried on mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequ ...
... he ibosome is a large molecular machine that plays an important role in the expression of genetic information. The information in genomic DNA is carried on mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequ ...
Marvelous Macromolecules - Pregitzersninjascienceclasses
... Small units that join together to make polymers Connected by covalent bonds using a condensation (dehydration) reaction One monomer gives a hydroxyl group, the other gives a hydrogen to form water Process requires ENERGY and ENZYMES ...
... Small units that join together to make polymers Connected by covalent bonds using a condensation (dehydration) reaction One monomer gives a hydroxyl group, the other gives a hydrogen to form water Process requires ENERGY and ENZYMES ...