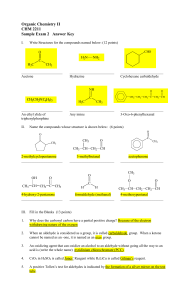
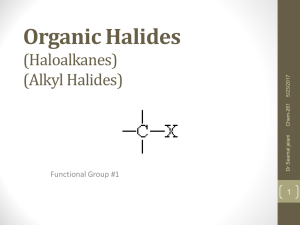carbonyl compound group
... On treatment with hydroxylamine in a weakly acidic medium, aldehydes or ketones form ...
... On treatment with hydroxylamine in a weakly acidic medium, aldehydes or ketones form ...
- Opus: Online Publications Store
... bond in a molecule it is necessary to activate this bond (making it more reactive) as the first step, followed by its subsequent functionalization [1a]. The activation process can be achieved effectively by using transition metal catalysts and others [1c,11]. It is well−known that complexes based on ...
... bond in a molecule it is necessary to activate this bond (making it more reactive) as the first step, followed by its subsequent functionalization [1a]. The activation process can be achieved effectively by using transition metal catalysts and others [1c,11]. It is well−known that complexes based on ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... reaction with PBr3 which transforms OH- into a better leaving group allowing substitution (SN2) to occur without rearrangement. ...
... reaction with PBr3 which transforms OH- into a better leaving group allowing substitution (SN2) to occur without rearrangement. ...
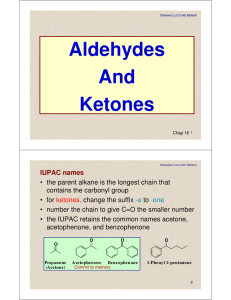
CHAPTER 15
... (1) Aldehydes and ketones readily undergo oxidation to carboxylic acids. (2) Propanone and dimethyl ketone are two names for the same compound. (3) The “silver mirror test” distinguishes between aldehydes and ketones. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only ...
... (1) Aldehydes and ketones readily undergo oxidation to carboxylic acids. (2) Propanone and dimethyl ketone are two names for the same compound. (3) The “silver mirror test” distinguishes between aldehydes and ketones. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... C in substitution reactions (and form C-Nu bonds) react with C-H protons to form Nu-H bonds. That is why we use the term "base" to describe nucleophiles that also remove protons from carbon in elimination reactions. E1 and E2 Reactions Can Compete (9.2B) E1 and E2 reactions may occur simultaneously ...
... C in substitution reactions (and form C-Nu bonds) react with C-H protons to form Nu-H bonds. That is why we use the term "base" to describe nucleophiles that also remove protons from carbon in elimination reactions. E1 and E2 Reactions Can Compete (9.2B) E1 and E2 reactions may occur simultaneously ...
Aldehydes And Ketones
... the flow of pairs of e• Draw the arrow from higher e- density to lower e- density i.e. from the nucleophile to the electrophile • Removing e- density from an atom will create a formal + charge • Adding e- density to an atom will create a formal - charge • Proton transfer is fast (kinetics) and usual ...
... the flow of pairs of e• Draw the arrow from higher e- density to lower e- density i.e. from the nucleophile to the electrophile • Removing e- density from an atom will create a formal + charge • Adding e- density to an atom will create a formal - charge • Proton transfer is fast (kinetics) and usual ...
10.4 Alcohols - SCIS Teachers
... •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •dissolve in water to some degree •are more polar ...
... •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •dissolve in water to some degree •are more polar ...
1990-Spring-Exam-2-student
... experimental support from text or below. Long, rambling answers are not necessary! Note: There is no particular order to questions presented here. Answer first those questions you know best. Partial credit will be given when/where appropriate. Brief answers are most welcome, citing specific experime ...
... experimental support from text or below. Long, rambling answers are not necessary! Note: There is no particular order to questions presented here. Answer first those questions you know best. Partial credit will be given when/where appropriate. Brief answers are most welcome, citing specific experime ...
Chapter 7 Hydrosilylation of Carbon
... Palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of styrene derivatives usually proceeds with high regioselectivity to produce benzylic silanes, 1-aryl-1-silylethanes, due to the participation of π-benzylic palladium intermediates [1, 2]. It is known that bisphosphine-palladium complexes are catalytically much l ...
... Palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of styrene derivatives usually proceeds with high regioselectivity to produce benzylic silanes, 1-aryl-1-silylethanes, due to the participation of π-benzylic palladium intermediates [1, 2]. It is known that bisphosphine-palladium complexes are catalytically much l ...
- Sacramento - California State University
... 7. Figure 7: Ligand used for the asymmetric sulfoxidation of tert-butyl disulfide. ........ 17 8. Figure 8: Ligands for the kinetic resolution of ethyl mandalate (racemic) ................. 18 9. Figure 9: Ligands used in Jacobsen’s Epoxidation ..................................................... 2 ...
... 7. Figure 7: Ligand used for the asymmetric sulfoxidation of tert-butyl disulfide. ........ 17 8. Figure 8: Ligands for the kinetic resolution of ethyl mandalate (racemic) ................. 18 9. Figure 9: Ligands used in Jacobsen’s Epoxidation ..................................................... 2 ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... • An ether has two organic groups (alkyl, aryl, or vinyl) bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Epoxides contain a C-O-C unit which make-up a three membered ring • Thiols (R–S–H) and sulf ...
... • An ether has two organic groups (alkyl, aryl, or vinyl) bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Epoxides contain a C-O-C unit which make-up a three membered ring • Thiols (R–S–H) and sulf ...
Process for preparing polycarbonates
... then cooled to 130° C. and 30 grams of ?nely divided 60 The reaction conditions of Examples 1 and 2 were magnesium silicate and 60 grams of celite clay were again duplicated except that a mixture of 44 grams (0.5 added to purify the mixture. The mixture was continu moles) of ethylene carbonate, 6.3 ...
... then cooled to 130° C. and 30 grams of ?nely divided 60 The reaction conditions of Examples 1 and 2 were magnesium silicate and 60 grams of celite clay were again duplicated except that a mixture of 44 grams (0.5 added to purify the mixture. The mixture was continu moles) of ethylene carbonate, 6.3 ...
Alkenes 3 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Notice that the requirements for a -elimination reaction are: (i) A base (ii) A leaving group in the substrate such as halide, tosylate etc. and ... (iii) A C-H bond - to the leaving group. We have already seen that most strong bases are also good nucleophiles - and vice versa. For this reason nuc ...
... Notice that the requirements for a -elimination reaction are: (i) A base (ii) A leaving group in the substrate such as halide, tosylate etc. and ... (iii) A C-H bond - to the leaving group. We have already seen that most strong bases are also good nucleophiles - and vice versa. For this reason nuc ...
CHEM 121. Chapter 15
... 2. Which of the following structural features is possessed by aldehydes but not ketones? A) At least one hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom. B) At least one hydroxyl group is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom. C) The carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. D) The ...
... 2. Which of the following structural features is possessed by aldehydes but not ketones? A) At least one hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom. B) At least one hydroxyl group is bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom. C) The carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. D) The ...
4.8 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... Hammond's Hammond'sPostulate Postulate If two succeeding states (such as a transition state and an unstable intermediate) are similar in energy, they are similar in structure. Hammond's postulate permits us to infer the structure of something we can't study (transition state) from something we can ...
... Hammond's Hammond'sPostulate Postulate If two succeeding states (such as a transition state and an unstable intermediate) are similar in energy, they are similar in structure. Hammond's postulate permits us to infer the structure of something we can't study (transition state) from something we can ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... • The negative part of the added molecule adds to the positive carbonyl carbon • The positive part of the added molecule adds to the negative carbonyl oxygen • d+ d- d+ d• -C=O + X-Y -C-O-X ...
... • The negative part of the added molecule adds to the positive carbonyl carbon • The positive part of the added molecule adds to the negative carbonyl oxygen • d+ d- d+ d• -C=O + X-Y -C-O-X ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... In acid: protonate the oxygen, establishing the very good leaving group. More substituted carbon (more positive charge although more sterically hindered) is attacked by a weak nucleophile. Very similar to opening of cyclic bromonium ion. ...
... In acid: protonate the oxygen, establishing the very good leaving group. More substituted carbon (more positive charge although more sterically hindered) is attacked by a weak nucleophile. Very similar to opening of cyclic bromonium ion. ...
Catalytic Asymmetric Induction. Highly Enantioselective Addition of
... Several examples have been reported for highly enantioselective alkylation of aldehydes by organometallic compounds combined with chiral modifiers.' In all cases, however, the procedures require stoichiometric or even excess amounts of the chiral sources.2 Accordingly, development of efficient chira ...
... Several examples have been reported for highly enantioselective alkylation of aldehydes by organometallic compounds combined with chiral modifiers.' In all cases, however, the procedures require stoichiometric or even excess amounts of the chiral sources.2 Accordingly, development of efficient chira ...
the suzuki-miyaura reaction and boron reagents – mechanism
... Properties of boronic acids. ¤ Are highly reactive towards transmetalation and are atom efficient. ¤ Can be difficult to handle as well as purify, many decompose in air. ¤ Are susceptible to side reactions in the SM coupling. n Under SM conditions base-catalysed protodeboronation is common31 ...
... Properties of boronic acids. ¤ Are highly reactive towards transmetalation and are atom efficient. ¤ Can be difficult to handle as well as purify, many decompose in air. ¤ Are susceptible to side reactions in the SM coupling. n Under SM conditions base-catalysed protodeboronation is common31 ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.