Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... endoplasmic reticulum Golgi (body) apparatus Ribosomes Chloroplast cell wall vacuole cytoplasm lysosomes cytoskeleton chromatin nucleolus ...
... endoplasmic reticulum Golgi (body) apparatus Ribosomes Chloroplast cell wall vacuole cytoplasm lysosomes cytoskeleton chromatin nucleolus ...
6 Active Transport 0809
... pumps to move materials against the concentration (UP concentration gradient) Similar to the steps of facilitated transport. Results in electrical impulses across nerve cells ...
... pumps to move materials against the concentration (UP concentration gradient) Similar to the steps of facilitated transport. Results in electrical impulses across nerve cells ...
Document
... B. Overview of major functions: 1. Keeping the goods concentrated, while keeping harmful materials out, requires transport in two directions 2. Communication with other cells ...
... B. Overview of major functions: 1. Keeping the goods concentrated, while keeping harmful materials out, requires transport in two directions 2. Communication with other cells ...
Section 7.3
... Sack surrounded by a membrane Plant cells have much larger water vacuoles than animal cells ...
... Sack surrounded by a membrane Plant cells have much larger water vacuoles than animal cells ...
Cell Membrane
... Cell Membrane - allows materials in or out of the cell Consists of: 1) Lipid Bilayer- 2 layers of fat tissue 2) Proteins- embedded into membrane - help move materials across Cell Membranes are: Selectively Permeable- controls what materials are allowed to cross. ...
... Cell Membrane - allows materials in or out of the cell Consists of: 1) Lipid Bilayer- 2 layers of fat tissue 2) Proteins- embedded into membrane - help move materials across Cell Membranes are: Selectively Permeable- controls what materials are allowed to cross. ...
Cell Membrane
... This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another. ...
... This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another. ...
Cell Transport Quiz KEY
... 13. Allowing some substances, but not others, to cross the membrane. 14. Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy input from the cell (high to low concentration). 15. Model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules (lipids, proteins, cholesterol) that make up ...
... 13. Allowing some substances, but not others, to cross the membrane. 14. Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy input from the cell (high to low concentration). 15. Model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules (lipids, proteins, cholesterol) that make up ...
Chapter 7-3
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
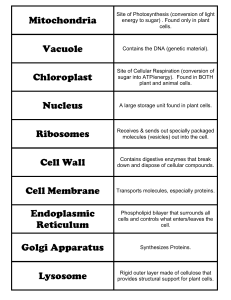
Mitochondria Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to
... sugar into ATP/energy). Found in BOTH plant and animal cells. ...
... sugar into ATP/energy). Found in BOTH plant and animal cells. ...
Cellular Transport – Active Transport Cells Review Questions
... __________________________________ are maintained at a ___________________________________ inside the cell, and ______________________ are maintained at ________________________________________________ inside the cell _________________________________ by protein molecules of the sodium and potassium ...
... __________________________________ are maintained at a ___________________________________ inside the cell, and ______________________ are maintained at ________________________________________________ inside the cell _________________________________ by protein molecules of the sodium and potassium ...
PGS: 124 – 138 - Lincoln County Schools
... 2. These molecules create the bi-layer and the structure is held intact by the presence of water outside and inside the cell. The negatively charged phosphorus line up to make a barrier preventing water from forming hydration shells around the phospholipids and thereby dissolving the membrane. B. Pr ...
... 2. These molecules create the bi-layer and the structure is held intact by the presence of water outside and inside the cell. The negatively charged phosphorus line up to make a barrier preventing water from forming hydration shells around the phospholipids and thereby dissolving the membrane. B. Pr ...
How Do Molecules Cross the Plasma Membrane? 1. Indicate the
... How Do Molecules Cross the Plasma Membrane? 1. Indicate the types of molecules that can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, then explain why this can occur. ...
... How Do Molecules Cross the Plasma Membrane? 1. Indicate the types of molecules that can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, then explain why this can occur. ...
WHAT LIMITS CELL SIZE
... DIFFUSION: Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over short distances, however becomes slow and inefficient as distance increases Ex: mitochondria at center of very large cell – can’t get necessary nutrients from diffusion ...
... DIFFUSION: Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over short distances, however becomes slow and inefficient as distance increases Ex: mitochondria at center of very large cell – can’t get necessary nutrients from diffusion ...
Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is
... 5) Fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are found 6) Produces a usable form of energy (ATP) for the cell 7) Stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins and other macromolecules into vesicles for transport to their final destination 8) Digests worn out cell organelles and breaks d ...
... 5) Fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are found 6) Produces a usable form of energy (ATP) for the cell 7) Stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins and other macromolecules into vesicles for transport to their final destination 8) Digests worn out cell organelles and breaks d ...
7-3 Transport Notes - Brookville Local Schools
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
CH3- part2
... ◦ Rough ER is covered in ribosomes is involved in production of ____________, which then move into the ER (cisternae) where they are modified before going to the Golgi apparatus. ◦ Smooth ER is connected to Rough ER and is active in synthesis and storage of __________. Lacks ribosomes. ...
... ◦ Rough ER is covered in ribosomes is involved in production of ____________, which then move into the ER (cisternae) where they are modified before going to the Golgi apparatus. ◦ Smooth ER is connected to Rough ER and is active in synthesis and storage of __________. Lacks ribosomes. ...
S3O1 Curr Map
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
Study Guide
... 11. Facilitated diffusion moves substances down their concentration gradient [with /without ] using the cell’s energy. Chapter 7 Study Guide - "The Cell" (pages 168-187) 1. Know all the vocabulary words in the chapter. Cell Nucleus Eukaryote Prokaryote Cell membrane Cell wall Lipid bil ...
... 11. Facilitated diffusion moves substances down their concentration gradient [with /without ] using the cell’s energy. Chapter 7 Study Guide - "The Cell" (pages 168-187) 1. Know all the vocabulary words in the chapter. Cell Nucleus Eukaryote Prokaryote Cell membrane Cell wall Lipid bil ...
Cell and Cell Plasma Membrane Diagrams
... solutes) and osmosis (movement of water). Examples of molecules that can diffuse include lipidsoluble molecules(ex. steroids) and respiratory gases(oxygen and carbon dioxide). Water can easily move through the cell membrane because it is small. In active transport, a substance is transported against ...
... solutes) and osmosis (movement of water). Examples of molecules that can diffuse include lipidsoluble molecules(ex. steroids) and respiratory gases(oxygen and carbon dioxide). Water can easily move through the cell membrane because it is small. In active transport, a substance is transported against ...
Cell Membranes
... Note: Plant Cell Walls are made of cellulose and are external to the cell membrane. They are also found in Prokaryotes and Fungi. ...
... Note: Plant Cell Walls are made of cellulose and are external to the cell membrane. They are also found in Prokaryotes and Fungi. ...
Function
... phosphate “head” which is hydrophilic (waterloving) and two non-polar fatty-acid “tails” that are hydrophobic (water-fearing); arranged in a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing the inside and the outside of the cell – Fluid mosaic model – plasma membrane behaves more like a fluid than a solid; ...
... phosphate “head” which is hydrophilic (waterloving) and two non-polar fatty-acid “tails” that are hydrophobic (water-fearing); arranged in a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing the inside and the outside of the cell – Fluid mosaic model – plasma membrane behaves more like a fluid than a solid; ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.