* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aldehydes and Ketones
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
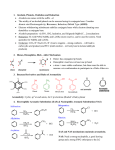
Chapter Fifteen Aldehydes And Ketones Aldehydes and Ketones In an aldehyde, an H atom is attached to a carbonyl group O carbonyl group CH3-C-H In a ketone, two carbon groups are attached to a carbonyl group O carbonyl group CH3-C-CH3 Chapter 15 | Slide 2 of 36 Chapter 15 | Slide 3 of 36 Ketones as Hormones Chapter 15 | Slide 4 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones cont’d ← Fig. 15.1 Aldehydes and ketones are related to alcohols in the same manner that alkenes are related to alkanes. Chapter 15 | Slide 5 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones → Fig. 15.3 Aldehydes and ketones with the same number of carbon atoms and the same degree of saturation are structural isomers. Chapter 15 | Slide 6 of 36 Naming Aldehydes • • • • Aldehydes are named by replacing the “e” with “____.” The parent chain must contain the –_______ group. The –CHO carbon is always carbon ___. When attached to a ring “carbaldehyde” is used. O O 3 5 O propaneal 6 4 2 1 4-ethyl 2,5-dimethyl 2- hexen eal cyclopentanecarbaldehyde Chapter 15 | Slide 7 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones cont’d ← Fig. 15.2 Benzaldehyde, the simplest aromatic aldehyde. . Chapter 15 | Slide 8 of 36 Naming Ketones • Ketones are named by replacing the “e” with “_____.” • The parent chain must contain the ______. • Numbering begins nearer the ______. O 7 O 6 5 4 3 2 1 5-ethyl 3,6-dimethyl 2- heptan eone 2- butan eone Chapter 15 | Slide 9 of 36 Name these aldehydes/ketones. O O 3-penten-2-one 5-methyl-3-cyclohexenone O O 2-phenylpropanal cyclohexanone Chapter 15 | Slide 10 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones cont’d ←C.C 15.1 ←Wood Smoke contains formaldehyde and causes eyes to tear. ←Formaldehyde is a lachrymator (eye irritant) © Harvey Lloyd/Peter Arnold, Inc. Chapter 15 | Slide 11 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones cont’d ← Fig. 15.4 Formalin is used to preserve biological specimens. © 2005 Norbert Wu / www.norbertwu.com Chapter 15 | Slide 12 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones → Fig. 15.5 The delightful odor of melted butter is largely due to butanedione. © Steven Needham / Envision Chapter 15 | Slide 13 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones cont’d Chapter 15 | Slide 14 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones Why are some aldehydes and ketones soluble in water? Chapter 15 | Slide 15 of 36 Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones • The polarity of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones, which is responsible for many of their physical properties. – They have boiling points _______ than alcohols but _______ than alkanes. • Why? – Nonpolar < Polar (Dipole-dipole) <H-bonds – _____ molecular weight aldehydes and ketones are __________ in water • Why not ________ molecular weight aldehydes and ketones? – Most aldehydes and ketones have odors Chapter 15 | Slide 16 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 15 | Slide 17 of 36 Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones O • Oxidation of alcohols. – Primary alcohols yield aldehydes. – Secondary alcohols yield ketones. From primary alcohols O From secondary alcohols Chapter 15 | Slide 18 of 36 • Oxidation reactions: OH PCC CH2Cl2 R PCC = Pyridinium chlorochromate OH Na2Cr2O7, H2O, CH3CO2H R R Chapter 15 | Slide 19 of 36 Oxidation of Aldehydes • Ketones are unreactive to oxidation because no hydrogens are on the carbon. O O R H AgNO3 NH4OH R OH O AgNO3 NH4OH R No Reaction R' Chapter 15 | Slide 20 of 36 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones • Reduction: Adding hydrogen across the carbonyl – Aldehyde primary alcohol – Ketone secondary alcohol CH CH2 O + H2 H3C H3C O OH + H2 C H3C OH CH3 CH H3C CH3 Chapter 15 | Slide 21 of 36 Addition Reactions • Polar molecules can add to the carbonyl in aldehydes and ketones • The negative part of the added molecule adds to the positive carbonyl carbon • The positive part of the added molecule adds to the negative carbonyl oxygen • d+ d- d+ d• -C=O + X-Y -C-O-X Y Chapter 15 | Slide 22 of 36 Acetal Formation • Alcohols add to the carbonyl of aldehydes and ketones • The addition of two alcohols forms an acetal. • O O-CH3 • CH3-C-H + 2 CH3-OH CH3-C-H + H2O • O-CH3 Hydrolysis of acetals yield the aldehyde or ketone and the alcohols that originally formed the acetal Chapter 15 | Slide 23 of 36 Hemiacetal Formation • The addition of one alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone forms an intermediate called a hemiacetal • Usually, hemiacetals are unstable and hard to isolate. • O O-CH3 • CH3-C-H + 2 CH3-OH CH3-C-H + H2O • O-H Chapter 15 | Slide 24 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones CC 15.3 Diabetes, aldehyde oxidation, and glucose testing Chapter 15 | Slide 25 of 36 Tests for Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones • Tollens’ test (AKA Silver Mirror test) – Tollens’ reagent, which contains Ag+, reacts with aldehydes, but not with ketones – The aldehyde is oxidized and Ag+ is reduced to Ag, which appears as a silver “mirror” in the test tube (or reaction vessel) Chapter 15 | Slide 26 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones cont’d Figs. 15.8 a-c (a) An aqueous solution of ethanal is added to a solution of silver nitrate. (b) The solution darkens as ethanal is oxidized to ethanoic acid. (c) The inside of the beaker becomes coated with metallic silver. Chapter 15 | Slide 27 of 36 Tests for Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones • Benedict’s Test – Benedict’s reagent, which contains Cu+2, reacts with aldehydes that have an adjacent OH group – The aldehyde is oxidized and Cu+2 is reduced Cu2O, which appears as a brick red solid in the test tube – Ketones do not react. Chapter 15 | Slide 28 of 36 Aldehydes and Ketones → Fig. 15.9 Benedict’s solution turns brick red when an aldehyde reacts with it. Chapter 15 | Slide 29 of 36 Chapter 15 | Slide 30 of 36 Work on the following learning checks as homework. Chapter 15 | Slide 31 of 36 Learning Check Classify each as an aldehyde (1), ketone (2) or neither(3). O A. CH3CH2CCH3 CH3 B. CH3-O-CH3 O C. CH3-C-CH2CH D. CH3 Chapter 15 | Slide 32 of 36 Learning Check Name the following O A. CH3CH2CCH3 B. CH3 O C. CH3-C-CH2CH CH3 Chapter 15 | Slide 33 of 36 Learning Check Draw the structural formulas for each: A. 3-Methylpentanal B. 2,3-Dichloropropanal C. 3-Methyl-2-butanone Chapter 15 | Slide 34 of 36 Learning Check • Select the compound that would have the higher boiling point – A. CH3-CH2-CH3 or CH3-CH2-OH – B. CH3-CH2-OH or CH3-O-CH3 – C. O OR Chapter 15 | Slide 35 of 36 Learning Check • Are the following compounds soluble in water? – A. CH3-CH2-CH3 – B. CH3-CH2-OH – C. O – D. O Chapter 15 | Slide 36 of 36