Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... 1. contains instructions for making specific proteins 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. ...
... 1. contains instructions for making specific proteins 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. ...
GENE MUTATIONS
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
GENE MUTATIONS - mrbemrose / FrontPage
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
Practice Exam II
... V. A mutation changes the middle base in a codon near the beginning of a gene from A to G: T The change could occur spontaneously in the DNA via tautomerization. T The change is an example of a point mutation. F The change is an example of a transversion. T The change would always create a missense ...
... V. A mutation changes the middle base in a codon near the beginning of a gene from A to G: T The change could occur spontaneously in the DNA via tautomerization. T The change is an example of a point mutation. F The change is an example of a transversion. T The change would always create a missense ...
Mutations File
... c. Rewrite the amino acid sequence with the mutated strand. d. Is this considered a “silent” mutation (a mutation that causes no changes) or is it an “expressed” mutation (a mutation that causes a change in the amino acid sequence, and therefore a change in the protein?) 5. What are two sources of m ...
... c. Rewrite the amino acid sequence with the mutated strand. d. Is this considered a “silent” mutation (a mutation that causes no changes) or is it an “expressed” mutation (a mutation that causes a change in the amino acid sequence, and therefore a change in the protein?) 5. What are two sources of m ...
mutations - Université d`Ottawa
... - frequency in population determined by natural selection and random genetic drift if allele frequency = 1, FIXATION ...
... - frequency in population determined by natural selection and random genetic drift if allele frequency = 1, FIXATION ...
✓ 10 FOLLOW-UP
... students to practice transcribing and translating sequences of DNA and mRNA. You might also ask them to make up their own sequences to work from. Be sure the sequences they select include a start codon. Analysis Question 4 is a Quick Check to assess students’ understanding that DNA mutations might o ...
... students to practice transcribing and translating sequences of DNA and mRNA. You might also ask them to make up their own sequences to work from. Be sure the sequences they select include a start codon. Analysis Question 4 is a Quick Check to assess students’ understanding that DNA mutations might o ...
Genetics
... • Genetics is the science of inheritance • Genetic information is carried on chromosomes in the nucleus of every ...
... • Genetics is the science of inheritance • Genetic information is carried on chromosomes in the nucleus of every ...
Evolution 1/e - SUNY Plattsburgh
... Another type of mutation occurs when bases are inserted or deleted from the DNA molecule. This causes a change in how the whole DNA strand is read (a frame shift mutation) and produces a nonfunctional protein. ...
... Another type of mutation occurs when bases are inserted or deleted from the DNA molecule. This causes a change in how the whole DNA strand is read (a frame shift mutation) and produces a nonfunctional protein. ...
GENE MUTATIONS
... Almost all mutations are neutral Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations Many mutations are repaired by enzymes ...
... Almost all mutations are neutral Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations Many mutations are repaired by enzymes ...
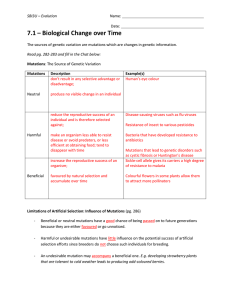
7.1 Solutions File
... Harmful or undesirable mutations have little influence on the potential success of artificial selection efforts since breeders do not choose such individuals for breeding. ...
... Harmful or undesirable mutations have little influence on the potential success of artificial selection efforts since breeders do not choose such individuals for breeding. ...
1 Questions: Concept Check 11.1 1. How did Griffith`s experiments
... parts of the body for use in respiration. Normal adult hemoglobin is a four part protein consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. Mutant forms of this gene is responsible for the sickling of red blood cells seen in sickle shape of sickle cell anemia. ...
... parts of the body for use in respiration. Normal adult hemoglobin is a four part protein consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. Mutant forms of this gene is responsible for the sickling of red blood cells seen in sickle shape of sickle cell anemia. ...
Gene Mutations - Lyndhurst School
... Cloning- a technique used to produce offspring with desired traits (identical to the traits of another organism) Clone- an organism that has identical gene as the ...
... Cloning- a technique used to produce offspring with desired traits (identical to the traits of another organism) Clone- an organism that has identical gene as the ...
Chapter 1-2: Genetics Progressed from Mendel to DNA in Less Than
... mechanism of inheritance, the stage was set in the discovery of its structure. 1953: Watson & Crick described the molecular structure of DNA. ...
... mechanism of inheritance, the stage was set in the discovery of its structure. 1953: Watson & Crick described the molecular structure of DNA. ...
Mutation: The Source of Genetic Variation
... • Missense mutation – replaces one amino acid with another • Nonsense mutations – an amino acid codon is changed to a stop codon • Sense mutation – a termination codon is changed into a one that codes for an amino acid, producing elongated proteins • Silent mutation – no effect on phenotype Frames ...
... • Missense mutation – replaces one amino acid with another • Nonsense mutations – an amino acid codon is changed to a stop codon • Sense mutation – a termination codon is changed into a one that codes for an amino acid, producing elongated proteins • Silent mutation – no effect on phenotype Frames ...
Lecture Outline
... Insertion mutation: one or more nucleotides inserted in DNA Deletion mutation: one or more nucleotides deleted from DNA Frameshift mutation: reading frame shifted by insertion or deletion mutation many deletion or insertion mutations shift reading frame frameshift mutations may change many amino aci ...
... Insertion mutation: one or more nucleotides inserted in DNA Deletion mutation: one or more nucleotides deleted from DNA Frameshift mutation: reading frame shifted by insertion or deletion mutation many deletion or insertion mutations shift reading frame frameshift mutations may change many amino aci ...
Cause and effect of mutation
... chromosome abnormalities as males produce new gametes throughout their lifetime ...
... chromosome abnormalities as males produce new gametes throughout their lifetime ...
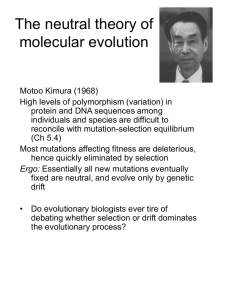
Null hypotheses in evolutionary biology
... individuals and species are difficult to reconcile with mutation-selection equilibrium (Ch 5.4) Most mutations affecting fitness are deleterious, hence quickly eliminated by selection Ergo: Essentially all new mutations eventually fixed are neutral, and evolve only by genetic drift • Do evolutionary ...
... individuals and species are difficult to reconcile with mutation-selection equilibrium (Ch 5.4) Most mutations affecting fitness are deleterious, hence quickly eliminated by selection Ergo: Essentially all new mutations eventually fixed are neutral, and evolve only by genetic drift • Do evolutionary ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation ...
... Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation ...
review sheet
... 2. Briefly describe the process of replication. Where in the cell does replication occur? When in the cell cycle does replication occur? ...
... 2. Briefly describe the process of replication. Where in the cell does replication occur? When in the cell cycle does replication occur? ...
What Should I Know for the HUMAN GENOME TEST? Chapter 14
... What’s the difference between a chromosome mutation and a gene mutation? ...
... What’s the difference between a chromosome mutation and a gene mutation? ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.