Development of Catalytic Ester Condensations and Hydrolysis of
... than that with N,N-diarylammonium salts because sulfonic acids can be separated by washing the crude product with a small amount of water. However, sulfonic acids are easily deactivated by water since they have high hydrophlicity. Therefore, the author first considered that the solvent effect might ...
... than that with N,N-diarylammonium salts because sulfonic acids can be separated by washing the crude product with a small amount of water. However, sulfonic acids are easily deactivated by water since they have high hydrophlicity. Therefore, the author first considered that the solvent effect might ...
Exam #3
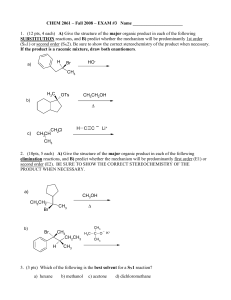
... A) Using mechanistic reasoning, EXPLAIN WHY menthyl chloride gives only 2-menthene as its E2 elimination product. B) Explain why 3-menthene (rather than 2- menthene) is the major product in the E2 elimination of neomenthyl chloride. H H3C ...
... A) Using mechanistic reasoning, EXPLAIN WHY menthyl chloride gives only 2-menthene as its E2 elimination product. B) Explain why 3-menthene (rather than 2- menthene) is the major product in the E2 elimination of neomenthyl chloride. H H3C ...
Alkenes notes
... Symmetrical alkenes only give one product when elecrophiles are added. Unsymmetrical alkenes only give one product if the electrophile is symmetrical (Eg propene Br2). Thus two products are only obtained when both the alkene and the electrophile are unsymmetrical. In such cases the identity of the m ...
... Symmetrical alkenes only give one product when elecrophiles are added. Unsymmetrical alkenes only give one product if the electrophile is symmetrical (Eg propene Br2). Thus two products are only obtained when both the alkene and the electrophile are unsymmetrical. In such cases the identity of the m ...
Copper-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions Using Carbon
... Amidation Reactions of Aldehydes with Amine HCI Salts ............................ 83 ...
... Amidation Reactions of Aldehydes with Amine HCI Salts ............................ 83 ...
Synthesis of a TREN in Which the Aryl Substituents are... Atom Macrocycle ̈ller *
... reduced. Eight of the proposed catalytic intermediates in the Mocatalyzed TREN-based system were characterized by X-ray crystallography. The proposed reaction mechanism also has been scrutinized through extensive calculations.2 All steric and electronic modifications of the successful “HIPT catalysts ...
... reduced. Eight of the proposed catalytic intermediates in the Mocatalyzed TREN-based system were characterized by X-ray crystallography. The proposed reaction mechanism also has been scrutinized through extensive calculations.2 All steric and electronic modifications of the successful “HIPT catalysts ...
New Applications for Sulfur-Based Leaving Groups in Synthesis
... reaction of an aliphatic potassium alkoxide with an aromatic alkynyl sulfonamide. The mechanism of this process has been explored via a combination of synthetic chemistry and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) and the findings of these experiments will be discussed. The synthesis of ...
... reaction of an aliphatic potassium alkoxide with an aromatic alkynyl sulfonamide. The mechanism of this process has been explored via a combination of synthetic chemistry and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) and the findings of these experiments will be discussed. The synthesis of ...
Chemistry 360 - Athabasca University
... experiments, making your products, and recording your results in this report workbook ...
... experiments, making your products, and recording your results in this report workbook ...
Alcohols
... is bonded to one R group Secondary (2º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to two R groups Tertiary (3º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to three R groups ...
... is bonded to one R group Secondary (2º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to two R groups Tertiary (3º) alcohol contains –OH group on carbon atom that is bonded to three R groups ...
isomeria geometrica
... • Different molecules (enantiomers) must have different names. • Usually only one enantiomer will be biologically active. • Configuration around the chiral carbon is specified with (R) and (S). ...
... • Different molecules (enantiomers) must have different names. • Usually only one enantiomer will be biologically active. • Configuration around the chiral carbon is specified with (R) and (S). ...
Topic 10 SL Mark Scheme Past exam paper questions
... chains of up to 6 carbon atoms with one of the following functional groups: (alkane), alkene, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid and halide. Examples of compounds containing amino, benzene ring (phenyl) and ester functional groups. Describe the volatility and solubility in water of compounds ...
... chains of up to 6 carbon atoms with one of the following functional groups: (alkane), alkene, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid and halide. Examples of compounds containing amino, benzene ring (phenyl) and ester functional groups. Describe the volatility and solubility in water of compounds ...
Novel Transition Metal-Catalysed Syntheses of Carboxylic Acid
... The largest category of such reactions features the ruthenium metathesis catalysts developed by Grubbs and co-workers.[14] These alkylidene complexes are truly remarkable in terms of scope of their activity, so much so that an account of their nonmetathetic reactions has been recently published.[15] ...
... The largest category of such reactions features the ruthenium metathesis catalysts developed by Grubbs and co-workers.[14] These alkylidene complexes are truly remarkable in terms of scope of their activity, so much so that an account of their nonmetathetic reactions has been recently published.[15] ...
Melt Modification of Poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride)
... amide formation via in situ generated carboxylic acids as shown in Figure 1 (pathway b). Consequently, C11OXA addition converted free carboxylic acid. In order to quantify the anhydride conversion, the ANH1780 signal of the products is compared with the ANH1780 signal of the educt SMA17. For the bin ...
... amide formation via in situ generated carboxylic acids as shown in Figure 1 (pathway b). Consequently, C11OXA addition converted free carboxylic acid. In order to quantify the anhydride conversion, the ANH1780 signal of the products is compared with the ANH1780 signal of the educt SMA17. For the bin ...
A Simple and Advantageous Protocol for the Oxidation of Alcohols
... they are inert and all byproducts are insoluble at room temperature, such that no purification is required beyond simple filtration. Reactions in several other solvents provided higher yields and shorter reaction times, but required chromatographic purification. The oxidation proceeds well with as f ...
... they are inert and all byproducts are insoluble at room temperature, such that no purification is required beyond simple filtration. Reactions in several other solvents provided higher yields and shorter reaction times, but required chromatographic purification. The oxidation proceeds well with as f ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
17: Oxidation and Reduction
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
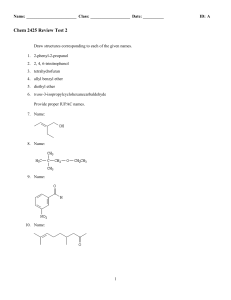
Chem 2425-Test 2 Review
... Consider the data below to answer the following question(s). Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed t ...
... Consider the data below to answer the following question(s). Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed t ...
HMDS - Sigma
... excellent solvents for the reagent and the reaction products; they do not accelerate the rate of reaction. Polar solvents such as pyridine, dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), tetrahydrofuran (THF), and acetonitrile are more often used because they can facilitate the reaction. Pyridin ...
... excellent solvents for the reagent and the reaction products; they do not accelerate the rate of reaction. Polar solvents such as pyridine, dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), tetrahydrofuran (THF), and acetonitrile are more often used because they can facilitate the reaction. Pyridin ...
Title Several Reactions of Isocyanide and Related Compounds
... mechanism through a mixed ligand complex has been proposed, in which both isocyanide and amine are coordinated with the common metal ion and the reaction takes place in the sphere of complex ligand. In Chapter 2, insertion reactions of isocyanide between oxygen and hydrogen bond of alcohols to produ ...
... mechanism through a mixed ligand complex has been proposed, in which both isocyanide and amine are coordinated with the common metal ion and the reaction takes place in the sphere of complex ligand. In Chapter 2, insertion reactions of isocyanide between oxygen and hydrogen bond of alcohols to produ ...
Aminoketone Rearrangements. 11. The Rearrangement of Phenyl a
... base removal of a n amine hydrogen and migration of a n alkyl group. The hydroxyimine can subsequently rearrange by base removal of a hydroxyl proton and migration of the phenyl grouping. An amine hydrogen has been shown to be necessary by the inactivity of tertiary aminoketones. Unconjugated hydrox ...
... base removal of a n amine hydrogen and migration of a n alkyl group. The hydroxyimine can subsequently rearrange by base removal of a hydroxyl proton and migration of the phenyl grouping. An amine hydrogen has been shown to be necessary by the inactivity of tertiary aminoketones. Unconjugated hydrox ...
New insights into the mechanism of sorbitol transformation
... pressure separator cooled by water circulation. The liquid effluents were collected in vials at the exit of the separator to be further analyzed. After the separator, the gaseous effluent flowed through a back pressure regulator and then through a gas bulb. A drumtype gas meter measured the gas flo ...
... pressure separator cooled by water circulation. The liquid effluents were collected in vials at the exit of the separator to be further analyzed. After the separator, the gaseous effluent flowed through a back pressure regulator and then through a gas bulb. A drumtype gas meter measured the gas flo ...
Buchwald-Hartwig Chemistry
... Kosugi, M.; Kameyama, M.; Migita, T. Chem. Lett., 1983, 927 Kosugi, M.; Kameyama, M.; Sano, H.; Migita, T. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi , 1985, 3, 547 ...
... Kosugi, M.; Kameyama, M.; Migita, T. Chem. Lett., 1983, 927 Kosugi, M.; Kameyama, M.; Sano, H.; Migita, T. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi , 1985, 3, 547 ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.