CELLS QQ#2 (TOC#4) HW: CELLS Notes (TOC#5)
... Inner membrane • Embedded with proteins • Pores that serve as molecular channels that restricts passage of molecules except RNA and some proteins. ...
... Inner membrane • Embedded with proteins • Pores that serve as molecular channels that restricts passage of molecules except RNA and some proteins. ...
Chapter 7 The Cell
... 7-1 Cell Discovery and Theory 1. Describe the discovery of the cell. Mention Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leeuwenhoek in your answer. 2. Summarize the three parts of the cell theory. 3. List three characteristics or structures that all cells share. 4. Evaluate the impact of microscope technology on th ...
... 7-1 Cell Discovery and Theory 1. Describe the discovery of the cell. Mention Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leeuwenhoek in your answer. 2. Summarize the three parts of the cell theory. 3. List three characteristics or structures that all cells share. 4. Evaluate the impact of microscope technology on th ...
Chapter 7 test review 2015
... 6. Know the structure and function of the organelles we discussed in class (we talked about 15) ...
... 6. Know the structure and function of the organelles we discussed in class (we talked about 15) ...
Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Ribosome Reticulum
... other materials from the ER. Packages them and distributes them to other parts of the cell stores water and ...
... other materials from the ER. Packages them and distributes them to other parts of the cell stores water and ...
Enzymes and Cell Transport study guide
... Endothermic: absorbs energy o Makes bonds o Dehydration synthesis Exothermic: releases energy o Breaks bonds o hydrolysis ...
... Endothermic: absorbs energy o Makes bonds o Dehydration synthesis Exothermic: releases energy o Breaks bonds o hydrolysis ...
The Cell Membrane
... c. Recognize foreign cells and communicate with other cells 2. The cell membrane consists of three components: a. The phospholipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids (fat). Each lipid has a phosphate molecule attached. The lipids are hydrophobic, which means that they repel water. The p ...
... c. Recognize foreign cells and communicate with other cells 2. The cell membrane consists of three components: a. The phospholipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids (fat). Each lipid has a phosphate molecule attached. The lipids are hydrophobic, which means that they repel water. The p ...
Slide 1
... •Endocytosis- Taking IN molecules by cell membranes folding into pockets. • Phagocytosis- When large particles are taken in through endocytosis • Pinocytosis- Cell taking in liquid •Exocytosis- Vacuoles fuse with cell membranes, forcing molecules OUT. ...
... •Endocytosis- Taking IN molecules by cell membranes folding into pockets. • Phagocytosis- When large particles are taken in through endocytosis • Pinocytosis- Cell taking in liquid •Exocytosis- Vacuoles fuse with cell membranes, forcing molecules OUT. ...
BIOL 150 - HCC Learning Web
... 9. Describe the two types of endosplasmic reticulum. What is the function of each? ...
... 9. Describe the two types of endosplasmic reticulum. What is the function of each? ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems - Blair Community Schools
... Phospholipid: specialized lipid made of a phosphate “head” and two fatty acid “tails Lipid bilayer: I. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane. A. B. C. Helps cell maintain constancy and control ...
... Phospholipid: specialized lipid made of a phosphate “head” and two fatty acid “tails Lipid bilayer: I. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane. A. B. C. Helps cell maintain constancy and control ...
Active and Passive Transport in Cells – Study Guide ____ 1. Using
... What is the name of the kind of transport occurring? ____________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____ 6. When particles move up the concentration gradient, they do what? ______________________________ What is the concentration gradient? _________________ ...
... What is the name of the kind of transport occurring? ____________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____ 6. When particles move up the concentration gradient, they do what? ______________________________ What is the concentration gradient? _________________ ...
Active Transport
... pumps to move materials against the concentration (UP concentration gradient) Similar to the steps of facilitated transport. Results in electrical impulses across nerve cells ...
... pumps to move materials against the concentration (UP concentration gradient) Similar to the steps of facilitated transport. Results in electrical impulses across nerve cells ...
Require energy (ATP) - Olympic High School
... Describe what properties allow a molecule to pass through a phospholipid membrane and what properties prevent a molecule from passing through a phospholipid membrane. ...
... Describe what properties allow a molecule to pass through a phospholipid membrane and what properties prevent a molecule from passing through a phospholipid membrane. ...
Chapter 1.3 cell processes_1
... Water does three things for our bodies: Chemical reactions depend on it Helps cells keep their shape Changes the temperature slowly in an organism ...
... Water does three things for our bodies: Chemical reactions depend on it Helps cells keep their shape Changes the temperature slowly in an organism ...
Trends in Biotechnology
... The following pictures are selected to give you an idea. The cell does not have many big spaces in it. The cell is really very crowded. ...
... The following pictures are selected to give you an idea. The cell does not have many big spaces in it. The cell is really very crowded. ...
Cells
... Does not dissolve in watery environment of the body. The membrane is nonpolar but the environment of the body is polar. The chemical composition is not the same so it’s like mixing oil and water. Consists of a lipid bilayer made up of polar heads and nonpolar tails. This lipid bilayer is chemically ...
... Does not dissolve in watery environment of the body. The membrane is nonpolar but the environment of the body is polar. The chemical composition is not the same so it’s like mixing oil and water. Consists of a lipid bilayer made up of polar heads and nonpolar tails. This lipid bilayer is chemically ...
Cell Analogies Worksheet
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
Biology Name: Block: ____ Learning Targets: Membrane
... Knowledge Targets “What I need to know!” Reasoning Targets “What I can do with what I know.” ...
... Knowledge Targets “What I need to know!” Reasoning Targets “What I can do with what I know.” ...
Cell Test Study Guide
... 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? 4) What limits how large a cell can grow? 5) What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote? 6) What does it mean when I say that the cell membrane is semipermeable/selectively permeable? 7) What two things is the cell membrane ma ...
... 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? 4) What limits how large a cell can grow? 5) What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote? 6) What does it mean when I say that the cell membrane is semipermeable/selectively permeable? 7) What two things is the cell membrane ma ...
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... b. Hydrophobic tails - fatty acids "water" "fearing" attracted to each other on inside of bilayer ...
... b. Hydrophobic tails - fatty acids "water" "fearing" attracted to each other on inside of bilayer ...
Cell membrane
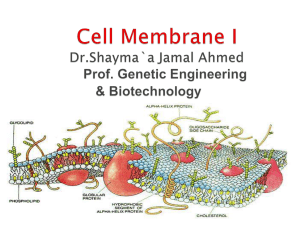
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.