Exam 1 - Chemistry Courses: About
... hemoglobin shifts the conformational equilibrium toward the tense state. H. ____________ Alanine, which has pKa values of 9 and 2, would serve as an effective buffer at pH 5.5. I. _____________ Myosin and actin are both NTP binding proteins. J. _____________ Ligases catalyze bond-forming reactions c ...
... hemoglobin shifts the conformational equilibrium toward the tense state. H. ____________ Alanine, which has pKa values of 9 and 2, would serve as an effective buffer at pH 5.5. I. _____________ Myosin and actin are both NTP binding proteins. J. _____________ Ligases catalyze bond-forming reactions c ...
From: From one amino acid to another: tRNA
... From: From one amino acid to another: tRNA-dependent amino acid biosynthesis Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(6):1813-1825. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn015 Nucleic Acids Res | © 2008 The Author(s)This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ...
... From: From one amino acid to another: tRNA-dependent amino acid biosynthesis Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(6):1813-1825. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn015 Nucleic Acids Res | © 2008 The Author(s)This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ...
Glossary Protein
... fluid balance maintenance of the proper types and amounts of fluid in each compartment of the body fluids. gene expression the process by which a cell converts the genetic code into RNA and protein. hemoglobin the globular protein of the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cell ...
... fluid balance maintenance of the proper types and amounts of fluid in each compartment of the body fluids. gene expression the process by which a cell converts the genetic code into RNA and protein. hemoglobin the globular protein of the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cell ...
Tutorial Kit (Biochemistry-200 L)
... Lipids: Lipids are used to store energy and are an important part of the cell membrane. Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Nucleotides are responsible for mor ...
... Lipids: Lipids are used to store energy and are an important part of the cell membrane. Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Nucleotides are responsible for mor ...
Protein Unit Study Guide/Review Sheets
... What element(s) ALWAYS comprise proteins? C, H, O, N Are proteins organic? YES What element(s) MAY be present in proteins? S What is the name of the monomer of proteins? AMINO ACID What type of bond links amino acids together? PEPTIDE BOND What functional groups is shared between ALL amino acids (gi ...
... What element(s) ALWAYS comprise proteins? C, H, O, N Are proteins organic? YES What element(s) MAY be present in proteins? S What is the name of the monomer of proteins? AMINO ACID What type of bond links amino acids together? PEPTIDE BOND What functional groups is shared between ALL amino acids (gi ...
Biological Molecules
... molecules eg. Starch and Glycogen have compact, coiled and branched molecules, making them ideal stores of energy ...
... molecules eg. Starch and Glycogen have compact, coiled and branched molecules, making them ideal stores of energy ...
Chap 5
... nutritional and environmental conditions 2. Metabolic pathways are subgroups as aerobic and anaerobic metabolism 3. Catabolism: the intracellular process of degrading a compound into smaller amd simpler products (ex: glucose to CO2 and H2O) and produces energy for the cell 4. Anabolism: involves in ...
... nutritional and environmental conditions 2. Metabolic pathways are subgroups as aerobic and anaerobic metabolism 3. Catabolism: the intracellular process of degrading a compound into smaller amd simpler products (ex: glucose to CO2 and H2O) and produces energy for the cell 4. Anabolism: involves in ...
Questions
... 2. Based on results described in question 1, investigators used the technique of sitedirected mutagenesis to synthesize five mutant CK proteins in which the Cys278 residue was replaced with either a Gly, Ser, Ala , Asn or Asp residue. The mutants were called C278G, C278S, C278A, C278N and C278D, re ...
... 2. Based on results described in question 1, investigators used the technique of sitedirected mutagenesis to synthesize five mutant CK proteins in which the Cys278 residue was replaced with either a Gly, Ser, Ala , Asn or Asp residue. The mutants were called C278G, C278S, C278A, C278N and C278D, re ...
Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Human E. coli
... share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage of their precursor proteins, and each corresponds to approximately one half of the N-terminal portion of the precursor mole ...
... share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage of their precursor proteins, and each corresponds to approximately one half of the N-terminal portion of the precursor mole ...
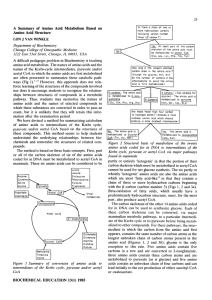
A summary of amino acid metabolism based on amino acid structure
... Figure 3 Examples of the relationship between amino acid structure and metabolism (a) Tryptophan has at least three hydrocarbon carbons in a row beginning with the f5 carbon (carbon 3) and thus must be converted, at least in part, to acetyl CoA (hydrocarbon carbons are labeled a, b, c, d, e, f, and ...
... Figure 3 Examples of the relationship between amino acid structure and metabolism (a) Tryptophan has at least three hydrocarbon carbons in a row beginning with the f5 carbon (carbon 3) and thus must be converted, at least in part, to acetyl CoA (hydrocarbon carbons are labeled a, b, c, d, e, f, and ...
Biochem-5012.1A - Center for Structural Biology
... Keq, Kw and pH As H2O is the medium of biological systems one must consider the role of this molecule in the dissociation of ions from biological molecules. Water is essentially a neutral molecule but will ionize to a small degree. This can be described by a simple equilibrium equation: H2O <------ ...
... Keq, Kw and pH As H2O is the medium of biological systems one must consider the role of this molecule in the dissociation of ions from biological molecules. Water is essentially a neutral molecule but will ionize to a small degree. This can be described by a simple equilibrium equation: H2O <------ ...
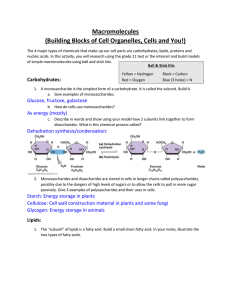
Macromolecules
... 3. Fatty acids can be attached (through dehydration synthesis) to different chemicals to perform different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
... 3. Fatty acids can be attached (through dehydration synthesis) to different chemicals to perform different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... meteorites and stability arguments suggest that RNA was preceded by a complex mixture of genetic polymers with different backbones and nucleobases; 3. The presence of twenty protein amino acids in extant biology does not means that they were essential for the origin of life nor that all of them were ...
... meteorites and stability arguments suggest that RNA was preceded by a complex mixture of genetic polymers with different backbones and nucleobases; 3. The presence of twenty protein amino acids in extant biology does not means that they were essential for the origin of life nor that all of them were ...
Genetic Code
... this tRNA, and which amino acid also bound in the active site of that enzyme, then you would know which amino acid will be found on this tRNA. And then you'd know what amino acid would go into the polypeptide when the mRNA had the codon UGG, which is complementary to this tRNA's anticodon. To make t ...
... this tRNA, and which amino acid also bound in the active site of that enzyme, then you would know which amino acid will be found on this tRNA. And then you'd know what amino acid would go into the polypeptide when the mRNA had the codon UGG, which is complementary to this tRNA's anticodon. To make t ...
Part I - OCCC.edu
... #6 is __________. Observe the structural formulae for these two amino acids: ...
... #6 is __________. Observe the structural formulae for these two amino acids: ...
Experimentally testing the hypothesis of a limited amino acid
... proteins that express biological functions. The modern genetic code, which encodes the standard 20 amino acids (and the termination signal) using 64 triplet codons, is shared by all of the extant organisms on the earth with a few exceptions. Therefore, the genetic code is thought to have been establ ...
... proteins that express biological functions. The modern genetic code, which encodes the standard 20 amino acids (and the termination signal) using 64 triplet codons, is shared by all of the extant organisms on the earth with a few exceptions. Therefore, the genetic code is thought to have been establ ...
Lipid Biosynthesis - Chemistry Courses: About: Department
... A) Condensation of precursors. B) Rearrangement. C) Reduction. D) Dehydration. 3. Which of the following is the regulated step of fatty acid synthesis in eukaryotes? A) Carboxylation of acetyl CoA. B) Transportation of mitochondrial acetyl CoA into the cytosol. C) Assembly of the fatty acid chain. D ...
... A) Condensation of precursors. B) Rearrangement. C) Reduction. D) Dehydration. 3. Which of the following is the regulated step of fatty acid synthesis in eukaryotes? A) Carboxylation of acetyl CoA. B) Transportation of mitochondrial acetyl CoA into the cytosol. C) Assembly of the fatty acid chain. D ...
Amino acid Catabolism
... • Measurements of the blood serum concentrations of the two aminotransferases and of another enzyme, creatine kinase, Provide information about the severity of the damage. ...
... • Measurements of the blood serum concentrations of the two aminotransferases and of another enzyme, creatine kinase, Provide information about the severity of the damage. ...
Fibers, Proteins and Membranes
... In this way amino acids can be made into long chains that are called peptide chains when they have less than about 30-50 amino acids long and polypeptide chains otherwise. ...
... In this way amino acids can be made into long chains that are called peptide chains when they have less than about 30-50 amino acids long and polypeptide chains otherwise. ...
chapter 4 pptol
... RNA nucleotides are complementary to DNA nucleotides (exception – no thymine in RNA; replaced with uracil) How Translation Works -Protein Synthesis The transfer RNA molecule for the last amino acid added holds the growing polypeptide chain and is attached to its complementary codon on mRNA. A second ...
... RNA nucleotides are complementary to DNA nucleotides (exception – no thymine in RNA; replaced with uracil) How Translation Works -Protein Synthesis The transfer RNA molecule for the last amino acid added holds the growing polypeptide chain and is attached to its complementary codon on mRNA. A second ...
Metabolism III
... direction of biosynthesis – done by coupling breakdown of ATP to certain reactions in biosynthetic pathways – drives the biosynthetic reaction to completion ...
... direction of biosynthesis – done by coupling breakdown of ATP to certain reactions in biosynthetic pathways – drives the biosynthetic reaction to completion ...
Essential Nutrients
... • Their main function is the transfer and expression of genetic information. ...
... • Their main function is the transfer and expression of genetic information. ...