protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... Write the mRNA that would be transcribed from the following strand of DNA: ...
... Write the mRNA that would be transcribed from the following strand of DNA: ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - Gull Lake Community Schools / Overview
... “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train moving down the tracks”. This process repeats until DNA signals to STOP! The stop signal m ...
... “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train moving down the tracks”. This process repeats until DNA signals to STOP! The stop signal m ...
Lecture #4 Translation
... Some amino acids may be specified by two, four, or even six different codons. Example: UCA and AGU both code for the amino acid serine. ...
... Some amino acids may be specified by two, four, or even six different codons. Example: UCA and AGU both code for the amino acid serine. ...
The genetic code is a degenerate, non-overlapping set of
... ambiguity. For example, although codons GAA and GAG both specify glutamic acid (redundancy), neither of them specifies any other amino acid (no ambiguity). The codons encoding one amino acid may differ in any of their three positions. For example, the amino acid glutamic acid is specified by GAA and ...
... ambiguity. For example, although codons GAA and GAG both specify glutamic acid (redundancy), neither of them specifies any other amino acid (no ambiguity). The codons encoding one amino acid may differ in any of their three positions. For example, the amino acid glutamic acid is specified by GAA and ...
Protein Synthesis
... code for all the necessary amino acids. • The same amino acid is often specified by more than one codon. However, the reverse is never true. • that is, any one codon only specifies ONE amino acid ...
... code for all the necessary amino acids. • The same amino acid is often specified by more than one codon. However, the reverse is never true. • that is, any one codon only specifies ONE amino acid ...
File
... – Exons • Sections of genes that do code for amino acids, so proteins are made • Less than 10% of a human gene ...
... – Exons • Sections of genes that do code for amino acids, so proteins are made • Less than 10% of a human gene ...
Protein synthesis
... • Explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation • Recognize that gene expression is a regulated process • Describe the roles of DNA and RNA in cell ...
... • Explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation • Recognize that gene expression is a regulated process • Describe the roles of DNA and RNA in cell ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... Translation Cont’d 4. A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. 5. One codon codes for one amino acid. 6. tRNA molecules enter the ribosome carrying the correct amino acid. The tRNA has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA. 7. Amino acids are linked together to form a ...
... Translation Cont’d 4. A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. 5. One codon codes for one amino acid. 6. tRNA molecules enter the ribosome carrying the correct amino acid. The tRNA has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA. 7. Amino acids are linked together to form a ...
Slide 1
... • Their experiment required a cell-free system • Nirenberg chose E. Coli bacteria cells ...
... • Their experiment required a cell-free system • Nirenberg chose E. Coli bacteria cells ...
DNAAlias - UBC Let`s Talk Science
... The kids write down their own name. On the worksheet is a code giving the nucleotides for each letter in the alphabet. The kids figure out the 3 letter code for each letter in their name. Each of the four nucleotides is represented by a different colour. The kids put a white bead on the string ...
... The kids write down their own name. On the worksheet is a code giving the nucleotides for each letter in the alphabet. The kids figure out the 3 letter code for each letter in their name. Each of the four nucleotides is represented by a different colour. The kids put a white bead on the string ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... If mutations occur in the gametes (sperm or ovum), then they can be transferred to offspring Gene mutation: Point mutations: 2 types of mutations: 1) Base substitution: a) could make no difference at all, why? GGC Æ GGU in mRNA; still codes for glycine b) could be: c) could be detrimental (useless p ...
... If mutations occur in the gametes (sperm or ovum), then they can be transferred to offspring Gene mutation: Point mutations: 2 types of mutations: 1) Base substitution: a) could make no difference at all, why? GGC Æ GGU in mRNA; still codes for glycine b) could be: c) could be detrimental (useless p ...
Protein Nomenclature
... Amino acids and peptides Properties of Amino Acids • Capacity to polymerize • Novel acid-base properties • varied structure and chemical functionality • Chirality ...
... Amino acids and peptides Properties of Amino Acids • Capacity to polymerize • Novel acid-base properties • varied structure and chemical functionality • Chirality ...
DNA Connection
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
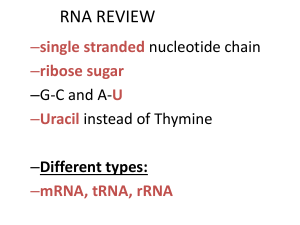
... 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: acts as an interpreter molecule, translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences 11. Ribosomal RNA: help build proteins; they function at the sites of translation 12. Codons: t ...
... 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: acts as an interpreter molecule, translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences 11. Ribosomal RNA: help build proteins; they function at the sites of translation 12. Codons: t ...
Additional Lab Exercise: Amino Acid Sequence in
... Background Information Enzymes are proteins. In order to carry on their very specific functions, the sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, m ...
... Background Information Enzymes are proteins. In order to carry on their very specific functions, the sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, m ...
3.12 Translation
... Table of CODONS From your three letter codon, you can use this table to figure out what amino acid it is. ...
... Table of CODONS From your three letter codon, you can use this table to figure out what amino acid it is. ...
Protein Synthesis
... Information is stored in DNA in three base units, called codons. • We can make 64 different codons, but we only use 20 amino acids. • One codon means “start here” • Three codons are “stop” codons. • More than one codon can be used for a particular amino acid. ...
... Information is stored in DNA in three base units, called codons. • We can make 64 different codons, but we only use 20 amino acids. • One codon means “start here” • Three codons are “stop” codons. • More than one codon can be used for a particular amino acid. ...
DNA RNA DNA RNA Short Answer 1. How many codons code for
... 6. __ Anticodons neutralize codons so they cannot function properly. 7. __ Only one codon indicates the start of a protein. 8. __ When multiple codons code for the same amino acid, the first two bases of the codon are ususally the same. 9. __ The STOP codons are UAA, UGA, and UAG. 10. __ The AUG cod ...
... 6. __ Anticodons neutralize codons so they cannot function properly. 7. __ Only one codon indicates the start of a protein. 8. __ When multiple codons code for the same amino acid, the first two bases of the codon are ususally the same. 9. __ The STOP codons are UAA, UGA, and UAG. 10. __ The AUG cod ...
Do Now: Wednesday, March 19
... for the protein that is needed is unwound Step 2: RNA polymerase (enzyme) uses the DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA ...
... for the protein that is needed is unwound Step 2: RNA polymerase (enzyme) uses the DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA ...
Biology Summary Sheet
... DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Bases always pair together in the same way; A with T, and G with C. This is known as complementary base pairing. The bases make up the genetic code. DNA contains the genetic ...
... DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Bases always pair together in the same way; A with T, and G with C. This is known as complementary base pairing. The bases make up the genetic code. DNA contains the genetic ...
Protein Synthesis Practice
... Given the following mRNA strands, draw a circle around the START CODONS and the STOP CODONS. Number the 3-base pair codons in between. A whole protein need to have a series of codons between a start (AUG) and a stop codon (UGA, UAG or UAA). Which strands will build whole proteins? Example: This str ...
... Given the following mRNA strands, draw a circle around the START CODONS and the STOP CODONS. Number the 3-base pair codons in between. A whole protein need to have a series of codons between a start (AUG) and a stop codon (UGA, UAG or UAA). Which strands will build whole proteins? Example: This str ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.