* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nuclear Envelope - Plain Local Schools
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
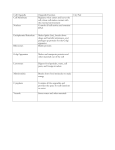
Plasma Membrane Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope Ribosome Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi Apparatus Vacuole Lysosome Chloroplast Cell Wall Mitochondria Cilia Flagella ATP Microfilaments Microtubules Main energy molecule used that Structure outside the plant’s cells use for work plasma membrane that protects and gives shape Responsible for controlling transport of substances across the cell Contains DNA which controls all the activities of the cell Inside the nucleus, contains parts to make ribosomes Structure with holes in it allows materials to pass in and out of the nucleus Produces proteins from DNA codes Modifies, stores, and routes proteins and other products to final destination Network of membranes which serves to manufacture and transport cell products – Ribosomes present – Makes proteins Network of membranes which serves to manufacture and transport cell products – Lacks ribosomes – Makes lipid molecules Membrane-bound sac that buds Membrane-bound sac from the endoplasmic reticulum containing digestive enzymes or the Golgi apparatus that can breakdown proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides Found in plant cells and unicellular organism where photosynthesis takes place Organelle where cellular respiration takes place Long, thin, whip-like structure responsible for locomotion containing a core of microtubules Hair-like structures made up of microtubules which are used for movement or the movement of fluid Straight, hollow tubes of Rods of protein that allow the proteins, that gives cells shape cell to move or change shape and organization Plasma Membrane Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Ribosome Nucleolus Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi apparatus Vacuoles Lysosomes Cell wall Chloroplasts Mitochondria Flagella Cilia ATP Microfilaments Microtubules