Cell Membrane Tutorial
... Once the activities within the tutorial have been completed, record the following in your science notebook: write a 1–2 paragraph summary about the cell membrane. It should include: a. Description and brief sketch of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane b. Function of the cell membrane c. What mol ...
... Once the activities within the tutorial have been completed, record the following in your science notebook: write a 1–2 paragraph summary about the cell membrane. It should include: a. Description and brief sketch of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane b. Function of the cell membrane c. What mol ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... o Describe why the cell membrane exhibits selective permeability o Explain why a phospholipid is considered amphipathic (use a sketch in your answer). o Describe the fluidity of cell membranes. o Using the components of the cell membrane, explain why the cell membrane is referred to as a “fluid mosa ...
... o Describe why the cell membrane exhibits selective permeability o Explain why a phospholipid is considered amphipathic (use a sketch in your answer). o Describe the fluidity of cell membranes. o Using the components of the cell membrane, explain why the cell membrane is referred to as a “fluid mosa ...
Lysosome small round structures that break down large food
... Lysosome small round structures that break down large food molecules ...
... Lysosome small round structures that break down large food molecules ...
Section 3.3 Introduction in Canvas
... The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the inside of a cell from the outside environment. It plays an active role by controlling the passage of materials into and out of a cell and by responding to signals. The membrane is made of molecules called phospholipids, which consist of three par ...
... The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the inside of a cell from the outside environment. It plays an active role by controlling the passage of materials into and out of a cell and by responding to signals. The membrane is made of molecules called phospholipids, which consist of three par ...
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and
... organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most likely to contain, respectively, A) mitochondria and chloroplasts. B) chloroplasts and peroxisomes. C) peroxisomes and chloroplasts. D) chloroplasts and mitochondria. E) mitochondria and pero ...
... organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most likely to contain, respectively, A) mitochondria and chloroplasts. B) chloroplasts and peroxisomes. C) peroxisomes and chloroplasts. D) chloroplasts and mitochondria. E) mitochondria and pero ...
Cell City - TeacherWeb
... Cell City Grading Rubric All 12 organelles represented _________(25) Each structure in your cell city must be clearly identified and paired with a specific cell structure. (Example: City Hall/Nucleus) This is to be written on the poster board next to the specific structure. Plasma membrane Nucleus N ...
... Cell City Grading Rubric All 12 organelles represented _________(25) Each structure in your cell city must be clearly identified and paired with a specific cell structure. (Example: City Hall/Nucleus) This is to be written on the poster board next to the specific structure. Plasma membrane Nucleus N ...
The Cell: Organelles and Functions
... Function: 1. Transport of cellular products Processing of cellular products - Lipids to cell membrane - Proteins for export ...
... Function: 1. Transport of cellular products Processing of cellular products - Lipids to cell membrane - Proteins for export ...
Tic Tac Toe Review Questions File
... with specific molecules) 15. What is the job of the Golgi apparatus? (Sort, package, and transport proteins) 16. What are the 3 products of Cellular respiration? (ATP, CO2, Water) 17. Give three reasons why Folded membranes are an advantage to the cell? (efficient, more work done in small space, cre ...
... with specific molecules) 15. What is the job of the Golgi apparatus? (Sort, package, and transport proteins) 16. What are the 3 products of Cellular respiration? (ATP, CO2, Water) 17. Give three reasons why Folded membranes are an advantage to the cell? (efficient, more work done in small space, cre ...
The Magic Universe of Cells Directions
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
... draw, label, and define the parts of an animal cell and a plant cell. You need to include at least: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, vacuoles, centrioles, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and chromatin. If there is ...
Membrane Function Review
... __________ across a membrane. This transport can dramatically affect cells. If a cell’s concentration of salt is higher than the surrounding liquid (meaning there is ______ water inside the cell), water will __________ the cell causing it to ____________. This type of solution is called ____________ ...
... __________ across a membrane. This transport can dramatically affect cells. If a cell’s concentration of salt is higher than the surrounding liquid (meaning there is ______ water inside the cell), water will __________ the cell causing it to ____________. This type of solution is called ____________ ...
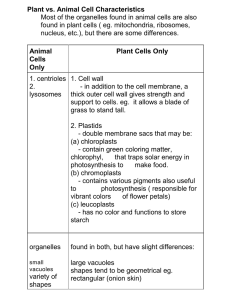
Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in
... nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
... nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
Live Casino Roulette System
... Cells have different shapes, according to the work they do. Cells might look like cubes, rods, snowflakes, or even blobs of jelly. Every cell’s outer layer is a thin skin called a membrane. It has openings to let materials in. Most of the cell is made of a jellylike fluid called cytoplasm. Cytoplasm ...
... Cells have different shapes, according to the work they do. Cells might look like cubes, rods, snowflakes, or even blobs of jelly. Every cell’s outer layer is a thin skin called a membrane. It has openings to let materials in. Most of the cell is made of a jellylike fluid called cytoplasm. Cytoplasm ...
Cell City - TeacherWeb
... Cell City Grading Rubric Due September 27, 2013 All 12 organelles represented _________(25) Each structure in your cell city must be clearly identified and paired with a specific cell structure. (Example: City Hall/Nucleus) This is to be written on the poster board next to the specific structure. Pl ...
... Cell City Grading Rubric Due September 27, 2013 All 12 organelles represented _________(25) Each structure in your cell city must be clearly identified and paired with a specific cell structure. (Example: City Hall/Nucleus) This is to be written on the poster board next to the specific structure. Pl ...
chapter 7 membranes
... o Transport o Enzymatic activity o Signal transduction o Intercellular joining o Cell-cell recognition, oligosaccharides or glycoproteins as tags o Attachment to cytoskeleton or ECM ER makes the plasma membrane Transport proteins: o Channel proteins have hydrophilic channels for specific ions an ...
... o Transport o Enzymatic activity o Signal transduction o Intercellular joining o Cell-cell recognition, oligosaccharides or glycoproteins as tags o Attachment to cytoskeleton or ECM ER makes the plasma membrane Transport proteins: o Channel proteins have hydrophilic channels for specific ions an ...
Transport Across Membranes
... Sugars or amino acids), though this is still based on concentration gradient ...
... Sugars or amino acids), though this is still based on concentration gradient ...
Answers - AP BIOLOGY!
... 4. What substances require the help of a transport protein? When is this considered active transport and when is this considered facilitated diffusion (passive)? Larger molecules, even if they are nonpolar, will sometimes have a protein that is specific to them to speed up the diffusion process. How ...
... 4. What substances require the help of a transport protein? When is this considered active transport and when is this considered facilitated diffusion (passive)? Larger molecules, even if they are nonpolar, will sometimes have a protein that is specific to them to speed up the diffusion process. How ...
Plasma Membranes1 Year 11 biology
... Cell must be able to take in wanted molecules and ions Cell must be able to excrete waste material of metabolism Relies on plasma membrane to do this ...
... Cell must be able to take in wanted molecules and ions Cell must be able to excrete waste material of metabolism Relies on plasma membrane to do this ...
Text 3
... proteins bound to membranes, which we have termed peripheral and integral1 proteins. […] A peripheral protein is held to the membrane only by rather weak noncovalent (perhaps mainly electrostatic) interactions and is not strongly associated with membrane lipid. […] An integral protein molecule with ...
... proteins bound to membranes, which we have termed peripheral and integral1 proteins. […] A peripheral protein is held to the membrane only by rather weak noncovalent (perhaps mainly electrostatic) interactions and is not strongly associated with membrane lipid. […] An integral protein molecule with ...
Cell Structure and Membrane Transport Study Guide
... Cell Theory: Know the three parts of the theory. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Bacteria are prokaryotic, do not have nucleus or other membranebound organelles. Do have cell membrane and ribosomes. Importance of Surface Area: Limits how much can enter or leave the cell. Ratio of surface area to v ...
... Cell Theory: Know the three parts of the theory. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Bacteria are prokaryotic, do not have nucleus or other membranebound organelles. Do have cell membrane and ribosomes. Importance of Surface Area: Limits how much can enter or leave the cell. Ratio of surface area to v ...
Exocytosis and Endocytosis
... • Pinocytosis: cells take up dissolved molecules by engulfing small volumes of the external solution. Ex: small intestine and fat droplets • Phagocytosis: process by which cells engulf solid particles. Ex: white blood cells and microbes • Cellular drinking vs. cellular eating ...
... • Pinocytosis: cells take up dissolved molecules by engulfing small volumes of the external solution. Ex: small intestine and fat droplets • Phagocytosis: process by which cells engulf solid particles. Ex: white blood cells and microbes • Cellular drinking vs. cellular eating ...
CP Biology
... of particles along its concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to low concentration 38 Another name for sugar 39 Factor that is manipulated by a scientist during an experiment 41 Moving materials across a membrane without using energy 42 A hydrocarbon plus an OH group 44 The soluti ...
... of particles along its concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to low concentration 38 Another name for sugar 39 Factor that is manipulated by a scientist during an experiment 41 Moving materials across a membrane without using energy 42 A hydrocarbon plus an OH group 44 The soluti ...
Life Science 2014 Trimester Exam- Study Guide Be able understand
... Know the organization of an organism from cells to organisms Know the structure and function of parts of the microscope Know what microscope we use in class Understand the difference between a simple microscope and a compound microscope Cell theory o 3 parts o Exceptions to the cell theory Antonie v ...
... Know the organization of an organism from cells to organisms Know the structure and function of parts of the microscope Know what microscope we use in class Understand the difference between a simple microscope and a compound microscope Cell theory o 3 parts o Exceptions to the cell theory Antonie v ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.