Sickle cell / mutations
... Part I: Preview Questions 1. Based on your current knowledge, how would you define a mutation? What does this word make you think of? (2 pts) ...
... Part I: Preview Questions 1. Based on your current knowledge, how would you define a mutation? What does this word make you think of? (2 pts) ...
Chapter 18 – 17 pts total - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... of your risk for cancer. 10. Cancer cannot be inherited directly from your parents, but a predisposition can be inherited allowing cancer to “run in families”. Imagine that this topic comes up during a family reunion. Explain to aunt Sally how this works as she is certain that she has inherited the ...
... of your risk for cancer. 10. Cancer cannot be inherited directly from your parents, but a predisposition can be inherited allowing cancer to “run in families”. Imagine that this topic comes up during a family reunion. Explain to aunt Sally how this works as she is certain that she has inherited the ...
Ch. 17 DNA mutations and Repair
... Suppressor Mutations is a genetic change that hides the effect of another mutation ...
... Suppressor Mutations is a genetic change that hides the effect of another mutation ...
Molecules of Life
... • Mutated genes normally code for a different shaped protein. • The new protein may be harmful and even cause death (cancer). • Sometimes a mutation can be beneficial (evolution). • Sometimes a mutation can be neutral (blue budgies). ...
... • Mutated genes normally code for a different shaped protein. • The new protein may be harmful and even cause death (cancer). • Sometimes a mutation can be beneficial (evolution). • Sometimes a mutation can be neutral (blue budgies). ...
The Flyswatter Game
... The rule stating that in DNA A on one strand always pairs with T on the opposite strand and G always pairs with C. ...
... The rule stating that in DNA A on one strand always pairs with T on the opposite strand and G always pairs with C. ...
Mutations Worksheet
... What’s the mRNA sequence? (Circle the change) What will be the amino acid sequence? Will there likely be effects? What kind of mutation is this? Mutated DNA Sequence #2: T A C G A C C T T G G C G A C G A C T What’s the mRNA sequence? (Circle the change) What will be the amino acid sequence? Will the ...
... What’s the mRNA sequence? (Circle the change) What will be the amino acid sequence? Will there likely be effects? What kind of mutation is this? Mutated DNA Sequence #2: T A C G A C C T T G G C G A C G A C T What’s the mRNA sequence? (Circle the change) What will be the amino acid sequence? Will the ...
4.13 notes
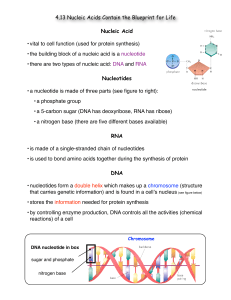
... • the building block of a nucleic acid is a nucleotide • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different ...
... • the building block of a nucleic acid is a nucleotide • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different ...
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... Changes hemoglobin molecules; one amino acid is different in polypeptide; inaffective at carrying oxygen Frameshift mutations – changes entire amino acid sequence after mutation Cancer – mutations in genes that control cell cycle Oncogenes – turned on to make cells divide too quickly Tumor ...
... Changes hemoglobin molecules; one amino acid is different in polypeptide; inaffective at carrying oxygen Frameshift mutations – changes entire amino acid sequence after mutation Cancer – mutations in genes that control cell cycle Oncogenes – turned on to make cells divide too quickly Tumor ...
Plant Breeding is the actual application of the genetics research
... by exposing plants to X-rays. "Mutation breeding" accelerated after World War II, when the techniques of the nuclear age became widely available. Plants were exposed to gamma rays, protons, neutrons, alpha particles, and beta particles to see if these would induce useful mutations. Chemicals, too, s ...
... by exposing plants to X-rays. "Mutation breeding" accelerated after World War II, when the techniques of the nuclear age became widely available. Plants were exposed to gamma rays, protons, neutrons, alpha particles, and beta particles to see if these would induce useful mutations. Chemicals, too, s ...
student - Shawnee Science
... generation. If this number is correct, every individual would be expected to have 2-3 mutations on average. Complicating the picture is the fact that mutation rates for different genes and chromosomes apparently vary. Mutations are common occurrences even in healthy people. The majority of these mut ...
... generation. If this number is correct, every individual would be expected to have 2-3 mutations on average. Complicating the picture is the fact that mutation rates for different genes and chromosomes apparently vary. Mutations are common occurrences even in healthy people. The majority of these mut ...
Handout
... 1. __________________________________ tend to have a big effect. Many genes are affected. 2. Some _______________________________________ change phenotype by: – causing a premature stop codon. – causing a change in protein shape or the active site. – causing a change in gene regulation. 3. Some gene ...
... 1. __________________________________ tend to have a big effect. Many genes are affected. 2. Some _______________________________________ change phenotype by: – causing a premature stop codon. – causing a change in protein shape or the active site. – causing a change in gene regulation. 3. Some gene ...
3rd- 9 Weeks Test Review
... ü The mRNA from transcription carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosome for protein synthesis. ü RNA catalyzes translation and reads the mRNA at ribosomes to link amino acids into protein. 3. Mutations are spontaneous changes in DNA. ü Mutations can be simple base-pair substitutio ...
... ü The mRNA from transcription carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosome for protein synthesis. ü RNA catalyzes translation and reads the mRNA at ribosomes to link amino acids into protein. 3. Mutations are spontaneous changes in DNA. ü Mutations can be simple base-pair substitutio ...
Genetics 101 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... make up — and therefore in their DNA. These subtle variations in DNA are called polymorphisms (literally "many forms"). Many of these gene polymorphisms account for slight differences between people such as hair and eye color. But some gene variations may result in disease or an increased risk for d ...
... make up — and therefore in their DNA. These subtle variations in DNA are called polymorphisms (literally "many forms"). Many of these gene polymorphisms account for slight differences between people such as hair and eye color. But some gene variations may result in disease or an increased risk for d ...
lecture 6 genetic languages and mutations_RECAP
... The Language of Genetics DNA Language vs. Protein Language • DNA is written in the language of nucleotides. • A message on DNA can be transcribed (copied) onto a piece of mRNA. • A message on mRNA can be translated into a chain of amino acids. • Proteins are written in the language of amino ...
... The Language of Genetics DNA Language vs. Protein Language • DNA is written in the language of nucleotides. • A message on DNA can be transcribed (copied) onto a piece of mRNA. • A message on mRNA can be translated into a chain of amino acids. • Proteins are written in the language of amino ...
Nucleotide - Jackson County School District
... Process by which a strand of mRNA is copied from a section of DNA enough information to code for 1 protein ...
... Process by which a strand of mRNA is copied from a section of DNA enough information to code for 1 protein ...
Biology Topics, Venn diagrams
... for protein synthesis • 2 stranded, double helix structure • Sequence of three bases calls for particular amino acid • Found in nucleus • Replicates • Eukaryote ...
... for protein synthesis • 2 stranded, double helix structure • Sequence of three bases calls for particular amino acid • Found in nucleus • Replicates • Eukaryote ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度
... exons is 266 base pairs. (i) Calculate the fraction of nucleotides in a gene that will be present in mRNA? (ii) What the fraction of the chromosome that is occupied by genes? (iii) Propose a simple procedure that would help us to establish the intron/exon structure of a gene. (9%) (2) How many diffe ...
... exons is 266 base pairs. (i) Calculate the fraction of nucleotides in a gene that will be present in mRNA? (ii) What the fraction of the chromosome that is occupied by genes? (iii) Propose a simple procedure that would help us to establish the intron/exon structure of a gene. (9%) (2) How many diffe ...
Review - Molecular and Cell Biology
... The origin of mutations most mutations are spontaneous and rare DNA repair mechanisms eliminate most mutations mutagens such as Xrays or chemicals like EMS can greatly increase the mutation rate, and are essential tools for experimental isolation of mutants Mutations can affect the DNA sequence of g ...
... The origin of mutations most mutations are spontaneous and rare DNA repair mechanisms eliminate most mutations mutagens such as Xrays or chemicals like EMS can greatly increase the mutation rate, and are essential tools for experimental isolation of mutants Mutations can affect the DNA sequence of g ...
Mutations Justified True or False
... mutated gene. Then in order to see the mutation the organism must have an offspring. But still then the mutation might not be ...
... mutated gene. Then in order to see the mutation the organism must have an offspring. But still then the mutation might not be ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.