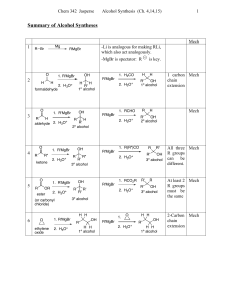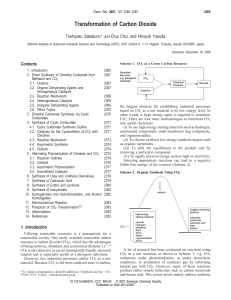
Transformation of Carbon Dioxide
... researcher in the same group at AIST. His research interest is focused on CO2 conversion and C−H bond activation by metal complexes. ...
... researcher in the same group at AIST. His research interest is focused on CO2 conversion and C−H bond activation by metal complexes. ...
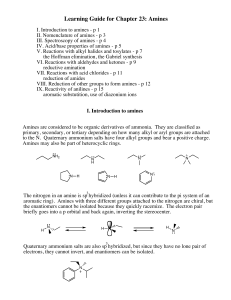
Learning Guide for Chapter 23: Amines
... VI. Reactions with aldehydes and ketones - p 9 reductive amination VII. Reactions with acid chlorides - p 11 reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are c ...
... VI. Reactions with aldehydes and ketones - p 9 reductive amination VII. Reactions with acid chlorides - p 11 reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are c ...
Document
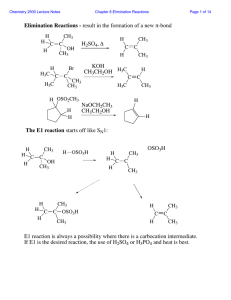
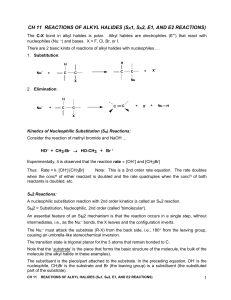
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Oxidative Cyclization Strategies Andreas K. Å. Persson
... oxidative carbocyclization of en-, dien- and aza-enallenes. In the first part of this thesis, a stereoselective oxidative carbocyclization of dienallenes was realized. By employing cheap and readily available palladium trifluoroacetate we were able to efficiently cyclize a variety of dienallenes int ...
... oxidative carbocyclization of en-, dien- and aza-enallenes. In the first part of this thesis, a stereoselective oxidative carbocyclization of dienallenes was realized. By employing cheap and readily available palladium trifluoroacetate we were able to efficiently cyclize a variety of dienallenes int ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... Tosylates Allow Control of Stereochemistry Preparation of tosylate does not affect any of the bonds to the chirality center, so configuration and optical purity of tosylate is the same as the alcohol from which it was formed. H ...
... Tosylates Allow Control of Stereochemistry Preparation of tosylate does not affect any of the bonds to the chirality center, so configuration and optical purity of tosylate is the same as the alcohol from which it was formed. H ...
Synthesis of Alcohols Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents
... O What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. ...
... O What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. ...
Alkyl Halides02
... This is also a qualitative test for identifying alcohols, i.e, the Lucas test. HCl with ZnCl 2 catalyst are used. 3 alcohols react quickly, 2 slowly, and 1 don’t react. Note that 1 and 2 alcohols will react with special reagents to produce alkyl halides (i.e., thionyl chloride, SOCl2, or PBr3) ...
... This is also a qualitative test for identifying alcohols, i.e, the Lucas test. HCl with ZnCl 2 catalyst are used. 3 alcohols react quickly, 2 slowly, and 1 don’t react. Note that 1 and 2 alcohols will react with special reagents to produce alkyl halides (i.e., thionyl chloride, SOCl2, or PBr3) ...
Document
... BH3 is a reactive gas that exists mostly as a dimer, diborane (B2H6). Borane is a strong Lewis acid that reacts readily with Lewis bases. ...
... BH3 is a reactive gas that exists mostly as a dimer, diborane (B2H6). Borane is a strong Lewis acid that reacts readily with Lewis bases. ...
Organic Chemistry II Introduction
... Thiols do not form H-bonds (EN of S is low) Alcohols and phenols are weakly basic Alcohols and phenols are weakly acidic Phenols and Thiols are more acidic than water ...
... Thiols do not form H-bonds (EN of S is low) Alcohols and phenols are weakly basic Alcohols and phenols are weakly acidic Phenols and Thiols are more acidic than water ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... Ethyl isopropyl ketone may be alternatively named 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Its longest continuous chain has five carbons. The carbonyl carbon is C-3 irrespective of the direction in which the chain is numbered, and so we choose the direction that gives the lower number to the position that bears the me ...
... Ethyl isopropyl ketone may be alternatively named 2-methyl-3-pentanone. Its longest continuous chain has five carbons. The carbonyl carbon is C-3 irrespective of the direction in which the chain is numbered, and so we choose the direction that gives the lower number to the position that bears the me ...
Full Text
... each hydroxyl in the many cases where multiple hydroxyls are present in a molecule.1,3 The methoxylmethyl (MOM) group is widely used as a hydroxyl-protecting group because MOM ethers can be easily prepared and are stable under the removal conditions of protecting groups such as silyl, alkoxyacyl, or ...
... each hydroxyl in the many cases where multiple hydroxyls are present in a molecule.1,3 The methoxylmethyl (MOM) group is widely used as a hydroxyl-protecting group because MOM ethers can be easily prepared and are stable under the removal conditions of protecting groups such as silyl, alkoxyacyl, or ...
Microsoft Word
... cyclopropylcarbinols. The reaction proceeds highly regioselectively and the outcome can be rationalized by the destabilizing inductive effect of the hydroxy/stabilizing inductive effect of the methyl groups. The reaction proceeds with clean inversion of configuration at the electrophilic carbon and ...
... cyclopropylcarbinols. The reaction proceeds highly regioselectively and the outcome can be rationalized by the destabilizing inductive effect of the hydroxy/stabilizing inductive effect of the methyl groups. The reaction proceeds with clean inversion of configuration at the electrophilic carbon and ...
Synthetic Strategies for the Construction of Enantiomeric
... [3+2] annulation9 utilizing 2-trimethylsilylmethyl-2-propen-1-yl acetate. Several attempts to access a bicyclic system via direct annulation of an existing olefin-containing ring were not successful. For example, reaction of 2-trimethylsilylmethyl-2-propen-1-yl acetate with maleimide, N-benzylmaleim ...
... [3+2] annulation9 utilizing 2-trimethylsilylmethyl-2-propen-1-yl acetate. Several attempts to access a bicyclic system via direct annulation of an existing olefin-containing ring were not successful. For example, reaction of 2-trimethylsilylmethyl-2-propen-1-yl acetate with maleimide, N-benzylmaleim ...
Chiral Enolate Equivalents
... many strategies could be identified as alternatives to chiral enolate chemistry if defined as approaches or methods that produce a compound possessing a carbonyl function with an αor β-chiral carbon. For that reason, the contents of this review article are restricted to processes that yield chiral p ...
... many strategies could be identified as alternatives to chiral enolate chemistry if defined as approaches or methods that produce a compound possessing a carbonyl function with an αor β-chiral carbon. For that reason, the contents of this review article are restricted to processes that yield chiral p ...
Anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine derivatives and a synthetic approach to aldingenin B
... [1,2]-Anionic rearrangements are important tools for altering the complexity of molecules at hand. In Part I of this dissertation, an anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine is described. Pyridine-directed metallation of the benzylic carbon leads to 1,2-migration of pyridine via a postulated as ...
... [1,2]-Anionic rearrangements are important tools for altering the complexity of molecules at hand. In Part I of this dissertation, an anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine is described. Pyridine-directed metallation of the benzylic carbon leads to 1,2-migration of pyridine via a postulated as ...
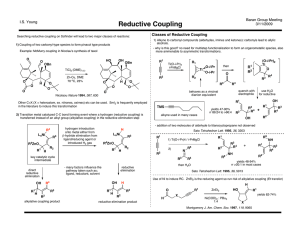
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.