* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibiotics - Dr Magrann
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
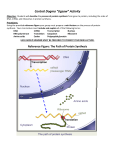
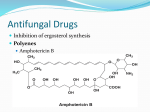
ANTIBIOTICS INHIBITORS OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS (Peptidoglycan) NAM SYNTHESIS: D-cycloserine mimics D-Alanine, prevents synthesis. SHUTTLE: Bacitracin interferes with C55 lipid shuttle by binding it. TRANSGLYCOSYLATION: Glycopeptides (e.g. Vancomycin) prevents it. CROSSLINKAGE: b- lactams mimic D-ALA-D-ALA of NAM and interfere with the enzymes that do the crosslinking. Penicillins Cephalosporins Monobactams CELL MEMBRANE TARGETS Lipopeptides are amphiphilic, contain D-amino acids, disrupt CM, are potent but not selective; for “compassionate use” Polymyxins Gramicidins INHIBITORS OF mRNA SYNTHESIS Rifamycins: Bind to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase β subunit, prohibits mRNA transcription. Rifampin INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (TRANSLATION) the concentration of these antibiotics can become toxic to us. BACTERIOSTATIC (are reversible) Tetracyclines (Target 30S ribosome) Amphenicols (Target 50S ribosome) Macrolides (Target 50S ribosome) Erythromycin Azithromycin Clindramycin BACTERIOCIDAL (are irreversible) Aminoglycosides: All bind on 50S. These are strong, but not very selective. They can cause kidney and inner ear damage. Gentamicin (made by microsporin fungus) Streptomycin (made by streptomyces fungus) Kanamycin (“ “ “) Tobramycin (“ “ “) Amikacin INHIBITORS OF DNA SYNTHESIS (Target is ENZYMES that control DNA) Quinolones: Target and block DNA gyrase Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Metronidazole (“Flagyl”): Used against ANAEROBIC bacteria. Generates toxic O 2 metabolites ANTIMETABOLITES (Inhibits Folate Synthesis) We need Folic acid from our normal flora in GI tract. These abs can cause a lack of folic acid in us. Sulfonamides mimic PABA (Sulfamethoxasole) Trimethoprim targets DHF reductase Cotrimoxazole (Bactrim): combination of above two antibiotics. This is a synergistic use of antibiotics; They target different sites. ANTIMYCOLATES: Inhibit trans Δ24 desaturase, required to go from lipid mycolipid. Lysosomes can now stick to phagosome and lyse the bacteria. Isoniazid Ethambutol P. Aminosalicylic Acid