AP BIOLOGY-EXAM REVIEW-Chapter 2
... 4. List the “special” properties of water and give an example of why the property may be important to living things. ...
... 4. List the “special” properties of water and give an example of why the property may be important to living things. ...
Can EVERY molecule pass through the cell membrane freely? Why
... Materials move across membranes because of concentration differences. ...
... Materials move across membranes because of concentration differences. ...
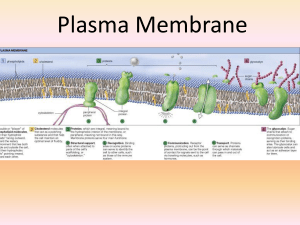
Plasma Membrane
... metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide temporary or permanent connections; these connections referred to as junctions ...
... metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide temporary or permanent connections; these connections referred to as junctions ...
Name
... 11) Which molecule is least able to cross a plasma membrane by simple diffusion due to its sphere of hydration? a) Water b) Bicarbonate c) Carbon dioxide d) Triglyceride 12) There are four types of transmembrane ATP-ase, which one is most important for moving very large molecules across the membrane ...
... 11) Which molecule is least able to cross a plasma membrane by simple diffusion due to its sphere of hydration? a) Water b) Bicarbonate c) Carbon dioxide d) Triglyceride 12) There are four types of transmembrane ATP-ase, which one is most important for moving very large molecules across the membrane ...
Chapter 8 Questions
... 4. What would happen if the cell membrane were fully permeable to all substances in the cell’s environment? 5. Why can’t ions pass through the cell membrane? 6. Why does oxygen diffuse into the cell? 7. Compare the functions of channel proteins and carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion. 8. Expla ...
... 4. What would happen if the cell membrane were fully permeable to all substances in the cell’s environment? 5. Why can’t ions pass through the cell membrane? 6. Why does oxygen diffuse into the cell? 7. Compare the functions of channel proteins and carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion. 8. Expla ...
Chapter 5 Lesson 1 and 2 PPt
... the membrane and organelles interact with water-based solutions. • Hydrophobic inside limits what can enter or exit the cell. • Cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane ...
... the membrane and organelles interact with water-based solutions. • Hydrophobic inside limits what can enter or exit the cell. • Cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane ...
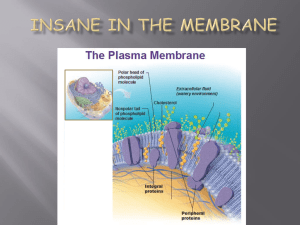
The Plasma Membrane aka the cell membrane http://sun
... • Attaches to a substrate outside of the cell or to other cells to help form tissues • Controls the transportation of substances across the membrane by using proteins as carriers and channels • Contains receptors that allow cells to communicate through chemical messages • Contains recognition protei ...
... • Attaches to a substrate outside of the cell or to other cells to help form tissues • Controls the transportation of substances across the membrane by using proteins as carriers and channels • Contains receptors that allow cells to communicate through chemical messages • Contains recognition protei ...
1. Name two functions of the cell membrane
... 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called______________________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape ...
... 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called______________________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape ...
Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose
... Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin ...
... Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin ...
sgCh1Cell
... Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek observe? 4. The function of the cell wall is _____________________________________. 5. Organelles that control ...
... Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek observe? 4. The function of the cell wall is _____________________________________. 5. Organelles that control ...
Cells are the units of structure and function of an organism
... The liquid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. ...
... The liquid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. ...
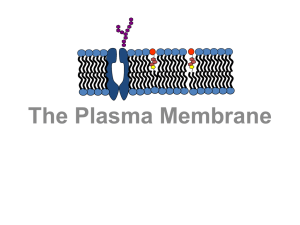
Cell Membrane aka Plasma Membrane
... Membrane Transport Pages 78-85 include information on membrane transport ...
... Membrane Transport Pages 78-85 include information on membrane transport ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
... Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
Ribosomes (20-30nm)
... Uses enzymes to modify these proteins (e.g. add a sugar chain, making glycoprotein) Adds directions for destination of protein package - vesicles that leave Golgi apparatus move to different locations in cell or proceed to plasma membrane for secretion Involved in processing, packaging, and secretio ...
... Uses enzymes to modify these proteins (e.g. add a sugar chain, making glycoprotein) Adds directions for destination of protein package - vesicles that leave Golgi apparatus move to different locations in cell or proceed to plasma membrane for secretion Involved in processing, packaging, and secretio ...
Q10 Describe transport mechanisms across cell membranes. Give
... o Primary à movement of a substance across the membrane against an energy gradient using a specific carrier protein. This requires additional energy such as ATP (eg; the Na/K ATPase pump) o Secondary à ...
... o Primary à movement of a substance across the membrane against an energy gradient using a specific carrier protein. This requires additional energy such as ATP (eg; the Na/K ATPase pump) o Secondary à ...
Membranes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Plasma Membrane: the outer boundary of a cell that encloses the cells contents. ...
... • Plasma Membrane: the outer boundary of a cell that encloses the cells contents. ...
Chapter 4: General Features of Cells
... When material reaches trans side, the material in package in ______ _______. - (materials leaving cell) secretory vesicles fuse with plasma membrane and contents released to outside. EndocytosisSecretory pathway- proteins move from _____ to golgi to vesicle to plasma membrane. Lysosomes: Functio ...
... When material reaches trans side, the material in package in ______ _______. - (materials leaving cell) secretory vesicles fuse with plasma membrane and contents released to outside. EndocytosisSecretory pathway- proteins move from _____ to golgi to vesicle to plasma membrane. Lysosomes: Functio ...
Test Review for AP Biology Chapter 5 What molecules make up the
... 3. Know how temperature effects the cell membrane. Ie. What is one of the ways that a membrane of winter vegetation can remain fluid when cold? 4. For a protein to be an integral membrane protein would it need to be hydrophilic, hydrophobic or amphipathic? 5. Why do unsaturated fatty acids help keep ...
... 3. Know how temperature effects the cell membrane. Ie. What is one of the ways that a membrane of winter vegetation can remain fluid when cold? 4. For a protein to be an integral membrane protein would it need to be hydrophilic, hydrophobic or amphipathic? 5. Why do unsaturated fatty acids help keep ...
Study Guide for Chapter 3 in Fox
... What is a gene? Where do you find them? What does the term “gene expression” mean” What are the definitions I gave you for: replications, transcriptions and translation? What is the “Human Genome”? What is chromatin? Nucleosomes? What does the genetic code, code for? What are “Triplets”? How many na ...
... What is a gene? Where do you find them? What does the term “gene expression” mean” What are the definitions I gave you for: replications, transcriptions and translation? What is the “Human Genome”? What is chromatin? Nucleosomes? What does the genetic code, code for? What are “Triplets”? How many na ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.