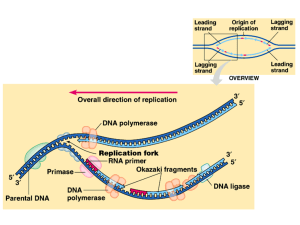
How does DNA copy itself?
... – Think of DNA as the entire cookbook, and RNA like a recipe out of that book ...
... – Think of DNA as the entire cookbook, and RNA like a recipe out of that book ...
DNA Transcription – A Simulation using Corticon
... If the codon at the current position of the ribosome is other than a STOP then the amino acid attached to the corresponding tRNA will be attached to the growing protein). This process continues with the ribosome moving up the mRNA strand (in units of three) until a STOP codon is encountered Once a S ...
... If the codon at the current position of the ribosome is other than a STOP then the amino acid attached to the corresponding tRNA will be attached to the growing protein). This process continues with the ribosome moving up the mRNA strand (in units of three) until a STOP codon is encountered Once a S ...
Name:
... Transcription directions: Transcribe the following DNA sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA.) It’s easiest to break the DNA sequence into triplets, and then find the mRNA codons from that point: i.e. AGA TTC CCC DNA triplets transcription UCU AAG GGG ...
... Transcription directions: Transcribe the following DNA sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA.) It’s easiest to break the DNA sequence into triplets, and then find the mRNA codons from that point: i.e. AGA TTC CCC DNA triplets transcription UCU AAG GGG ...
Biomolecules Review
... 14. To which of the four classes of amino acid does cysteine belong? 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? ala ...
... 14. To which of the four classes of amino acid does cysteine belong? 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? ala ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
Condition: Maple syrup urine disease
... MSUD results from deficiency of activity of branched chain amino acid dehydrogenase, leading to accumulation of leucine, isoleucine, and valine in infancy after the first feeding. Left untreated, severe neurological impairment ensues, leading to coma and death. Initial diagnosis is based on finding ...
... MSUD results from deficiency of activity of branched chain amino acid dehydrogenase, leading to accumulation of leucine, isoleucine, and valine in infancy after the first feeding. Left untreated, severe neurological impairment ensues, leading to coma and death. Initial diagnosis is based on finding ...
organic compounds outline
... ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copyin ...
... ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copyin ...
Mutations
... Somatic-Cell Mutations ◦ Take place in an organism’s body cells Can affect organism (certain types of cancer) Cannot be inherited ...
... Somatic-Cell Mutations ◦ Take place in an organism’s body cells Can affect organism (certain types of cancer) Cannot be inherited ...
bio_ch08-5_transcript redo
... You might consider it to be odd to describe the genetic as a punctuation of stop and start codes. The Latin word puctum means “point” and is derived form an older form meaning “to pierce or puncture.” Punctuation, in a general sense, signifies an interruption. The word punctuate can also be used to ...
... You might consider it to be odd to describe the genetic as a punctuation of stop and start codes. The Latin word puctum means “point” and is derived form an older form meaning “to pierce or puncture.” Punctuation, in a general sense, signifies an interruption. The word punctuate can also be used to ...
Transcription & Translation PowerPoint
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
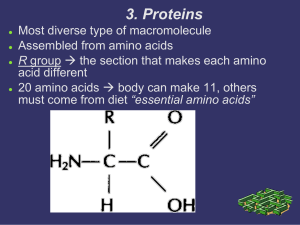
3. Proteins
... Exposing a protein to excess heat, radiation or a change in pH will alter its shape • Denaturation • Occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing an often permanent change in shape • ex. X-ray radiation or nuclear radioactivity can disrupt protein structure and can lead to cancer or gen ...
... Exposing a protein to excess heat, radiation or a change in pH will alter its shape • Denaturation • Occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing an often permanent change in shape • ex. X-ray radiation or nuclear radioactivity can disrupt protein structure and can lead to cancer or gen ...
anth-260-midterm-review-sheet
... • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
... • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
Chapter 3 Section 4 Protein Synthesis
... • Each type or protein has a specific job based on its shape. ...
... • Each type or protein has a specific job based on its shape. ...
TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION: From DNA to Protein
... amino acids to make a Protein • Codon = the nitrogenous bases of 3 adjacent nucleotides in mRNA that code for – Start Signal (starts the protein making process) – 1 of 20 different amino acids (parts of a protein) – Stop Signal (stops the protein making process) ...
... amino acids to make a Protein • Codon = the nitrogenous bases of 3 adjacent nucleotides in mRNA that code for – Start Signal (starts the protein making process) – 1 of 20 different amino acids (parts of a protein) – Stop Signal (stops the protein making process) ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... across multiple chromosomes • Prokaryotes have fewer genes all located on one chromosome ...
... across multiple chromosomes • Prokaryotes have fewer genes all located on one chromosome ...
Protein Synthesis: Translation
... mRNA, tRNAs with their anticodons (matching the mRNA codons) carry the proper amino acids to the ribosomes. ...
... mRNA, tRNAs with their anticodons (matching the mRNA codons) carry the proper amino acids to the ribosomes. ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of a SNORK
... 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? ____________________ 4) What is the side that is NOT copied called? _______________________________ 5) What different nitrogen base had to be used to make mRNA? ____ ...
... 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? ____________________ 4) What is the side that is NOT copied called? _______________________________ 5) What different nitrogen base had to be used to make mRNA? ____ ...
BioH From DNA to proteins
... • Promoter sequence on mRNA - signals “start” for transcribing DNA sequence into RNA sequence • ONE strand only – forming juvenile RNA • Uracil used instead of Thymine • Use Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine (same as DNA) ...
... • Promoter sequence on mRNA - signals “start” for transcribing DNA sequence into RNA sequence • ONE strand only – forming juvenile RNA • Uracil used instead of Thymine • Use Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine (same as DNA) ...
DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis with Answers
... 3. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below ...
... 3. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below ...
How does DNA control cell activities?
... pairs with the nucleotides on the DNA strand mRNA strand breaks away and DNA strand rejoins mRNA strand leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm through nuclear pores ...
... pairs with the nucleotides on the DNA strand mRNA strand breaks away and DNA strand rejoins mRNA strand leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm through nuclear pores ...
DNA
... Before the mRNA can go to the ribosome, it needs to be spliced. – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
... Before the mRNA can go to the ribosome, it needs to be spliced. – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
Lecture #7 Date ______
... 1) 5’ cap: modified guanine; protection; recognition site for ribosomes 2) 3’ tail: poly(A) tail (adenine); protection; recognition; transport ...
... 1) 5’ cap: modified guanine; protection; recognition site for ribosomes 2) 3’ tail: poly(A) tail (adenine); protection; recognition; transport ...
RNA
... • Each codon along mRNA specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be incorporated • AUG for methionin and ...
... • Each codon along mRNA specifies which one of the 20 amino acids will be incorporated • AUG for methionin and ...
Protein Synthesis
... codons for mRNA and also tRNA anti-codons. The code is degenerate which means there are more codes possible than required and therefore there are often three or four codes for a single amino acid. There are also three triplet codes which signal to stop transcription and one which signals the start o ...
... codons for mRNA and also tRNA anti-codons. The code is degenerate which means there are more codes possible than required and therefore there are often three or four codes for a single amino acid. There are also three triplet codes which signal to stop transcription and one which signals the start o ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.