Cellular Transport Across the Membrane
... The pocket will break off inside of the cell and form a vesicle The vesicle will fuse with a lysosome and be digested. The substance is released into the cell. ...
... The pocket will break off inside of the cell and form a vesicle The vesicle will fuse with a lysosome and be digested. The substance is released into the cell. ...
Outline
... Lecture Outline: Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic unit of life (all life is cellular and smaller than a cell isn’t alive) 2. All cells come from other cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells prokaryote no internal membranes (or true organelles). 1-10m eg bacteria eukaryote 10-100m always have in ...
... Lecture Outline: Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic unit of life (all life is cellular and smaller than a cell isn’t alive) 2. All cells come from other cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells prokaryote no internal membranes (or true organelles). 1-10m eg bacteria eukaryote 10-100m always have in ...
Cell Study Guide - Miss Gleason`s Science
... structure: The basic framework of the cell membrane consists of a double layer of _________________ _________________ are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral membrane. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm consists of a clear liquid called ____________ ...
... structure: The basic framework of the cell membrane consists of a double layer of _________________ _________________ are found in the cell membrane, including some which are transmembrane and some that are peripheral membrane. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm consists of a clear liquid called ____________ ...
MICROSCOPE cell LEARNING TARGETS `16
... compound light microscope and accurately draw the object to scale based on my field of view. MS 03. I can use a compound light microscope to observe and draw objects at different magnifications. Vocabulary: eyepiece, base, arm, stage, tube, revolving nosepiece, low powered objective, medium powered ...
... compound light microscope and accurately draw the object to scale based on my field of view. MS 03. I can use a compound light microscope to observe and draw objects at different magnifications. Vocabulary: eyepiece, base, arm, stage, tube, revolving nosepiece, low powered objective, medium powered ...
Chap 7 HW Biology Due Date: Please compl
... 1. What are the two major parts of the cell? 2. What is the difference between the smooth ER and rough ER? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell li ...
... 1. What are the two major parts of the cell? 2. What is the difference between the smooth ER and rough ER? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell li ...
BIO508: Cell Biology, Trimester III, 2016 Assignment Topics for
... Assignment Topics for Students 1. The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Prof. Yoshinori Ohsumi for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. 2. Different types of cancer in Fiji: Factors concerning for emerging cancer in Fiji. 3. Principles of Electron Microscopy: Contribution in Cell ...
... Assignment Topics for Students 1. The 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Prof. Yoshinori Ohsumi for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy. 2. Different types of cancer in Fiji: Factors concerning for emerging cancer in Fiji. 3. Principles of Electron Microscopy: Contribution in Cell ...
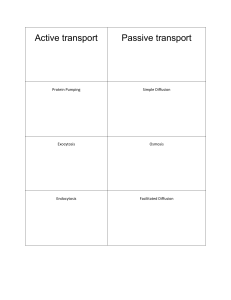
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... What is the difference between active transport and passive transport? ...
... What is the difference between active transport and passive transport? ...
No Slide Title
... • No nuclear membrane • No membrane bound organelles • Cell wall • Single loop of DNA ...
... • No nuclear membrane • No membrane bound organelles • Cell wall • Single loop of DNA ...
cell membrane - McEachern High School
... too long for necessary chemicals to get around the cell. • Insects and elephants have cells that are the same size, the elephant just has more of them and the ones they have are more specialized. ...
... too long for necessary chemicals to get around the cell. • Insects and elephants have cells that are the same size, the elephant just has more of them and the ones they have are more specialized. ...
CHAPTER 4: Cell Structure and Function Review
... 14. The folded inner membranes inside mitochondria are called _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __. 15. A cell membrane is a _B_ __ __ __ __ __ __ because the phospholipids line up in TWO ROWS to try and keep their hydrophobic tails away from water. 16. The _C_ __ __ __ _M_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ surrounds all cells ...
... 14. The folded inner membranes inside mitochondria are called _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __. 15. A cell membrane is a _B_ __ __ __ __ __ __ because the phospholipids line up in TWO ROWS to try and keep their hydrophobic tails away from water. 16. The _C_ __ __ __ _M_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ surrounds all cells ...
Carbohydrate: an organic molecule that provides energy for the cell
... Hypertonic: this occurs when the solute concentration is more outside than inside of the cell. Diffusion: the movement of “anything” from high to low concentrations. Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from high to low concentrations. Concentration Gradient: the difference between concentration ...
... Hypertonic: this occurs when the solute concentration is more outside than inside of the cell. Diffusion: the movement of “anything” from high to low concentrations. Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from high to low concentrations. Concentration Gradient: the difference between concentration ...
How does a cell survive
... • The cells “power plant” • Food molecules are broken down in the cell to release energy. • Then, ATP moves energy to Mitochondria • Bean shaped • 2 membranes • Work only with oxygen Outer and Inner Membranes ...
... • The cells “power plant” • Food molecules are broken down in the cell to release energy. • Then, ATP moves energy to Mitochondria • Bean shaped • 2 membranes • Work only with oxygen Outer and Inner Membranes ...
TAKS Obj 2 -BIOLOGY
... that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — These would F be softer indicate G grow at a faster rate more water, not less H be thinner J photosynthesize at a faster rate ...
... that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — These would F be softer indicate G grow at a faster rate more water, not less H be thinner J photosynthesize at a faster rate ...
The Cell School to Home LESSON 2 1.
... Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
... Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
Ch. 7 part 2 (PM and Osmosis)
... watery contents of the cell separate from the watery environment? FATS ...
... watery contents of the cell separate from the watery environment? FATS ...
Chapter 6- Cell membrane and Cell transport study guide:
... Identify all the functions of proteins in cellular membranes. Describe how phospholipid molecules are oriented in the plasma membrane of a cell. What is the function of a transport protein? ...
... Identify all the functions of proteins in cellular membranes. Describe how phospholipid molecules are oriented in the plasma membrane of a cell. What is the function of a transport protein? ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essential for the locomotion of individual organisms. In multicellular orga ...
... nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essential for the locomotion of individual organisms. In multicellular orga ...
Cell membrane
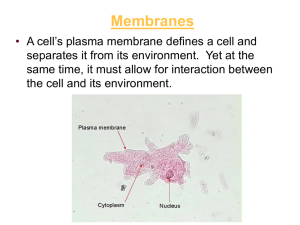
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.