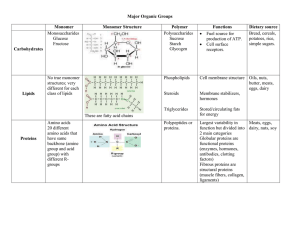
Reading the Blueprint of Life Chromosome DNA Gene Transcription
... Let’s Read A Gene and Transcribe a mRNA 5’TTATGGGCTCGAAGTAGGG ...
... Let’s Read A Gene and Transcribe a mRNA 5’TTATGGGCTCGAAGTAGGG ...
Amino Acid Sidechains have Different Chemical Characteristics
... Amino Acid Sidechains have Different Chemical Characteristics There are 20 amino acids that are the building blocks of all protein structures within our cells. Each amino acid has same backbone (NH2CHR-COOH). It is the R group that makes the amino acids different from one another. 1. Organize the 19 ...
... Amino Acid Sidechains have Different Chemical Characteristics There are 20 amino acids that are the building blocks of all protein structures within our cells. Each amino acid has same backbone (NH2CHR-COOH). It is the R group that makes the amino acids different from one another. 1. Organize the 19 ...
Translation
... • tRNA (translator molecule) – Anticodon of tRNA attracts a specific amino acid – tRNA matches the codon in the mRNA – Part of the tRNA binds an amino acid and the other end has three nucleotides, anticodon that forms a base pair with the codon in the mRNA) – Amino acids of neighboring tRNA’s link t ...
... • tRNA (translator molecule) – Anticodon of tRNA attracts a specific amino acid – tRNA matches the codon in the mRNA – Part of the tRNA binds an amino acid and the other end has three nucleotides, anticodon that forms a base pair with the codon in the mRNA) – Amino acids of neighboring tRNA’s link t ...
A - Alanine (Ala)
... S - Serine (Ser) T - Threonine (Thr) V - Valine (Val) W - Tryptophan (Trp) Y - Tyrosine (Tyr) ...
... S - Serine (Ser) T - Threonine (Thr) V - Valine (Val) W - Tryptophan (Trp) Y - Tyrosine (Tyr) ...
Gene Expression
... sequence of a genome, as the “blueprint” of a cell, organism or species. Sequence the steps of how DNA’s code is transcribed into RNA through the process of transcription. Sequence the steps of how proteins are made from the mRNA transcript through the process of translation. Predict the location wh ...
... sequence of a genome, as the “blueprint” of a cell, organism or species. Sequence the steps of how DNA’s code is transcribed into RNA through the process of transcription. Sequence the steps of how proteins are made from the mRNA transcript through the process of translation. Predict the location wh ...
doc
... on from one generation of cells to the next. Made of DNA and protein Codon — a set of three mRNA nucleotides that codes for an amino acid or signals the end of an amino acid sequence DNA — deoxyribonucleic acid. A chain of nucleic acid molecules that contains your genetic information DNA fingerprint ...
... on from one generation of cells to the next. Made of DNA and protein Codon — a set of three mRNA nucleotides that codes for an amino acid or signals the end of an amino acid sequence DNA — deoxyribonucleic acid. A chain of nucleic acid molecules that contains your genetic information DNA fingerprint ...
E1-3 NotesProtein Synth
... 2. Sequence of amino acids determines the proteins shape. 3. The shape determines how protein will bind with other molecules B. Genetic Code 1. mRNA’s sequence of nucleotides correlates to specific amino acids. 2. Genetic Code – correlation B/T nucleotides and amino acids 3. Codon – a. 3 mRNA nucleo ...
... 2. Sequence of amino acids determines the proteins shape. 3. The shape determines how protein will bind with other molecules B. Genetic Code 1. mRNA’s sequence of nucleotides correlates to specific amino acids. 2. Genetic Code – correlation B/T nucleotides and amino acids 3. Codon – a. 3 mRNA nucleo ...
powerpoint
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
From DNA to Protein (11.2)
... code for one Amino Acid • Each group is known as a codon • Ex: The codon GCU results in the amino acid Alanine ...
... code for one Amino Acid • Each group is known as a codon • Ex: The codon GCU results in the amino acid Alanine ...
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
Chapter 8 DNA: the universal molecule of life All living things share
... • Not all the DNA segments in a gene translate to protein –introns are cut from the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus. Exons - sections of gene that do code for proteins are spliced back together. • This post translation modification includes the intron cutting, addition of a methylated cap and a po ...
... • Not all the DNA segments in a gene translate to protein –introns are cut from the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus. Exons - sections of gene that do code for proteins are spliced back together. • This post translation modification includes the intron cutting, addition of a methylated cap and a po ...
8.5 Translation - Clinton Public Schools
... – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. ...
... – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. ...
DNA to Proteins
... cytoplasm. It is fed through a ribosome The bases on the mRNA strand are matched by another type of RNA called transfer RNA or tRNA. • Every group of 3 bases on mRNA codes for 1 amino acid ...
... cytoplasm. It is fed through a ribosome The bases on the mRNA strand are matched by another type of RNA called transfer RNA or tRNA. • Every group of 3 bases on mRNA codes for 1 amino acid ...
Transcription and Translation
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
Sickle Cell Mutation WS - Lincoln Park High School
... Sickle Cell Allele Mutation WS Sickle cell disease is a disorder that gets its name from the sickle shape of red blood cells (RBCs) which normally have a round, disk-like shape. The sickle-shaped RBCs are caused by a faulty hemoglobin resulting from a point mutation in which just one nucleotide base ...
... Sickle Cell Allele Mutation WS Sickle cell disease is a disorder that gets its name from the sickle shape of red blood cells (RBCs) which normally have a round, disk-like shape. The sickle-shaped RBCs are caused by a faulty hemoglobin resulting from a point mutation in which just one nucleotide base ...
Translation
... Transcription occurs in the ________, creating a single stranded ________. This _______ contains the Nitrogen base ______ instead of __________. Word Bank: Uracil, DNA, mRNA, Adenine, Guanine, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Thymine ...
... Transcription occurs in the ________, creating a single stranded ________. This _______ contains the Nitrogen base ______ instead of __________. Word Bank: Uracil, DNA, mRNA, Adenine, Guanine, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Thymine ...
Protein Synthesis: Like a Banana Split
... 3. Examine the mRNA sequences for each amino acid recorded in Data Table 2. What pattern do you see?_______________________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. Examine the mRNA sequences for each amino acid recorded in Data Table 2. What pattern do you see?_______________________________________________________________________ ...
From DNA to Protein
... (found in castor-oil plant used in plastics, paints, cosmetics) is toxic because it inactivates ribosomes, the organelles which assemble amino acids into proteins, critical to life processes ...
... (found in castor-oil plant used in plastics, paints, cosmetics) is toxic because it inactivates ribosomes, the organelles which assemble amino acids into proteins, critical to life processes ...
Simulating Protein Synthesis
... Post Lab Questions: List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
... Post Lab Questions: List at least 3 differences between transcription and translation? (3) Transcription ...
Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dnalc.org/view/15510-TranscriptionDNA-c ...
... In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dnalc.org/view/15510-TranscriptionDNA-c ...
Translation Notes 2015 - Liberty Union High School District
... ribosomes, which are all needed for protein synthesis. ...
... ribosomes, which are all needed for protein synthesis. ...
protein synthesis (simplified)
... If the protein is the wrong shape it will not work properly (it may work differently) So if the sequence in the DNA is wrong it may result in a genetic disease ...
... If the protein is the wrong shape it will not work properly (it may work differently) So if the sequence in the DNA is wrong it may result in a genetic disease ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.