Chapter-5-worksheet
... ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. ...
... ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. ...
7-3_cell_boundaries
... a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ ...
... a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ ...
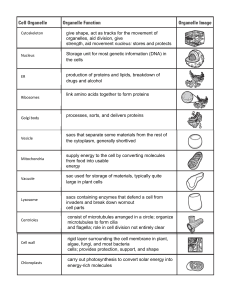
Cell Organelles
... • Controls what enters and leaves the cell Maintains Homeostasis “steady state” ...
... • Controls what enters and leaves the cell Maintains Homeostasis “steady state” ...
Slide 1
... of the membrane and orient themselves AWAY from water •phospholipids form a bilayer; • cholesterol also found among fatty acid tails ...
... of the membrane and orient themselves AWAY from water •phospholipids form a bilayer; • cholesterol also found among fatty acid tails ...
Sections 3
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... sacs that separate some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm, generally shortlived ...
... sacs that separate some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm, generally shortlived ...
cell membrane
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
Chapter 7 Reading Guide
... Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. ...
... Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. ...
element Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
... instructions that cells need to carry out all of the functions of life Genetic material that carries info. about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring ...
... instructions that cells need to carry out all of the functions of life Genetic material that carries info. about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring ...
Endocytosis - Cloudfront.net
... • Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) – 1) Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs a solid particle – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way ...
... • Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) – 1) Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs a solid particle – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way ...
Cell Walls and Boundaries Cells protect themselves by their cell
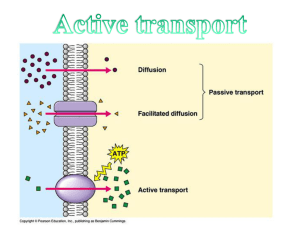
... o At equilibrium, the particles will continue to move across the membrane in both directions = no net change Facilitated Diffusion = molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels (diffusion with help) Proteins act as carriers, or channels, making ...
... o At equilibrium, the particles will continue to move across the membrane in both directions = no net change Facilitated Diffusion = molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels (diffusion with help) Proteins act as carriers, or channels, making ...
View PDF
... 19. How does Paramecium osmoregulate? You may not know it, but this is something you really want to know. In fact, whether you care or not, you’ve reached a crossroads in your journey to be as awesome as me. Choose the right path and you might just walk the rice paper without leaving a trace. ...
... 19. How does Paramecium osmoregulate? You may not know it, but this is something you really want to know. In fact, whether you care or not, you’ve reached a crossroads in your journey to be as awesome as me. Choose the right path and you might just walk the rice paper without leaving a trace. ...
Ch.4 Cell Notes - Milan Area Schools
... This surrounds the cell & controls what moves in and out of the cell like a gatekeeper Made of two layers of phospholipids (aka phospholipid bilayer) ...
... This surrounds the cell & controls what moves in and out of the cell like a gatekeeper Made of two layers of phospholipids (aka phospholipid bilayer) ...
Structure and Function of Cells
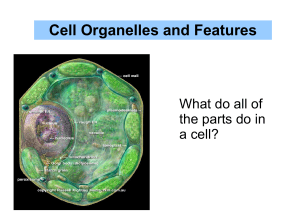
... The structures within a cell function in providing protection and support, forming a barrier between the cell and its environment, building and repairing cells parts, transporting materials, storing and releasing energy, getting rid of waste materials, and increasing in number. The following diagram ...
... The structures within a cell function in providing protection and support, forming a barrier between the cell and its environment, building and repairing cells parts, transporting materials, storing and releasing energy, getting rid of waste materials, and increasing in number. The following diagram ...
Basic features of all cells
... with the help of energy. It uses energy to move solutes against their gradients. ...
... with the help of energy. It uses energy to move solutes against their gradients. ...
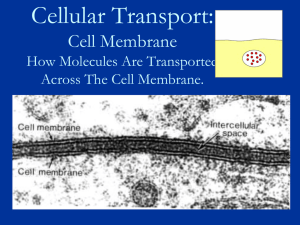
Cell membrane – boundary that separates the interior of
... Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules ...
... Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... Strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the c ...
... Strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the c ...
Biozentrum: Research group Martin Spiess
... divide the cell interior into separate compartments and organelles. They consist of lipids and embedded membrane proteins. Our group works for a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of how ...
... divide the cell interior into separate compartments and organelles. They consist of lipids and embedded membrane proteins. Our group works for a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of how ...
The Cell Membrane 2015
... Many substances can diffuse across biological membranes, but some are too large or too strongly charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Mos ...
... Many substances can diffuse across biological membranes, but some are too large or too strongly charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Mos ...
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
... -You will understand that membranes are fluid -The structure results in a semi-permeable membrane -Passive transport requires no energy -Active transport requires energy -Bulk transport of molecules either by exocytosis or by endocytosis. ...
... -You will understand that membranes are fluid -The structure results in a semi-permeable membrane -Passive transport requires no energy -Active transport requires energy -Bulk transport of molecules either by exocytosis or by endocytosis. ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.