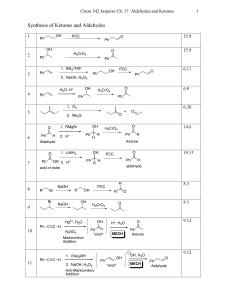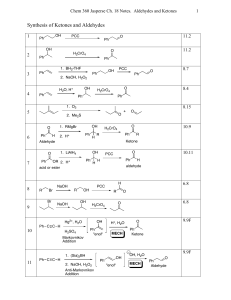
Synthesis of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
Synthesis of Ketones and Aldehydes
... 2. Recognize cationic mechanisms • Recipes that involve acid will be cationic • In a cationic mechanism, the first step will routinely involve protonation • In a cationic mechanism, the last step will frequently involve deprotonation to return to neutral • Normally the main step or steps are sandwic ...
... 2. Recognize cationic mechanisms • Recipes that involve acid will be cationic • In a cationic mechanism, the first step will routinely involve protonation • In a cationic mechanism, the last step will frequently involve deprotonation to return to neutral • Normally the main step or steps are sandwic ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... The Sn 1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the ratedetermining step. 3°, benzylic and allylic substrates undergo Sn 1 reaction because they form relatively stable carbocations. 1° substrates undergo Sn2 reaction because they are sterically uncluttered. 2° substrates u ...
... The Sn 1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the ratedetermining step. 3°, benzylic and allylic substrates undergo Sn 1 reaction because they form relatively stable carbocations. 1° substrates undergo Sn2 reaction because they are sterically uncluttered. 2° substrates u ...
OR Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
... Phenols react with NaOH solutions (but alcohols do not), forming salts that are soluble in dilute aqueous solutions ...
... Phenols react with NaOH solutions (but alcohols do not), forming salts that are soluble in dilute aqueous solutions ...
Grignard-syn-12-ques
... ethylmagnesium bromide (CH3CH2MgBr) with butanal (CH3CH2CH2CH=O) followed by dilute ...
... ethylmagnesium bromide (CH3CH2MgBr) with butanal (CH3CH2CH2CH=O) followed by dilute ...
OC 2/e Ch 15
... 16 Add’n of S Nucleophiles • a 1,3-dithiane anion is a good nucleophile and undergoes SN2 reactions with methyl, 1° alkyl, allylic, and benzylic halides • hydrolysis gives a ketone ...
... 16 Add’n of S Nucleophiles • a 1,3-dithiane anion is a good nucleophile and undergoes SN2 reactions with methyl, 1° alkyl, allylic, and benzylic halides • hydrolysis gives a ketone ...
Some uses of mischmetall in organic synthesis
... moderate to good yields. In some cases a slow addition of the carbonyl compound was necessary in order to allow regeneration of Sm(II) species thus preventing formation of by-products. The quantities of each reagent (mischmetall, samarium, tetrabromoethane) have been optimised according to the proce ...
... moderate to good yields. In some cases a slow addition of the carbonyl compound was necessary in order to allow regeneration of Sm(II) species thus preventing formation of by-products. The quantities of each reagent (mischmetall, samarium, tetrabromoethane) have been optimised according to the proce ...
Chem 240 - Napa Valley College
... between phenyl magnesium bromide and benzaldehyde. To make sure his yield was good he added twice as much benzaldehyde as Grignard reagent and got a lot of white crystalline product. When he analyzed his product he found that he had not made diphenyl methanol, but diphenyl methanal (also called benz ...
... between phenyl magnesium bromide and benzaldehyde. To make sure his yield was good he added twice as much benzaldehyde as Grignard reagent and got a lot of white crystalline product. When he analyzed his product he found that he had not made diphenyl methanol, but diphenyl methanal (also called benz ...
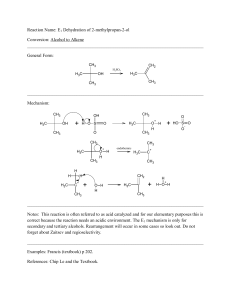
13-Elimination Reactions
... the SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanisms, which are covered in Chapter 12. The E1 reaction mechanism is a two-step process that, as with the SN1 mechanism, usually loses all the stereochemical information of the substrate as the reaction proceeds. The E2 mechanism, similar to the SN2 mechanism, is a conc ...
... the SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanisms, which are covered in Chapter 12. The E1 reaction mechanism is a two-step process that, as with the SN1 mechanism, usually loses all the stereochemical information of the substrate as the reaction proceeds. The E2 mechanism, similar to the SN2 mechanism, is a conc ...
Document
... – Reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol (-CH2OH). – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
... – Reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol (-CH2OH). – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
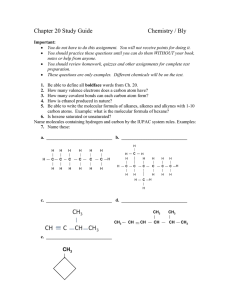
Chapter 22 and 23 Study Guide
... You should review homework, quizzes and other assignments for complete test preparation. These questions are only examples. Different chemicals will be on the test. ...
... You should review homework, quizzes and other assignments for complete test preparation. These questions are only examples. Different chemicals will be on the test. ...
File - Rasapalli Research Group
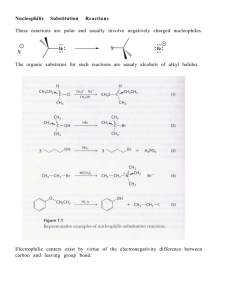
... 12. Alcohols and alkyl halides are produced via each other, and also they participate in some common type of reactions . 13. Nucleophilic substitution and eliminations – When a lone pair of electrons on a reagent attacks a positively polarized (or electrophilic) center. If a substituent is replaced, ...
... 12. Alcohols and alkyl halides are produced via each other, and also they participate in some common type of reactions . 13. Nucleophilic substitution and eliminations – When a lone pair of electrons on a reagent attacks a positively polarized (or electrophilic) center. If a substituent is replaced, ...
top organomet chem-2006-19-207 pauson
... Continuing with the reaction pathway, from complex F, insertion of CO follows giving G, and a subsequent complex reorganization forms H. Finally a reductive elimination leads to the cyclopentenone I. Several reports show different ways to accelerate the reaction. These are important for the aims of ...
... Continuing with the reaction pathway, from complex F, insertion of CO follows giving G, and a subsequent complex reorganization forms H. Finally a reductive elimination leads to the cyclopentenone I. Several reports show different ways to accelerate the reaction. These are important for the aims of ...
Aromatic Compounds
... • Addition of a reagent such as HCl to an alkene • The electrophilic hydrogen approaches the p electrons of ...
... • Addition of a reagent such as HCl to an alkene • The electrophilic hydrogen approaches the p electrons of ...
Chloroperbenzoic_aci..
... epoxidation) is observed when the bulkier O-t-Bu is located on the allylic carbon (eq 4).18 Due to steric and other factors, the norbornene (11) undergoes selective (99%) epoxidation from the exo face.19 In 7,7-dimethylnorbornene (12), approach to the exo face is effectively blocked by the methyl su ...
... epoxidation) is observed when the bulkier O-t-Bu is located on the allylic carbon (eq 4).18 Due to steric and other factors, the norbornene (11) undergoes selective (99%) epoxidation from the exo face.19 In 7,7-dimethylnorbornene (12), approach to the exo face is effectively blocked by the methyl su ...
Chapter 10
... A cyclic transition state occurs instead where one of the B-H bonds is transferred to the carbon, this process stabilizes the structure as the carbon never bears a full positive charge ...
... A cyclic transition state occurs instead where one of the B-H bonds is transferred to the carbon, this process stabilizes the structure as the carbon never bears a full positive charge ...
Review of Organic Chem II
... 4. Cations and radicals both fall short of octet rule. As a result, they are both electron deficient. Carbanions, by contrast, are electron rich. 5. Alkyl substituents are electron donors. As a result, they are good for electron deficient cations and radicals (3º > 2º > 1º > methyl) but bad for carb ...
... 4. Cations and radicals both fall short of octet rule. As a result, they are both electron deficient. Carbanions, by contrast, are electron rich. 5. Alkyl substituents are electron donors. As a result, they are good for electron deficient cations and radicals (3º > 2º > 1º > methyl) but bad for carb ...
13. amines - WordPress.com
... Structure-basicity relationship of amines Basicity of amines is related to their structure. Basic character of an amine depends upon the ease of formation of the cation by accepting a proton from the acid. As the stability of the cation increases, the basicity also increases. a) Comparison of basici ...
... Structure-basicity relationship of amines Basicity of amines is related to their structure. Basic character of an amine depends upon the ease of formation of the cation by accepting a proton from the acid. As the stability of the cation increases, the basicity also increases. a) Comparison of basici ...
carboxylic acid
... Relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives • Both addition and elimination steps affect the overall rate of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction • Addition step is generally rate-limiting due to steric and electronic factors ...
... Relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives • Both addition and elimination steps affect the overall rate of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction • Addition step is generally rate-limiting due to steric and electronic factors ...
Organic Chemistry - Rutgers University, Newark
... Conversion of an alcohol to a sulfonate ester converts HOH, a very poor leaving group, into a sulfonic ester, a very good leaving group ...
... Conversion of an alcohol to a sulfonate ester converts HOH, a very poor leaving group, into a sulfonic ester, a very good leaving group ...
RheniumCatalyzed Deoxydehydration of Diols and Polyols
... While the majority of oil, coal, and gas is used for energy production, the realization of an economy completely independent of fossil resources also requires biomass-based substitutes for polymers, medicine, pesticides, and so forth.[1] The evergrowing world population makes it questionable to use ...
... While the majority of oil, coal, and gas is used for energy production, the realization of an economy completely independent of fossil resources also requires biomass-based substitutes for polymers, medicine, pesticides, and so forth.[1] The evergrowing world population makes it questionable to use ...
J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1672
... The aliphatic carboxylic group was efficiently reduced to the methyl group by HSiEt3 in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of a direct exhaustive reduction of aliphatic carboxylic function. Aliphatic aldehydes, acyl chlorides, anhyd ...
... The aliphatic carboxylic group was efficiently reduced to the methyl group by HSiEt3 in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of a direct exhaustive reduction of aliphatic carboxylic function. Aliphatic aldehydes, acyl chlorides, anhyd ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.