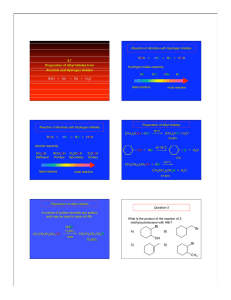
cleavage of methyl ethers with iodotrimethylsilane
... modifications of early methods for cleavage of aliphatic methyl ethers utilize hydrogen iodide generated in situ10 and magnesium bromide in acetic anhydride.20 Recently described methods for the hydrolysis of methyl ethers include the use of sodium cyanide in dimethyl sulfoxide,21 anhydrous hydrogen ...
... modifications of early methods for cleavage of aliphatic methyl ethers utilize hydrogen iodide generated in situ10 and magnesium bromide in acetic anhydride.20 Recently described methods for the hydrolysis of methyl ethers include the use of sodium cyanide in dimethyl sulfoxide,21 anhydrous hydrogen ...
View/Open - AURA - Alfred University
... that triflic acid is not responsible for the progress of the reaction, suggests that PEDOT can mediate the Ritter reaction under mild conditions and it may now be possible to use unprotected, acid-sensitive functional groups. In an attempt to determine the scope of the PEDOT-mediated Ritter reactio ...
... that triflic acid is not responsible for the progress of the reaction, suggests that PEDOT can mediate the Ritter reaction under mild conditions and it may now be possible to use unprotected, acid-sensitive functional groups. In an attempt to determine the scope of the PEDOT-mediated Ritter reactio ...
Unit-8-Alcohols-Aldehydes
... Unit 8 - Organic Molecules III Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes and Ketones In this unit we continue surveying some of the families of organic molecules that play important roles in biochemistry; looking both at their physical and chemical properties. The Group VIA elements, oxygen and sulfur, ty ...
... Unit 8 - Organic Molecules III Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes and Ketones In this unit we continue surveying some of the families of organic molecules that play important roles in biochemistry; looking both at their physical and chemical properties. The Group VIA elements, oxygen and sulfur, ty ...
98 pts
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry-II
... followed by Wieland (1922), Meerwein (1927), Colonge (1939), and Dilthey (1938). During the usual work-up involving quenching the reaction mixture by adding ice–water, any diacylation products which are water-soluble salts remained undetected and were thrown away, although in some cases they were pr ...
... followed by Wieland (1922), Meerwein (1927), Colonge (1939), and Dilthey (1938). During the usual work-up involving quenching the reaction mixture by adding ice–water, any diacylation products which are water-soluble salts remained undetected and were thrown away, although in some cases they were pr ...
Learning materials
... I2 does not react this way, because I. is too stable to split the C-H bond. F2 is so reactive that it breaks both C-H and C-C bonds: 7F2 + C2H6 = 2CF4 + 6HF ...
... I2 does not react this way, because I. is too stable to split the C-H bond. F2 is so reactive that it breaks both C-H and C-C bonds: 7F2 + C2H6 = 2CF4 + 6HF ...
16 Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes
... A. Solubility in Water: 1. Obtain 9 stoppered test tubes (labeled #1-8), each containing 1 mL of water.1 2. Leave tube #1 as a control for comparison. Into tube #2 put 5 drops ethanol, (ethyl alcohol). Into tube #3 put 5 drops of 1-propanol, (n-propyl alcohol). Into tube #4 put 5 drops 1-butanol, (n ...
... A. Solubility in Water: 1. Obtain 9 stoppered test tubes (labeled #1-8), each containing 1 mL of water.1 2. Leave tube #1 as a control for comparison. Into tube #2 put 5 drops ethanol, (ethyl alcohol). Into tube #3 put 5 drops of 1-propanol, (n-propyl alcohol). Into tube #4 put 5 drops 1-butanol, (n ...
Dehydration of n-propanol and methanol to produce
... alcohols. When methanol and n-propanol are reacted together, three types of ethers can be produced; i.e., dimethyl ether, methyl-propyl ether (also referred to as methoxypropane), and di-propyl ether. The latter two ethers are of more fuel interest due to their ability to stay in liquid phase at roo ...
... alcohols. When methanol and n-propanol are reacted together, three types of ethers can be produced; i.e., dimethyl ether, methyl-propyl ether (also referred to as methoxypropane), and di-propyl ether. The latter two ethers are of more fuel interest due to their ability to stay in liquid phase at roo ...
The First Chiral Organometallic Triangle for Asymmetric Catalysis
... exhibit expected ν(CtC) stretches at ∼2100 cm-1. The formulations of 1-4 are also supported by microanalysis results. All of these spectroscopic data are consistent with a cyclic trinuclear structure with approximate D3 symmetry for 1-4. Numerous attempts have however failed to produce X-ray diffrac ...
... exhibit expected ν(CtC) stretches at ∼2100 cm-1. The formulations of 1-4 are also supported by microanalysis results. All of these spectroscopic data are consistent with a cyclic trinuclear structure with approximate D3 symmetry for 1-4. Numerous attempts have however failed to produce X-ray diffrac ...
Catalytic Nucleophilic Fluorination of Secondary and Tertiary
... to the pharmaceutical[1] and agrochemical industries,[2] positron-emission tomography,[3] and materials science.[4] Catalytic fluorination has been the focus of many investigations,[5] in which either electrophilic or nucleophilic fluorine sources have been used.[6] Despite these significant advance ...
... to the pharmaceutical[1] and agrochemical industries,[2] positron-emission tomography,[3] and materials science.[4] Catalytic fluorination has been the focus of many investigations,[5] in which either electrophilic or nucleophilic fluorine sources have been used.[6] Despite these significant advance ...
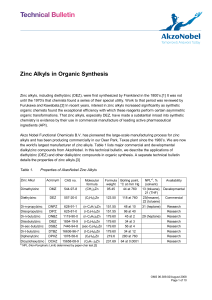
Zinc Alkyls in Organic Synthesis
... Asymmetric Additions to Aldehydes and Ketones DEZ is also useful in catalytic asymmetric addition to aldehydes or ketones forming chiral secondary or tertiary alcohols. These reactions typically involve an amine or a sulfonamide ligand in combination with tetraisopropyl titanate (TIPT). The added s ...
... Asymmetric Additions to Aldehydes and Ketones DEZ is also useful in catalytic asymmetric addition to aldehydes or ketones forming chiral secondary or tertiary alcohols. These reactions typically involve an amine or a sulfonamide ligand in combination with tetraisopropyl titanate (TIPT). The added s ...
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and
... potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.] (c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) also give red ppt. of CU2O. (d) Schiff’s reagent It is an aqueous solution of magenta or pink coloured rosaniline hydrochloride which has been decolourised by passing SO2, Aldehyde ...
... potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.] (c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) also give red ppt. of CU2O. (d) Schiff’s reagent It is an aqueous solution of magenta or pink coloured rosaniline hydrochloride which has been decolourised by passing SO2, Aldehyde ...
metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactoins
... transition metals for cross-coupling reactions.7 The rate, yield, and scope of palladium-catalyzed crosscoupling reactions are influenced by both the reaction partners and the choice of ligands, allowing for a wide substrate scope through judicious choice of these parameters. Historically, palladiu ...
... transition metals for cross-coupling reactions.7 The rate, yield, and scope of palladium-catalyzed crosscoupling reactions are influenced by both the reaction partners and the choice of ligands, allowing for a wide substrate scope through judicious choice of these parameters. Historically, palladiu ...
Full-Text PDF
... The high reactivity of aldehydes makes them a key functional group in organic chemistry. This group is widespread in Nature, and its use in the synthesis of natural products is noteworthy. Furthermore, as efficient electrophiles, aldehydes can undergo further transformations to be converted into an ...
... The high reactivity of aldehydes makes them a key functional group in organic chemistry. This group is widespread in Nature, and its use in the synthesis of natural products is noteworthy. Furthermore, as efficient electrophiles, aldehydes can undergo further transformations to be converted into an ...
Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics and Chemical Equilibrium
... Strong, bulky bases give a mixture of Saytzeff’s product (more substituted) and the Hoffmann product (least highly substituted alkene) bulky bases often abstract a proton from a less hindered carbon ...
... Strong, bulky bases give a mixture of Saytzeff’s product (more substituted) and the Hoffmann product (least highly substituted alkene) bulky bases often abstract a proton from a less hindered carbon ...
Aromatic Substitution Reactions
... ophile, in a fashion very similar to the addition reactions described in Chapter 11, which begin by reaction of an electrophile with the pi electrons of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation called an arenium ion. Removal of a proton from the arenium ion by some weak base that is ...
... ophile, in a fashion very similar to the addition reactions described in Chapter 11, which begin by reaction of an electrophile with the pi electrons of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation called an arenium ion. Removal of a proton from the arenium ion by some weak base that is ...
Acidity of Alcohols
... Only 5% of the ethene is converted into ethanol • at each pass through the reactor. By removing the ethanol from the equilibrium mixture and recycling the ethene, it is possible to achieve an overall 95% conversion. ...
... Only 5% of the ethene is converted into ethanol • at each pass through the reactor. By removing the ethanol from the equilibrium mixture and recycling the ethene, it is possible to achieve an overall 95% conversion. ...
4.7 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... Dissociation of the alkyloxonium ion involves H ...
... Dissociation of the alkyloxonium ion involves H ...
Lecture - Ch 19
... of Aldehydes and Ketones • Nucleophilic additions to aldehydes and ketones have two general variations – Product is a direct result of the tetrahedral intermediate being protonated by water or acid – Carbonyl oxygen atom is protonated and eliminated as HO- or H2O to give a product with a C=Nu double ...
... of Aldehydes and Ketones • Nucleophilic additions to aldehydes and ketones have two general variations – Product is a direct result of the tetrahedral intermediate being protonated by water or acid – Carbonyl oxygen atom is protonated and eliminated as HO- or H2O to give a product with a C=Nu double ...
Aromatic Compounds
... • Addition of a reagent such as HCl to an alkene • The electrophilic hydrogen approaches the p electrons of ...
... • Addition of a reagent such as HCl to an alkene • The electrophilic hydrogen approaches the p electrons of ...
Exam 3 - Napa Valley College
... 1) Please discuss, and give examples, of the relative acidity of 1, 2, and 3 alcohols. Why is one more acidic than another? The more acidic alcohol is the smaller alcohol (ie: 1). They have the fewest methyl groups pushing into the OH group. This causes the oxygen to pull as many electrons from ...
... 1) Please discuss, and give examples, of the relative acidity of 1, 2, and 3 alcohols. Why is one more acidic than another? The more acidic alcohol is the smaller alcohol (ie: 1). They have the fewest methyl groups pushing into the OH group. This causes the oxygen to pull as many electrons from ...
Chapter 24. Amines - Houston Community College System
... compound and reduction of the nitro group Reduction by catalytic hydrogenation over platinum is suitable if no other groups can be reduced Iron, zinc, tin, and tin(II) chloride are effective in acidic solution ...
... compound and reduction of the nitro group Reduction by catalytic hydrogenation over platinum is suitable if no other groups can be reduced Iron, zinc, tin, and tin(II) chloride are effective in acidic solution ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... compound and reduction of the nitro group Reduction by catalytic hydrogenation over platinum is suitable if no other groups can be reduced Iron, zinc, tin, and tin(II) chloride are effective in acidic solution ...
... compound and reduction of the nitro group Reduction by catalytic hydrogenation over platinum is suitable if no other groups can be reduced Iron, zinc, tin, and tin(II) chloride are effective in acidic solution ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.