- Wiley Online Library
... hydrogen shift/halogenation for the preparation of a-fluoroketones.[9c,d] While this represented a success in terms of merging a transition-metal-catalyzed isomerization with an electrophilic halogenation, the formation of nonfluorinated ketones (5–20 %) could not be avoided and led to challenging s ...
... hydrogen shift/halogenation for the preparation of a-fluoroketones.[9c,d] While this represented a success in terms of merging a transition-metal-catalyzed isomerization with an electrophilic halogenation, the formation of nonfluorinated ketones (5–20 %) could not be avoided and led to challenging s ...
Carbonyl Compounds I. Aldehydes and Ketones
... Compared to carboxylic and carbonic acid derivatives, the less highly oxidized carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones are not so widespread in nature. That is not to say that they are unimportant. To the contrary. Aldehydes and ketones are of great importance both in biological chemistry a ...
... Compared to carboxylic and carbonic acid derivatives, the less highly oxidized carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones are not so widespread in nature. That is not to say that they are unimportant. To the contrary. Aldehydes and ketones are of great importance both in biological chemistry a ...
HOMOLOGATION OF HETEROCYCLES BY A SEQUENTIAL REDUCTIVE OPENING LITHIATION – S
... Functionalized organolithium compounds (91MI3, 95OPP383, 97MI4, 03T9255, 04CRV2667) are of great interest in organic synthesis because polyfunctionalized molecules are obtained in a single synthetic operation by reaction with electrophilic reagents.(95MI5, 02MI6) Functionalized organolithium compoun ...
... Functionalized organolithium compounds (91MI3, 95OPP383, 97MI4, 03T9255, 04CRV2667) are of great interest in organic synthesis because polyfunctionalized molecules are obtained in a single synthetic operation by reaction with electrophilic reagents.(95MI5, 02MI6) Functionalized organolithium compoun ...
A manganese catalyst for highly reactive yet chemoselective
... 90%), which would be challenging to accomplish with traditional synthetic methods. Under [Mn(tBuPc)] 3 catalysis, amination of γ C–H bonds to form six-membered oxathiazinanes is generally preferred over β C–H bonds to form five-membered oxathiazoles, regardless of the relative bond strength. For exam ...
... 90%), which would be challenging to accomplish with traditional synthetic methods. Under [Mn(tBuPc)] 3 catalysis, amination of γ C–H bonds to form six-membered oxathiazinanes is generally preferred over β C–H bonds to form five-membered oxathiazoles, regardless of the relative bond strength. For exam ...
View/Open
... product on hydrogenation. The results of such an experiment involving platinumcatalyzed hydrogenation of three butene isomers are shown in Fig. 7.2. All three isomers yield the same product—butane—but the heat of reaction is different in each case. On conversion to butane, 1-butene liberates the mos ...
... product on hydrogenation. The results of such an experiment involving platinumcatalyzed hydrogenation of three butene isomers are shown in Fig. 7.2. All three isomers yield the same product—butane—but the heat of reaction is different in each case. On conversion to butane, 1-butene liberates the mos ...
CH 2
... with the idea that the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is stronger than the carbon-carbon single bond in alkanes, however, as the majority of the reactions of alkenes involve the rupture of this bond to form two new single bonds. ...
... with the idea that the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is stronger than the carbon-carbon single bond in alkanes, however, as the majority of the reactions of alkenes involve the rupture of this bond to form two new single bonds. ...
Latest Publication (still not complete)
... qualitatively explained using the Dewar-ChattDuncanson model. However, studies have been published which have quantified this model by determining the relative number of electrons involved in both charge-donation and back-donation using computational methodologies. Cases et al. have used charge deco ...
... qualitatively explained using the Dewar-ChattDuncanson model. However, studies have been published which have quantified this model by determining the relative number of electrons involved in both charge-donation and back-donation using computational methodologies. Cases et al. have used charge deco ...
homogeneous catalysis
... criteria. We have tried to include most of the homogeneous catalytic reactions with proven industrial applications and well-established mechanisms. The basic aim has been to highlight the connections that exist between imaginative academic research and successful technology. In the process, topics a ...
... criteria. We have tried to include most of the homogeneous catalytic reactions with proven industrial applications and well-established mechanisms. The basic aim has been to highlight the connections that exist between imaginative academic research and successful technology. In the process, topics a ...
synthetic approaches for quinoline and isoquinoline
... The Quinoline and Isoquinoline nucleus is found to be very important in pharmacy field. In recent years, a lot of synthetic drugs have been synthesized in different yield. In the present review, several other synthetic approaches are discussed involving easily available che ...
... The Quinoline and Isoquinoline nucleus is found to be very important in pharmacy field. In recent years, a lot of synthetic drugs have been synthesized in different yield. In the present review, several other synthetic approaches are discussed involving easily available che ...
university of london thesis
... Z-Carvone 3 is the major constituent and also the principal odour component o f spearmint oil from which it is extracted by steam distillation. Both the oil and synthetic Z-Carvone 3 are used as perfume and flavour ingredients bearing a refreshingly cool, minty odour and taste. The synthetic materia ...
... Z-Carvone 3 is the major constituent and also the principal odour component o f spearmint oil from which it is extracted by steam distillation. Both the oil and synthetic Z-Carvone 3 are used as perfume and flavour ingredients bearing a refreshingly cool, minty odour and taste. The synthetic materia ...
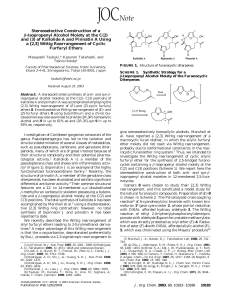
Stereoselective Construction of a β
... 1018 or (S,S)-bis(oxazoline) 1119) at -78 °C. The use of BuLi and 10 in THF resulted in poor enantioselectivity (entries 1 and 3), while in hexane the reactions gave none of the [2,3] Wittig rearrangement products (entries 2 and 4). Interestingly, the combination of t-BuLi and 11 in hexane was found ...
... 1018 or (S,S)-bis(oxazoline) 1119) at -78 °C. The use of BuLi and 10 in THF resulted in poor enantioselectivity (entries 1 and 3), while in hexane the reactions gave none of the [2,3] Wittig rearrangement products (entries 2 and 4). Interestingly, the combination of t-BuLi and 11 in hexane was found ...
Pseudoasymmetry as a Means for Distinguishing Meso
... A ketone of the type 7a (where A and B are equivalent or enantiomeric chiral ligands) which gives rise to two isomers upon reduction must be a meso isomer, while a ketone which gives only a single isomer upon reduction, which exhibits chemical-shift nonequivalence upon conversion to the benzyl ether ...
... A ketone of the type 7a (where A and B are equivalent or enantiomeric chiral ligands) which gives rise to two isomers upon reduction must be a meso isomer, while a ketone which gives only a single isomer upon reduction, which exhibits chemical-shift nonequivalence upon conversion to the benzyl ether ...
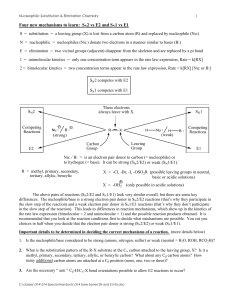
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
Organic Chemistry Notes by Jim Maxka jim.maxka
... Oxidation means gain of bonds Æ O; Loss of bonds Æ H. Reduction means gain of bonds Æ H; Loss of bonds Æ O. CH4 is the most oxidized or reduced organic molecule? What is the oxidation state of C? What is the most oxidized? What is the oxidation state of C? How about the reactions we just reviewed: o ...
... Oxidation means gain of bonds Æ O; Loss of bonds Æ H. Reduction means gain of bonds Æ H; Loss of bonds Æ O. CH4 is the most oxidized or reduced organic molecule? What is the oxidation state of C? What is the most oxidized? What is the oxidation state of C? How about the reactions we just reviewed: o ...
A mechanistic approach to solvolysis of n-caproyl chloride (n
... Raveendran & Jayasree, Orient. J. Chem., Vol. 25(4), 1017-1022 (2009) All these obser vations lead to the conclusion that hydrolysis in benzoyl chloride and to a larger extent in acetyl chloride proceeds largely by SN2 mechanism with simultaneous involvement of addition-ionization mechanism propose ...
... Raveendran & Jayasree, Orient. J. Chem., Vol. 25(4), 1017-1022 (2009) All these obser vations lead to the conclusion that hydrolysis in benzoyl chloride and to a larger extent in acetyl chloride proceeds largely by SN2 mechanism with simultaneous involvement of addition-ionization mechanism propose ...
aldehydes
... uncertain. As with DIBAH for aldehyde reductions, a low temperature (78 C) solvent (ether) is used to prevent further alkyl addition to the ketone to form an alcohol. (Acid chlorides are very good electrophiles). Carboxylic acids, esters, anhydrides and amides are not reduced by diorganocopper reag ...
... uncertain. As with DIBAH for aldehyde reductions, a low temperature (78 C) solvent (ether) is used to prevent further alkyl addition to the ketone to form an alcohol. (Acid chlorides are very good electrophiles). Carboxylic acids, esters, anhydrides and amides are not reduced by diorganocopper reag ...
New Exp8
... No deuterium isotope effect seen. The E1 reaction has no geometric requirement because of the two separate elimination steps. Limitations of E1 Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydrations Competition can occur with SN1 reaction if reaction conditions are not ‘controlled’ (when protic solvents, non-basic n ...
... No deuterium isotope effect seen. The E1 reaction has no geometric requirement because of the two separate elimination steps. Limitations of E1 Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydrations Competition can occur with SN1 reaction if reaction conditions are not ‘controlled’ (when protic solvents, non-basic n ...
Notes 10
... eliminations and rearrangements. These terms describe the overall process, simply comparing the structure of starting materials and products. They do not indicate anything about the pathway (“mechanism”) by which the reaction proceeds. Substitutions Additions Eliminations Rearrangements (often in co ...
... eliminations and rearrangements. These terms describe the overall process, simply comparing the structure of starting materials and products. They do not indicate anything about the pathway (“mechanism”) by which the reaction proceeds. Substitutions Additions Eliminations Rearrangements (often in co ...
synthesis, chemistry and optical resol
... reagent and (1-pentyny1)copper in the presence of 2 equiv of hexamethylphosphorous triamide1° to give the trans adduct 11 in 72% yield after purification (Scheme I). A minor amount of the corresponding 5,9& product was also obtained (-4% yield). Reduction of the trans product 11 with L-Selectride in ...
... reagent and (1-pentyny1)copper in the presence of 2 equiv of hexamethylphosphorous triamide1° to give the trans adduct 11 in 72% yield after purification (Scheme I). A minor amount of the corresponding 5,9& product was also obtained (-4% yield). Reduction of the trans product 11 with L-Selectride in ...
4.9 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen Halides
... The overall reaction mechanism involves three elementary steps; the first two steps lead to the carbocation intermediate, the third step is the conversion of this carbocation to the alkyl halide. ...
... The overall reaction mechanism involves three elementary steps; the first two steps lead to the carbocation intermediate, the third step is the conversion of this carbocation to the alkyl halide. ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within impor ...
... activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within impor ...
Alkene-Addn-PartB-2012-ques
... Question The product isolated from the acid-catalyzed hydration of (E)- or (Z)-3-methyl-2-pentene is: A) optically active B) an optically inactive racemic mixture C) an optically inactive enantiomer ...
... Question The product isolated from the acid-catalyzed hydration of (E)- or (Z)-3-methyl-2-pentene is: A) optically active B) an optically inactive racemic mixture C) an optically inactive enantiomer ...
Group Meeting Special Topic: EJ Corey
... • More stable silyl ether than TMS and dimethylisopropylsilyl ether • First time used imidazole and DMF ...
... • More stable silyl ether than TMS and dimethylisopropylsilyl ether • First time used imidazole and DMF ...
Reactions of alcohols File
... -CH2OH -C-CH(OH)-Calcohols! NB Oxidant = hot acidified Cr2O72- [dichromate(VI)] ion] Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
... -CH2OH -C-CH(OH)-Calcohols! NB Oxidant = hot acidified Cr2O72- [dichromate(VI)] ion] Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.