3.3 Cell Membrane
... monitoring what enters and exits cells. For Example: • Small molecules and larger ...
... monitoring what enters and exits cells. For Example: • Small molecules and larger ...
cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were demonstrated: Plant and Animal Cell Lab, Eggmosis Lab E. Know the struct ...
... C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were demonstrated: Plant and Animal Cell Lab, Eggmosis Lab E. Know the struct ...
individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired
... sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
... sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
Prokaryotes
... – No membrane bound organelles – 70S ribosomes – Perform all functions of life – Range in size from .5µm to 1µm ...
... – No membrane bound organelles – 70S ribosomes – Perform all functions of life – Range in size from .5µm to 1µm ...
Ch. 7 Test Review Guide
... 6. What organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use? 7. What structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? 8. What organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use? 9. What two organelles ...
... 6. What organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use? 7. What structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? 8. What organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use? 9. What two organelles ...
Cell Organelles Quiz
... 6. _____Cells that lack membrane bound organelles 7. _____Chemical reactions and protein transport occur in this ribosome covered structure 8. _____Clear jelly-like or gelatinous fluid within the cell which aids in protein transport 9. _____Longer projection that whips to help a cell move (Like the ...
... 6. _____Cells that lack membrane bound organelles 7. _____Chemical reactions and protein transport occur in this ribosome covered structure 8. _____Clear jelly-like or gelatinous fluid within the cell which aids in protein transport 9. _____Longer projection that whips to help a cell move (Like the ...
The Cell Content Vocabulary Clues
... Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word terms. ...
... Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word terms. ...
Chapter 4
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction wi ...
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction wi ...
Here
... Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, osmosis, passive transport, and active transport, and why they are important to the cell. Predict the effect of a hypotonic , hypertonic, and isotonic solution on a cell. Define osmosis - _____________________________________________________________ ...
... Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, osmosis, passive transport, and active transport, and why they are important to the cell. Predict the effect of a hypotonic , hypertonic, and isotonic solution on a cell. Define osmosis - _____________________________________________________________ ...
S10 Cell membrane properties
... Phospholipids self assemble into different structures because their hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends repel each other ...
... Phospholipids self assemble into different structures because their hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends repel each other ...
Slide ()
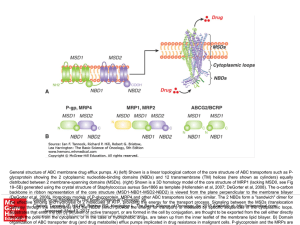
... the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the transport process. Signaling between the MSDs (translocation Citation: IF, Hill RG, Harrington L. The Basicfor Science of Oncology, 5e; by ...
... the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the transport process. Signaling between the MSDs (translocation Citation: IF, Hill RG, Harrington L. The Basicfor Science of Oncology, 5e; by ...
Cells - Uplift Education
... ◦ Arranged in a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads outside, and hydrophobic tails inside ...
... ◦ Arranged in a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads outside, and hydrophobic tails inside ...
Ch. 3 Notes: Membrane Physiology Page | 1 Cellular Physiology
... Interstitial fluid – fluid on the exterior of the cell ...
... Interstitial fluid – fluid on the exterior of the cell ...
Oct_7
... Note that sphingomyelin high in plasma membrane [ Inner / Outer membranes - curvature stress - phosphatidyl choline, big methyl group on outer membranes. Which ones on the inside? –those with small head group phosphotidyl serine (?) ] Cholesterol Fig 7.4 o Going to stick into a membrane o Choles ...
... Note that sphingomyelin high in plasma membrane [ Inner / Outer membranes - curvature stress - phosphatidyl choline, big methyl group on outer membranes. Which ones on the inside? –those with small head group phosphotidyl serine (?) ] Cholesterol Fig 7.4 o Going to stick into a membrane o Choles ...
CELL PROCESSES
... substances through a cell membrane. • Endocytosis - the process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the _____, forming a sphere called a vesicle. • Exocytosis - the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s contents are ...
... substances through a cell membrane. • Endocytosis - the process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the _____, forming a sphere called a vesicle. • Exocytosis - the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s contents are ...
H/Ws 1 to 4
... - Food vacuole =formed by phagocytosis. - Contractile vacuole = pumps out excess water Ex. in fresh water protists. - Central vacuole (plants) = holds food reserves (proteins, inorganic ions). - Disposal of metabolic byproducts. ...
... - Food vacuole =formed by phagocytosis. - Contractile vacuole = pumps out excess water Ex. in fresh water protists. - Central vacuole (plants) = holds food reserves (proteins, inorganic ions). - Disposal of metabolic byproducts. ...
Membrane structure, I
... Shows Selective permeability Known as the plasma membrane Amphipathic - hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions Singer-Nicolson developed the fluid mosaic model ...
... Shows Selective permeability Known as the plasma membrane Amphipathic - hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions Singer-Nicolson developed the fluid mosaic model ...
Cell Organelle Organelle Function City Part Cell Membrane
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
... Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus ...
Honors Biology Test Review Sheet: Chapter 5 Plasma Membrane
... matching, and/or diagram analysis questions whose answers will be placed on a Scantron sheet. This is one of two parts to each test. The second part is a Short Answer part which requires you to write complete sentence answers to a variety of questions. The questions may be for you to explain, analyz ...
... matching, and/or diagram analysis questions whose answers will be placed on a Scantron sheet. This is one of two parts to each test. The second part is a Short Answer part which requires you to write complete sentence answers to a variety of questions. The questions may be for you to explain, analyz ...
Unit 4: Cells and Transport Short Answer Five of
... 6. What are the types of passive transport? Give descriptions of each. 7. The concentration of glucose in a healthy red blood cell is about 2%. Glucose cannot pass through the membrane, but water and urea can. If the blood cell is placed in an environment with 25% sucrose and 75% water. In which dir ...
... 6. What are the types of passive transport? Give descriptions of each. 7. The concentration of glucose in a healthy red blood cell is about 2%. Glucose cannot pass through the membrane, but water and urea can. If the blood cell is placed in an environment with 25% sucrose and 75% water. In which dir ...
CELL TRANSPORT
... 2. The cell membrane is able to maintain homeostasis by being selectively permeable - allowing some molecules into cell while keeping others out. ...
... 2. The cell membrane is able to maintain homeostasis by being selectively permeable - allowing some molecules into cell while keeping others out. ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.