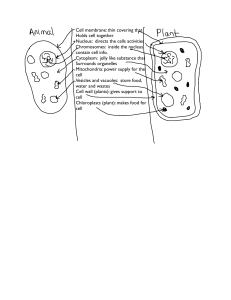
Cellular Processes
... to get out, and water is constantly moving back and forth. • Substances that can easily pass through the semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ...
... to get out, and water is constantly moving back and forth. • Substances that can easily pass through the semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ...
3-1 part 2
... Contains 2 types: rough and smooth. *rough is abundant in WBC. It contains ribosomes and works in protein synthesis *smooth is abundant in liver cells. It does not have ribosomes and it is used in lipid synthesis. ...
... Contains 2 types: rough and smooth. *rough is abundant in WBC. It contains ribosomes and works in protein synthesis *smooth is abundant in liver cells. It does not have ribosomes and it is used in lipid synthesis. ...
review for second six weeks common assessment
... 1. Know stages of Mitosis and what happens in each phase 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynth ...
... 1. Know stages of Mitosis and what happens in each phase 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynth ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... 1935 Davison and Danielli figured out where proteins fit in bilayer, accepted until early 1970's ...
... 1935 Davison and Danielli figured out where proteins fit in bilayer, accepted until early 1970's ...
Cell Structures
... Endoplasmic reticulum Membrane that serves as a place for ribosomes to sit (rough endoplasmic reticulum) Makes the lipids that form vacuoles (so the proteins being made by the ribosomes can be transported) – this happens at the smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... Endoplasmic reticulum Membrane that serves as a place for ribosomes to sit (rough endoplasmic reticulum) Makes the lipids that form vacuoles (so the proteins being made by the ribosomes can be transported) – this happens at the smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
Anatomy of Plants
... Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes or very few. • Proteins produced by ribosomes are passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen, where they are sealed in vesicles for transport to the cell organelles ...
... Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes or very few. • Proteins produced by ribosomes are passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen, where they are sealed in vesicles for transport to the cell organelles ...
Nuclear Envelope - Plain Local Schools
... transport cell products – Lacks ribosomes – Makes lipid molecules ...
... transport cell products – Lacks ribosomes – Makes lipid molecules ...
Name - DiBiasioScience
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells are able to reproduce. d. All cells ...
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells are able to reproduce. d. All cells ...
Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for
... Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for Emerging Therapeutic Applications Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatm ...
... Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for Emerging Therapeutic Applications Cell membranes present a unique interface that governs numerous biological events in physiology as well as in disease pathogenesis; exploiting this interface for therapeutic development promises novel treatm ...
Part 2: EOC Review Questions
... Describe the structure of a cell membrane? Why are some membranes considered selectively permeable? What is the function of proteins found within the cell membrane? What type of cellular transport does not require energy? What type of cellular transport requires energy What is meant by a concentrati ...
... Describe the structure of a cell membrane? Why are some membranes considered selectively permeable? What is the function of proteins found within the cell membrane? What type of cellular transport does not require energy? What type of cellular transport requires energy What is meant by a concentrati ...
The Cell Membrane
... • Marker proteins extend across the cell membrane and serve to identify the cell. The immune system uses these proteins to tell friendly cells from foreign invaders. They are as unique as fingerprints. They play an important role in organ transplants. If the marker proteins on a transplanted organ ...
... • Marker proteins extend across the cell membrane and serve to identify the cell. The immune system uses these proteins to tell friendly cells from foreign invaders. They are as unique as fingerprints. They play an important role in organ transplants. If the marker proteins on a transplanted organ ...
Cell Membrane Structure and Fluid Movement
... 4. Why does your body make cholesterol even if you do not eat any foods that contain cholesterol? How is cholesterol important to the cell membrane? 5. Explain why the electron microscope is better than the light microscope at looking at the cell membrane. 6. List three other names for the cell memb ...
... 4. Why does your body make cholesterol even if you do not eat any foods that contain cholesterol? How is cholesterol important to the cell membrane? 5. Explain why the electron microscope is better than the light microscope at looking at the cell membrane. 6. List three other names for the cell memb ...
Active Cellular Transport Lesson 7 Biology 10 Movement of ions and
... mitochondria turns glucose into a usable form of energy (ATP) ...
... mitochondria turns glucose into a usable form of energy (ATP) ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... CM allows some substances across more easily than others… some it helps and some it inhibits or rejects all together. ...
... CM allows some substances across more easily than others… some it helps and some it inhibits or rejects all together. ...
Cell Membranes
... The outer layer of an animal cell. The tail part of a phospholipid molecule. Another name for the plasma membrane. This term means to “see little things”. The measurement used to measure the size of cells. Molecule that is repeated in a cell membrane. Another name for the Cytoplasmic membrane. The w ...
... The outer layer of an animal cell. The tail part of a phospholipid molecule. Another name for the plasma membrane. This term means to “see little things”. The measurement used to measure the size of cells. Molecule that is repeated in a cell membrane. Another name for the Cytoplasmic membrane. The w ...
QUEST Study guide Organic molecules Proteins, carbohydrates
... Know what molecules use simple diffusion, what molecules use facilitated diffusion, and what molecules use Active transport across the membrane Be able to discuss how the cell membrane allows the cell to maintain HOMEOSTASIS (oh yeah, you should know what this term means!) Know the terms isotonic, h ...
... Know what molecules use simple diffusion, what molecules use facilitated diffusion, and what molecules use Active transport across the membrane Be able to discuss how the cell membrane allows the cell to maintain HOMEOSTASIS (oh yeah, you should know what this term means!) Know the terms isotonic, h ...
Unit 6 Objectives Chapter 4 • Understand the basic tenets of the cell
... Describe the organelles associated with the endomembrane system, and tell the general function of each ...
... Describe the organelles associated with the endomembrane system, and tell the general function of each ...
File
... Capsule- Outside the cell wall. For additional protection. Plasma membrane- Regulates what crosses into the cell Nucleiod Region- where circular DNA is found Ribosomes- Workbench, where proteins are made ...
... Capsule- Outside the cell wall. For additional protection. Plasma membrane- Regulates what crosses into the cell Nucleiod Region- where circular DNA is found Ribosomes- Workbench, where proteins are made ...
CELL MEMBRANE: Structure and Function
... the cell together. Maintains cellular homeostasis by regulating what enters (food and nutrients) and leaves (waste). ...
... the cell together. Maintains cellular homeostasis by regulating what enters (food and nutrients) and leaves (waste). ...
ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
... 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6. What is a phospholipid? (3 basic parts) 7. Why do phospholipids form a double layer? 8. How is the organelle like a tiny organ? 9. Briefly expl ...
... 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6. What is a phospholipid? (3 basic parts) 7. Why do phospholipids form a double layer? 8. How is the organelle like a tiny organ? 9. Briefly expl ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.