1 Name: Date: Block: _____ PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: MAKING
... tRNA (transfer RNA) is a strand of nucleotides that has an ___________________attached to it. tRNA carries the appropriate amino acid to the mRNA/ribosome complex. If mRNA is UGG then the tRNA is _______. Translation begins with the start codon. Each amino acid that is brought in to the ri ...
... tRNA (transfer RNA) is a strand of nucleotides that has an ___________________attached to it. tRNA carries the appropriate amino acid to the mRNA/ribosome complex. If mRNA is UGG then the tRNA is _______. Translation begins with the start codon. Each amino acid that is brought in to the ri ...
Unit 7 Review – DNA Replication, Gene Expression, and Gene
... sure you describe the actors involved in the process (e.g. donor gene, chromosome, vector, restriction enzyme, DNA ligase, target organism, cloning, etc.) ...
... sure you describe the actors involved in the process (e.g. donor gene, chromosome, vector, restriction enzyme, DNA ligase, target organism, cloning, etc.) ...
two ald “mutations”
... Intragenic suppression: “pseudo-reversion”; can be same codon or different/interacting region of gene. ...
... Intragenic suppression: “pseudo-reversion”; can be same codon or different/interacting region of gene. ...
Mutations (1 of 2)
... In frameshifts, a similar error occurs at the DNA level, causing the codons to be parsed incorrectly. This usually generates proteins that are as useless as single “hef atc ats at” is uninformative. There are other types of mutations as well, but this short list should give you an idea of the possib ...
... In frameshifts, a similar error occurs at the DNA level, causing the codons to be parsed incorrectly. This usually generates proteins that are as useless as single “hef atc ats at” is uninformative. There are other types of mutations as well, but this short list should give you an idea of the possib ...
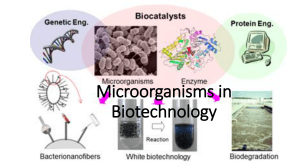
Microorganisms in Biotechnology
... • Viral vectors are viruses to carry altered DNA into cells and are created by removing genes in a virus and replacing them with the gene to be transferred • The vector is then mixed with growing cells and enter the cell, depositing the new gene in the chromosome of that cell • The gene is then pass ...
... • Viral vectors are viruses to carry altered DNA into cells and are created by removing genes in a virus and replacing them with the gene to be transferred • The vector is then mixed with growing cells and enter the cell, depositing the new gene in the chromosome of that cell • The gene is then pass ...
DNA Mutations - pams
... Codon for glutamic acid has been changed to code for valine because of a substitution in one codon in the gene for the protein hemoglobin. Four hemoglobin proteins carry oxygen inside red blood cells. The change in the amino acid causes the hemoglobin to fold abnormally causing a sickle shaped red b ...
... Codon for glutamic acid has been changed to code for valine because of a substitution in one codon in the gene for the protein hemoglobin. Four hemoglobin proteins carry oxygen inside red blood cells. The change in the amino acid causes the hemoglobin to fold abnormally causing a sickle shaped red b ...
How are protein made in our cells?
... Codons will move through the ribosome by tRNA. Codons on mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, the amino acid on (top) tRNA will “pop” off (bottom) tRNA. Like an assemble line, amino acids will assemble onto each other and create a polypeptide (or a protein). ...
... Codons will move through the ribosome by tRNA. Codons on mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, the amino acid on (top) tRNA will “pop” off (bottom) tRNA. Like an assemble line, amino acids will assemble onto each other and create a polypeptide (or a protein). ...
ppt
... Point mutations in our lives! -Sickle cell anemia is a blood disease caused by a SUBSTITUTION point mutation. -A single nucleotide is changed from “A” to “T” which causes the amino acid to change from glutamic acid to valine: Amino acids: Thr – Pro – Glu – Glu Normal: ACT CCT GAG GAG Sickle cell: A ...
... Point mutations in our lives! -Sickle cell anemia is a blood disease caused by a SUBSTITUTION point mutation. -A single nucleotide is changed from “A” to “T” which causes the amino acid to change from glutamic acid to valine: Amino acids: Thr – Pro – Glu – Glu Normal: ACT CCT GAG GAG Sickle cell: A ...
Frameshift Mutations
... – RNA has uracil instead of thymine. – RNA is a single-stranded structure. ...
... – RNA has uracil instead of thymine. – RNA is a single-stranded structure. ...
4TH 6 WEEKS EXAM REVIEW!
... The 3 bases on the tRNA are known as the _________ and are complimentary to mRNA’s __________ (3 bases) ...
... The 3 bases on the tRNA are known as the _________ and are complimentary to mRNA’s __________ (3 bases) ...
Origin and Nature of Genetic Variation
... • Number of bases involved is a multiple of 3 • e.g. Cystic Fibrosis. • A 3-base pair deletion at amino acid position 508, deletes the codon for phenylalanine • The ΔF508 mutation accounts for 70% of all mutant CF alleles. • This mutations results in synthesis of an abnormal gene CFTR gene product ...
... • Number of bases involved is a multiple of 3 • e.g. Cystic Fibrosis. • A 3-base pair deletion at amino acid position 508, deletes the codon for phenylalanine • The ΔF508 mutation accounts for 70% of all mutant CF alleles. • This mutations results in synthesis of an abnormal gene CFTR gene product ...
Mutations
... • Mutations are recognized as the primary source of the hereditary variations that make evolution possible • Mutations may be either harmful or useful to a species • Mutations that help are continued because it is the survivors that reproduce and pass the traits on to their offspring • Mutations tha ...
... • Mutations are recognized as the primary source of the hereditary variations that make evolution possible • Mutations may be either harmful or useful to a species • Mutations that help are continued because it is the survivors that reproduce and pass the traits on to their offspring • Mutations tha ...
Variation and Evolution
... 1. The sequence of DNA may be changed by radiation or mistakes in replication 2. The mutated DNA could cause a new characteristic to be seen. More often the mutation leads to genetic problems or death ...
... 1. The sequence of DNA may be changed by radiation or mistakes in replication 2. The mutated DNA could cause a new characteristic to be seen. More often the mutation leads to genetic problems or death ...
File
... encoded protein, owing to the redundancy of the genetic code. For example, if 3′-CCG-5′ on the template strand mutated to 3′-CCA-5′, the mRNA codon that used to be GGC would become GGU, but a glycine would still be inserted at the proper location in the protein (see Figure 14.6). In other words, a c ...
... encoded protein, owing to the redundancy of the genetic code. For example, if 3′-CCG-5′ on the template strand mutated to 3′-CCA-5′, the mRNA codon that used to be GGC would become GGU, but a glycine would still be inserted at the proper location in the protein (see Figure 14.6). In other words, a c ...
Mutations I
... first one has a single chromosome that matches with the banding pattern of two separate chromosomes of each of the other three species. (In this case, fusion is the most likely reason why— we’ll get to that later. . . . ) Translocation in a human—note that an extra copy of chromosome 21 has attache ...
... first one has a single chromosome that matches with the banding pattern of two separate chromosomes of each of the other three species. (In this case, fusion is the most likely reason why— we’ll get to that later. . . . ) Translocation in a human—note that an extra copy of chromosome 21 has attache ...
Mutation Study Guide
... A chromosomal mutation typically affects more genes because it takes place at a chromosomal level. Chromosomal mutations can have a large effect and may result in a disrupted gene or abnormal regulation of genes. 6. What is translocation? The attachment of a piece of one chromosome to a non-homologo ...
... A chromosomal mutation typically affects more genes because it takes place at a chromosomal level. Chromosomal mutations can have a large effect and may result in a disrupted gene or abnormal regulation of genes. 6. What is translocation? The attachment of a piece of one chromosome to a non-homologo ...
How Things Go Wrong
... Explore Show student Overhead 1 and tell them, “There are many types of mutations: Point mutations: A single nucleotide base being changed. This type of mutation can affect a gene’s protein production in several ways. Missense Mutation: A point mutation that results in a single amino acid change in ...
... Explore Show student Overhead 1 and tell them, “There are many types of mutations: Point mutations: A single nucleotide base being changed. This type of mutation can affect a gene’s protein production in several ways. Missense Mutation: A point mutation that results in a single amino acid change in ...
Gene Mutations
... Adding or deleting a letter is worse because ALL words change The Rat Hix Dan Dth Eca Tsa Tan Dgo Tfa T The Rah Ida Ndt Hec Ats Atat Ndg Otf At ...
... Adding or deleting a letter is worse because ALL words change The Rat Hix Dan Dth Eca Tsa Tan Dgo Tfa T The Rah Ida Ndt Hec Ats Atat Ndg Otf At ...
Mutations
... - Can involve rearranging chromosome structure or changes in the number of chromosomes. - Can be harmful (genetic disorder or death), neutral, or beneficial ...
... - Can involve rearranging chromosome structure or changes in the number of chromosomes. - Can be harmful (genetic disorder or death), neutral, or beneficial ...
Section 8.7: Mutations
... • Chromosomal mutations affect lots of genes and tend to have a big effect on an organism. • A mutation may break up a gene causing the gene not to work, or it could make a new hybrid gene with a new function (which might turn out to be adaptive – or not). • Translocated genes may also come under th ...
... • Chromosomal mutations affect lots of genes and tend to have a big effect on an organism. • A mutation may break up a gene causing the gene not to work, or it could make a new hybrid gene with a new function (which might turn out to be adaptive – or not). • Translocated genes may also come under th ...
Human Genetics
... (the inability for blood to clot properly) Also Colorblindness (the inability to distinguish certain colors) Gene that can cause it found on X chrom. ...
... (the inability for blood to clot properly) Also Colorblindness (the inability to distinguish certain colors) Gene that can cause it found on X chrom. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.