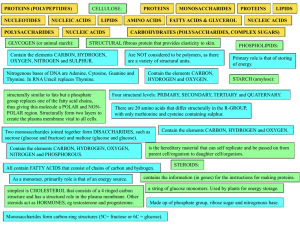
Section 1 Workbook Unit 1 ANSWERS File
... from the hydrogen). This creates 2 areas of different charge. The H+ of one water molecule will bond with the O of another water molecule due to the attractive forces of the opposite charges. ...
... from the hydrogen). This creates 2 areas of different charge. The H+ of one water molecule will bond with the O of another water molecule due to the attractive forces of the opposite charges. ...
Amino Acids Proteins, and Enzymes Types of Proteins Amino Acids
... Nonpolar R = H, CH3, alkyl groups, aromatic O Polar ll R = –CH2OH, –CH2SH, –CH2C–NH2, (polar groups with –O-, -SH, -N-) Polar/Acidic R = –CH2COOH, or -COOH Polar/ Basic R = –CH2CH2NH2 ...
... Nonpolar R = H, CH3, alkyl groups, aromatic O Polar ll R = –CH2OH, –CH2SH, –CH2C–NH2, (polar groups with –O-, -SH, -N-) Polar/Acidic R = –CH2COOH, or -COOH Polar/ Basic R = –CH2CH2NH2 ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... List the five natural elements which make up 96% of the human body. What is an organic compound vs. inorganic? List the total number of atoms in the following compound: C18H36O2 Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Ex ...
... List the five natural elements which make up 96% of the human body. What is an organic compound vs. inorganic? List the total number of atoms in the following compound: C18H36O2 Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Ex ...
msc mlt-1st sem(1563)
... How is the energy generated during metabolic processes usually stored for later use? ...
... How is the energy generated during metabolic processes usually stored for later use? ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Amino Acids and Proteins
... acids are in a chain. Above the x-axis is most hydrophobic, and below the xaxis is hydrophilic. What is the maximal UV absorption of a protein? 280 What is the maximal UV absorption of DNA? 260 To form a peptide bond what happens? Hydrolysis – water is removed. What percentage of “likeness” do two p ...
... acids are in a chain. Above the x-axis is most hydrophobic, and below the xaxis is hydrophilic. What is the maximal UV absorption of a protein? 280 What is the maximal UV absorption of DNA? 260 To form a peptide bond what happens? Hydrolysis – water is removed. What percentage of “likeness” do two p ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... See table 26.1 to examine names, abbreviations, physical properties, and structures of 20 commonly occurring amino acids ...
... See table 26.1 to examine names, abbreviations, physical properties, and structures of 20 commonly occurring amino acids ...
Slide 1 - Denton ISD
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
macromolecules new
... and carbon ( C ) with a little oxygen ( O )? • 8. Which contains C , H, O in a 1:2:1 ratio? • 9. Which also contains nitrogen (N)? ...
... and carbon ( C ) with a little oxygen ( O )? • 8. Which contains C , H, O in a 1:2:1 ratio? • 9. Which also contains nitrogen (N)? ...
Chapter 2 - Biochemistry
... 1. Enzyme forms a temporary association with a the substance it affects ...
... 1. Enzyme forms a temporary association with a the substance it affects ...
Functional groups - Montgomery County Schools
... 4. Inhibitors – can stop/slow rate a. competitive – resemble substrate & compete for active site b. non-competitive – attach to enzyme some place other than active site, altering shape of active site; substrate cannot fit ...
... 4. Inhibitors – can stop/slow rate a. competitive – resemble substrate & compete for active site b. non-competitive – attach to enzyme some place other than active site, altering shape of active site; substrate cannot fit ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
BCHM 463 Supplemental Problems for Friday, April 9, 2004 1. a
... of 3 enzymes. a) Name these enzymes and give all species that inhibit (negatively modulate) the enzymes’ activities. Citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and ∝-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase are the control points for the citric acid cycle. See figure 16-14 for the intermediates and products whi ...
... of 3 enzymes. a) Name these enzymes and give all species that inhibit (negatively modulate) the enzymes’ activities. Citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and ∝-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase are the control points for the citric acid cycle. See figure 16-14 for the intermediates and products whi ...
Syllabus Notes - Southwest High School
... – They MAKE or BREAK stuff generally. – The long chain of amino acids fold into a specific shape. (FYI: Change one amino acid? Primary, secondary, and tertiary structure all change… the function could change too!) – This 3D shape of the enzyme fits its substrate EXACTLY. Just like a lock fits only o ...
... – They MAKE or BREAK stuff generally. – The long chain of amino acids fold into a specific shape. (FYI: Change one amino acid? Primary, secondary, and tertiary structure all change… the function could change too!) – This 3D shape of the enzyme fits its substrate EXACTLY. Just like a lock fits only o ...
Phosphate group
... •Notice all the single bonds between carbons. •Notice 2 hydrogen's attached to all the carbons, except for the ends. ...
... •Notice all the single bonds between carbons. •Notice 2 hydrogen's attached to all the carbons, except for the ends. ...
Antibiotics - Dr Magrann
... CROSSLINKAGE: b- lactams mimic D-ALA-D-ALA of NAM and interfere with the enzymes that do the crosslinking. Penicillins Cephalosporins Monobactams CELL MEMBRANE TARGETS Lipopeptides are amphiphilic, contain D-amino acids, disrupt CM, are potent but not selective; for “compassionate use” Polymyxins Gr ...
... CROSSLINKAGE: b- lactams mimic D-ALA-D-ALA of NAM and interfere with the enzymes that do the crosslinking. Penicillins Cephalosporins Monobactams CELL MEMBRANE TARGETS Lipopeptides are amphiphilic, contain D-amino acids, disrupt CM, are potent but not selective; for “compassionate use” Polymyxins Gr ...
Classification of amino acids: -
... Note/ amino acids are classified into three groups depending on their reactions: 1. Neutral: aliphatic, aromatic, cyclic and hydroxyl or sulfur containing amino acids: (Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Phe, Tyr, Trp, Ser, Thr, Cys, Met, Pro) 2. Acidic: this class contain 4 standard amino acids: (Asp, Asn, G ...
... Note/ amino acids are classified into three groups depending on their reactions: 1. Neutral: aliphatic, aromatic, cyclic and hydroxyl or sulfur containing amino acids: (Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Phe, Tyr, Trp, Ser, Thr, Cys, Met, Pro) 2. Acidic: this class contain 4 standard amino acids: (Asp, Asn, G ...
AMINOACID METABOLISM
... The aminoacids undergo certain common reactions like TRANSAMINATION followed by DEAMINATION for the liberation of Ammonia. The amino group of aa is utilized for the formation of UREA. The carbon skeleton of aa is first converted to ketoacids which meet one or more of the following fates: ...
... The aminoacids undergo certain common reactions like TRANSAMINATION followed by DEAMINATION for the liberation of Ammonia. The amino group of aa is utilized for the formation of UREA. The carbon skeleton of aa is first converted to ketoacids which meet one or more of the following fates: ...
File
... Protein: Metabolism and Function The body cells will use only the amount of amino acids necessary to meet their protein needs. They cannot store excess amino acids. Because the human body does not have a mechanism to store excess nitrogen, it cannot store amino acids. Through the process of deamina ...
... Protein: Metabolism and Function The body cells will use only the amount of amino acids necessary to meet their protein needs. They cannot store excess amino acids. Because the human body does not have a mechanism to store excess nitrogen, it cannot store amino acids. Through the process of deamina ...
hydroxyproline
... dentin and cementum (see note #1 below). 1. Hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine are nonstandard amino acids that are present in Notes few other proteins. For this reason, their concentration in a particular tissue is a good estimate of the collagen content as well. They are not used directly in the rea ...
... dentin and cementum (see note #1 below). 1. Hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine are nonstandard amino acids that are present in Notes few other proteins. For this reason, their concentration in a particular tissue is a good estimate of the collagen content as well. They are not used directly in the rea ...
Reading Guide
... 13. What type of reaction is catalyzed by fumarase? 14. What type of reaction is necessary to transform malate into oxaloacetate? Is any cofactor needed? How is this reaction, with a very positive standard free energy, driven to completion? 15. Provide an overview accounting of how a glucose molecul ...
... 13. What type of reaction is catalyzed by fumarase? 14. What type of reaction is necessary to transform malate into oxaloacetate? Is any cofactor needed? How is this reaction, with a very positive standard free energy, driven to completion? 15. Provide an overview accounting of how a glucose molecul ...
ppt-file
... producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable that the yield is lower than when ATP and AD ...
... producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable that the yield is lower than when ATP and AD ...
Chapter 15 - Translation of mRNA
... 1. The genetic basis for protein synthesis a. Archibald Garrod proposed that some genes code for the production of a single enzyme b. Beadle and Tatum’s experiments with Neurospora led them to propose the one-gene/oneenzyme hypothesis 2. The relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesi ...
... 1. The genetic basis for protein synthesis a. Archibald Garrod proposed that some genes code for the production of a single enzyme b. Beadle and Tatum’s experiments with Neurospora led them to propose the one-gene/oneenzyme hypothesis 2. The relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesi ...