12/10/09
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
Study Guide for Membranes and Transport
... compare and contrast the structure of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids compare and contrast the function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids describe the structure and properties of a water molecule, including its polarity Membranes and transport: Understa ...
... compare and contrast the structure of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids compare and contrast the function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids describe the structure and properties of a water molecule, including its polarity Membranes and transport: Understa ...
The Cell
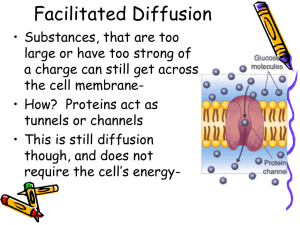
... ◦ Protein carrier is used because molecules are too large to enter pores ◦ Still passive transport, just needs help ◦ No energy because it is using a gradient ...
... ◦ Protein carrier is used because molecules are too large to enter pores ◦ Still passive transport, just needs help ◦ No energy because it is using a gradient ...
Slide 1
... Facilitated Diffusion Some material just can’t get through the membrane without a little help. Carrier molecules are happy to lend a hand. This does not use any energy. FYI only ...
... Facilitated Diffusion Some material just can’t get through the membrane without a little help. Carrier molecules are happy to lend a hand. This does not use any energy. FYI only ...
Active Transport
... transport: moving molecules in a direction across the concentration gradient. Requires energy Molecular Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis ...
... transport: moving molecules in a direction across the concentration gradient. Requires energy Molecular Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis ...
Unit 2 Part1 wksht
... 1. According to the cell theory, all cells carry on ____________________________________________, come from __________________________________ and all organisms are made of _____________. ...
... 1. According to the cell theory, all cells carry on ____________________________________________, come from __________________________________ and all organisms are made of _____________. ...
Moving Molecules and Cellular Energy Crossword
... 9. process by which glucose is broken down 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reac ...
... 9. process by which glucose is broken down 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reac ...
Cytology
... parasitic relationships with bacteria, all of the cells of our body are eukaryotic. • What does this mean? ...
... parasitic relationships with bacteria, all of the cells of our body are eukaryotic. • What does this mean? ...
Cells how to post it activity
... 1. Think of a place you could draw that would represent the cell and all of its organelles. EX: A drawing of a basketball court with teams playing basketball, match up the cell words with the drawing. Don’t use our classroom since that is the analogy I will use in class (coach – nucleus, gym walls – ...
... 1. Think of a place you could draw that would represent the cell and all of its organelles. EX: A drawing of a basketball court with teams playing basketball, match up the cell words with the drawing. Don’t use our classroom since that is the analogy I will use in class (coach – nucleus, gym walls – ...
Biology Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Notes
... Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have a head and a tail. The tail or fatty acid end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic (water hating) and carries a neutral charge and is nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a ph ...
... Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have a head and a tail. The tail or fatty acid end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic (water hating) and carries a neutral charge and is nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a ph ...
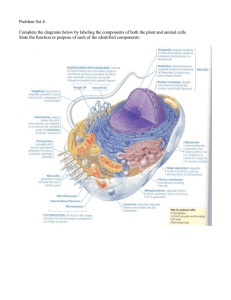
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
Slide 1
... Phospholipid bilayer that separates the living environment from the nonliving environment. Controls what may enter or leave the cell. ...
... Phospholipid bilayer that separates the living environment from the nonliving environment. Controls what may enter or leave the cell. ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
Structures and Organelles
... digest excess organelles and/or food particles also digest bacteria and viruses ...
... digest excess organelles and/or food particles also digest bacteria and viruses ...
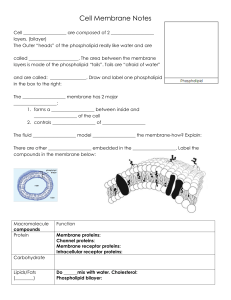
Membrane Transport notes
... b. -proteins inserted in bilayer for movement of molecules c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible ...
... b. -proteins inserted in bilayer for movement of molecules c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible ...
Chapter 5.1 Notes
... of membrane Proteins: peripheral (inside surface of membrane) or integral (embedded in membrane) Some integral proteins protrude from one surface of bilayer, some protrude from both (transmembrane) Phospholipids and proteins can have attached carbohydrate (sugar) chains. These are called glyco ...
... of membrane Proteins: peripheral (inside surface of membrane) or integral (embedded in membrane) Some integral proteins protrude from one surface of bilayer, some protrude from both (transmembrane) Phospholipids and proteins can have attached carbohydrate (sugar) chains. These are called glyco ...
AP BIOLOGY-EXAM REVIEW The Cell
... The organelles that contain their own DNA are all enclosed in double membranes. Relate this observation to the endosymbiotic theory. ...
... The organelles that contain their own DNA are all enclosed in double membranes. Relate this observation to the endosymbiotic theory. ...
Slide 1
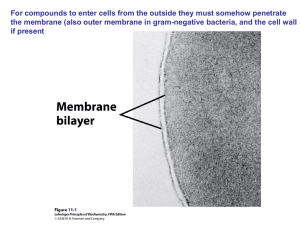
... are not like a concrete wall and also not like the thin membrane in a soap-bubble. It is a much more complex barrier that lets certain selected compounds through in a strictly controlled manner. •Macromolecules and charged smaller molecules do not generally pass through membranes passively (by diffu ...
... are not like a concrete wall and also not like the thin membrane in a soap-bubble. It is a much more complex barrier that lets certain selected compounds through in a strictly controlled manner. •Macromolecules and charged smaller molecules do not generally pass through membranes passively (by diffu ...
Name Date The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Part Structure
... Name ___________________________________________ ...
... Name ___________________________________________ ...
Chp3-Cells_TEST REVIEW
... 1. Review and be able to complete the functions of organelles. Close attention to: lysosomes, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum(rough/smooth), Nucleolus, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments), ribosomes, cilia and flagella: 2. The Plasma(cell) Membrane: W ...
... 1. Review and be able to complete the functions of organelles. Close attention to: lysosomes, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum(rough/smooth), Nucleolus, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments), ribosomes, cilia and flagella: 2. The Plasma(cell) Membrane: W ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.