Protein Synthesis
... Traits are determined by proteins (often enzymes) *Protein – 1 or more polypeptide chains *Polypeptide – chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds ...
... Traits are determined by proteins (often enzymes) *Protein – 1 or more polypeptide chains *Polypeptide – chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced together in forming messenger RNA. For Questions 8–16, match the term with its definition. ...
... DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand begins is called the intron. 7. Exons are spliced together in forming messenger RNA. For Questions 8–16, match the term with its definition. ...
(RNA and Protein Synthesis) Section 11.4 Questions
... 24. How many nitrogenous bases make up a codon? __________ 25. What does a codon code for? _________________________ 26. Several codons make what? _________________________ 27. Which amino acid does the codon UUU code for? _________________________ 28. How many different triplet codes can be made wi ...
... 24. How many nitrogenous bases make up a codon? __________ 25. What does a codon code for? _________________________ 26. Several codons make what? _________________________ 27. Which amino acid does the codon UUU code for? _________________________ 28. How many different triplet codes can be made wi ...
Mutations
... 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. A baby can be born with an extra chromosome or missing one chromosome. -Example: Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome ...
... 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. A baby can be born with an extra chromosome or missing one chromosome. -Example: Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome ...
Translation Notes
... bond between the previous amino acid and its tRNA. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon. The first tRNA exits the ribosome, and another codon is exposed. ...
... bond between the previous amino acid and its tRNA. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon. The first tRNA exits the ribosome, and another codon is exposed. ...
Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab [1/13/2016]
... your body. 4. What traits can proteins determine? 5. What does DNA stand for? 6. What does RNA stand for? 7. Summarize how a protein is made? ...
... your body. 4. What traits can proteins determine? 5. What does DNA stand for? 6. What does RNA stand for? 7. Summarize how a protein is made? ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... • Codon = three nucleotides on mRNA • One codon specifies one amino acid • Some codons are redundant (code for the same amino acid) • The genetic code is universal to all organisms ...
... • Codon = three nucleotides on mRNA • One codon specifies one amino acid • Some codons are redundant (code for the same amino acid) • The genetic code is universal to all organisms ...
What meaning(s) do these two photos represent? (Hint* dna,rna
... The same mRNA may be used hundreds of times during translation by many ribosomes before it is degraded (broken down) by the cell. ...
... The same mRNA may be used hundreds of times during translation by many ribosomes before it is degraded (broken down) by the cell. ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... bond that links adjacent amino acids in a protein. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Given the mRNA below, what protein would result if it was successfully translated by a ribosome? a) Number of amino acids ...
... bond that links adjacent amino acids in a protein. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Given the mRNA below, what protein would result if it was successfully translated by a ribosome? a) Number of amino acids ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... bond that links adjacent amino acids in a protein. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Given the mRNA below, what protein would result if it was successfully translated by a ribosome? a) Number of amino acids ...
... bond that links adjacent amino acids in a protein. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1) Given the mRNA below, what protein would result if it was successfully translated by a ribosome? a) Number of amino acids ...
Section 5-4
... • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins – A gene is a section of DNA – DNA is made of four nitrogen bases • Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) • Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) ...
... • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins – A gene is a section of DNA – DNA is made of four nitrogen bases • Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) • Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) ...
Genes - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... Overlaping: AUGGUGCACCUGACUC Comma: ...
... Overlaping: AUGGUGCACCUGACUC Comma: ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... What would the mRNA strand be? AUG GCU AAC UGA What would the tRNA sequence be? UAC CGA UUG ACU What would the amino acid sequence be? (base it on the mRNA strand!) methionine, alanine, asparagine, “stop” ...
... What would the mRNA strand be? AUG GCU AAC UGA What would the tRNA sequence be? UAC CGA UUG ACU What would the amino acid sequence be? (base it on the mRNA strand!) methionine, alanine, asparagine, “stop” ...
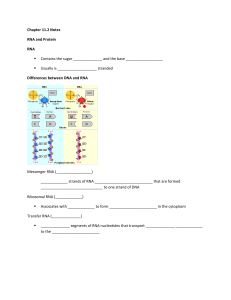
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... Messenger RNA (_________________) _____________ strands of RNA ____________________________ that are formed ______________________________ to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (_____________) ...
... Messenger RNA (_________________) _____________ strands of RNA ____________________________ that are formed ______________________________ to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (_____________) ...
Make an Animal Activity: Cat
... Find out what your animal looks like using only the DNA from your animal's chromosomes. Below is the key that is needed to determine what traits correspond to each amino acid sequence. 1. The DNA for your animal is coded on one side of the helix. Transcribe the DNA strand into mRNA. Don't forget the ...
... Find out what your animal looks like using only the DNA from your animal's chromosomes. Below is the key that is needed to determine what traits correspond to each amino acid sequence. 1. The DNA for your animal is coded on one side of the helix. Transcribe the DNA strand into mRNA. Don't forget the ...
Homework Assignment #7
... the top strand are labeled. Use the lines to illustrate a eukaryotic gene that has two introns. Include the following in your drawing: promoter, transcription start site, all exons, both introns, the 5’ and 3’ splice site of the introns, a reasonable location for the ATG start codon and a TAA stop c ...
... the top strand are labeled. Use the lines to illustrate a eukaryotic gene that has two introns. Include the following in your drawing: promoter, transcription start site, all exons, both introns, the 5’ and 3’ splice site of the introns, a reasonable location for the ATG start codon and a TAA stop c ...
CHAPTER 39: The Genetic Code
... Three nucleotides encode an amino acid. •DNA – only four bases (A,T,G,C) •Must code for 20 amino acids •Two-base code: 42 = 16 combinations •Four-base code: 44 = 256 combinations •Three-base code: 43 = 64 combinations ...
... Three nucleotides encode an amino acid. •DNA – only four bases (A,T,G,C) •Must code for 20 amino acids •Two-base code: 42 = 16 combinations •Four-base code: 44 = 256 combinations •Three-base code: 43 = 64 combinations ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of ...
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of ...
BUILDING THE LIFE MOLECULES: DNA AND RNA The
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
Dr Ishtiaq genetic code
... Examples: 5′- A UG- 3′ codes for methionine 5′- UCU- 3′ codes for serine 5′ - CCA- 3′ codes for proline Termination (stop or nonsense) codons: Three of the 64 codons; UAA, UAG, UGA do not code for any amino acid. They are termination codes which when one of them appear in mRNA sequence, it indicate ...
... Examples: 5′- A UG- 3′ codes for methionine 5′- UCU- 3′ codes for serine 5′ - CCA- 3′ codes for proline Termination (stop or nonsense) codons: Three of the 64 codons; UAA, UAG, UGA do not code for any amino acid. They are termination codes which when one of them appear in mRNA sequence, it indicate ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... Making a Protein—Transcription • First Step: Copying of genetic information from DNA to RNA called Transcription Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. ...
... Making a Protein—Transcription • First Step: Copying of genetic information from DNA to RNA called Transcription Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis Life Science RNA – Ribonucleic Acid
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of expo ...
... Each codon specifies a particular amino acid There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 different combinations of A, U, G, and C that a codon could have ( 4x4x4) There are three “stop” codons acting as a “period” in a sentence The “sentence” is that strip of mRNA produced by the section of expo ...
RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The process of producing RNA molecules by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA Requires the enzyme RNA polymerase • Binds to and separates the DNA strands • Uses one strand of DNA as a template to form RNA • Binds to regions of DNA known as promoter ...
... The process of producing RNA molecules by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA Requires the enzyme RNA polymerase • Binds to and separates the DNA strands • Uses one strand of DNA as a template to form RNA • Binds to regions of DNA known as promoter ...
10-Genes
... D. proteins assume a specific three dimensional shape to become functional 3. Transcription and DNA replication are similar in all the following ways, EXCEPT; A. The new strand is polymerized in the 5-to-3 direction. B. During synthesis, nucleotide triphosphates are hydrolyzed to release PPi (pyro ...
... D. proteins assume a specific three dimensional shape to become functional 3. Transcription and DNA replication are similar in all the following ways, EXCEPT; A. The new strand is polymerized in the 5-to-3 direction. B. During synthesis, nucleotide triphosphates are hydrolyzed to release PPi (pyro ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.



![Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab [1/13/2016]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010042148_1-49212ed4f857a63328959930297729c5-300x300.png)