biology quiz chapter 12
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three types of RNA? 2. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA 3. What is a Codon? 4. If there are 64 possible codons and only 20 amino acids what has to be true? 5. Why does mRNA have to carry DNA’s message to t ...
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three types of RNA? 2. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA 3. What is a Codon? 4. If there are 64 possible codons and only 20 amino acids what has to be true? 5. Why does mRNA have to carry DNA’s message to t ...
Biology - secondary
... • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
... • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations - Mrs. Gracie Gonzalez Biology Class
... Amino Acid Sequence = Protein (use mRNA codon and the chart below to find the amino acid) ...
... Amino Acid Sequence = Protein (use mRNA codon and the chart below to find the amino acid) ...
Translation March 32, 2009000 *10-3
... DNA is the genetic code. What part of DNA is the genetic code? Choose an answer and then explain why the other choices are wrong. A. ...
... DNA is the genetic code. What part of DNA is the genetic code? Choose an answer and then explain why the other choices are wrong. A. ...
Genes, Protein Synthesis, and Mutations
... A. mutation = any permanent change in the code on the DNA (this changes the code for the gene on a chromosome). 1. Often these errors occur in the code when a molecule of DNA makes a copy of itself. a. There are 3 ways mutations can occur: 1. deletion = occurs when a base pair is left out. 2. insert ...
... A. mutation = any permanent change in the code on the DNA (this changes the code for the gene on a chromosome). 1. Often these errors occur in the code when a molecule of DNA makes a copy of itself. a. There are 3 ways mutations can occur: 1. deletion = occurs when a base pair is left out. 2. insert ...
Les 6b RNA Transcription and Translation
... http://www.biologycorner.com/bio4/notes/gene-expression.php ...
... http://www.biologycorner.com/bio4/notes/gene-expression.php ...
PDF file - the Houpt Lab
... Put simple artificial RNA into an in vitro translation system, and see what peptides come out. ...
... Put simple artificial RNA into an in vitro translation system, and see what peptides come out. ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... 4. Name three types of RNA (one is from DNA replication, two from protein synthesis) described and explain the function of each. 5. How many different DNA triplets are possible? 6. The DNA triplet “CGA” is transcribed into which RNA codon? a) GUT (b) GUC (c) GCU (d) AUG 7. Which enzyme “reads” the m ...
... 4. Name three types of RNA (one is from DNA replication, two from protein synthesis) described and explain the function of each. 5. How many different DNA triplets are possible? 6. The DNA triplet “CGA” is transcribed into which RNA codon? a) GUT (b) GUC (c) GCU (d) AUG 7. Which enzyme “reads” the m ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ____________ a) mRNA b) tRNA arrives at the ___________a) ribosome b) nucleus, where complem ...
... __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ____________ a) mRNA b) tRNA arrives at the ___________a) ribosome b) nucleus, where complem ...
TRANSLATION
... The small subunit of the ribosome recognizes the 5' cap on the mRNA transcript and binds to the RNA. The ribosome will position itself at AUG (the first codon read for every protein) ...
... The small subunit of the ribosome recognizes the 5' cap on the mRNA transcript and binds to the RNA. The ribosome will position itself at AUG (the first codon read for every protein) ...
5.4 Translation
... The small subunit of the ribosome recognizes the 5' cap on the mRNA transcript and binds to the RNA. The ribosome will position itself at AUG (the first codon read for every protein) ...
... The small subunit of the ribosome recognizes the 5' cap on the mRNA transcript and binds to the RNA. The ribosome will position itself at AUG (the first codon read for every protein) ...
Gene Action
... Overview of Protein Synthesis … the short version DNA contained in genes provides instructions for making protein Information from a specific section of DNA is first transcribed to produce a specific molecule of RNA RNA attaches to a ribosome where the information is translated into a corresponding ...
... Overview of Protein Synthesis … the short version DNA contained in genes provides instructions for making protein Information from a specific section of DNA is first transcribed to produce a specific molecule of RNA RNA attaches to a ribosome where the information is translated into a corresponding ...
Transcrip_Translation
... We Shall Start the Process of Transcribing the DNA (Genetic Blue Print) 1. Open up and Read the DNA strand 2. Make a copy of the DNA sequence in RNA that we will call Messenger RNA (mRNA) 3. Send the copy out of the Nucleus to be read off of, so that proteins can be made ...
... We Shall Start the Process of Transcribing the DNA (Genetic Blue Print) 1. Open up and Read the DNA strand 2. Make a copy of the DNA sequence in RNA that we will call Messenger RNA (mRNA) 3. Send the copy out of the Nucleus to be read off of, so that proteins can be made ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
DNA Transcription - Kayla snyder`s biology world
... following three codons: _AUG__ _UAA__ _AUU_. The order of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the amino acids in a protein. There are _64_ possible codons but only _20_ Possible Amino Acids Stop codons = _UAA UAG UGA Start codon = _AUG (Methionine or Met)_ ...
... following three codons: _AUG__ _UAA__ _AUU_. The order of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the amino acids in a protein. There are _64_ possible codons but only _20_ Possible Amino Acids Stop codons = _UAA UAG UGA Start codon = _AUG (Methionine or Met)_ ...
Activating Strategy AP Lesson #51 What is the code? What is
... What is the code? • Code for ALL life! – strongest support for a common origin for all life ...
... What is the code? • Code for ALL life! – strongest support for a common origin for all life ...
DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
... have ________________(amt.) of rings and consist of the bases of _______________ and ___________________. 9. Singular ringed bases pair with double-ringed bases when forming DNA, what are the 2 combination of base pairs? 10. What is the bond between the sugars and the phosphates and the nitrogen bas ...
... have ________________(amt.) of rings and consist of the bases of _______________ and ___________________. 9. Singular ringed bases pair with double-ringed bases when forming DNA, what are the 2 combination of base pairs? 10. What is the bond between the sugars and the phosphates and the nitrogen bas ...
Protein Synthesis
... and initiation factors. Met attached to tRNA is brought to the 30S subunit. At the same time the mRNA is attached to the ribosome subunit at the start codon position The 50S subunit is combined to the 30S subunit to form the ribosome and the initiation complex. Eukaryotic initiation - substitute 30S ...
... and initiation factors. Met attached to tRNA is brought to the 30S subunit. At the same time the mRNA is attached to the ribosome subunit at the start codon position The 50S subunit is combined to the 30S subunit to form the ribosome and the initiation complex. Eukaryotic initiation - substitute 30S ...
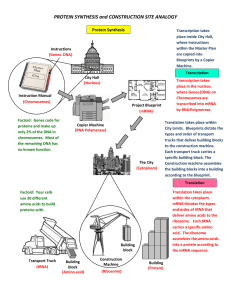
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truc ...
... Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truc ...
8.5 Translation TEKS 4B, 6C
... – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. ...
... – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation
... 5. Look at the “Universal Genetic Code Chart.” Which codon (set of 3 bases) in RNA codes for the “Met” amino acid? Write the correct bases below. ___ ___ ___ 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green wind ...
... 5. Look at the “Universal Genetic Code Chart.” Which codon (set of 3 bases) in RNA codes for the “Met” amino acid? Write the correct bases below. ___ ___ ___ 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green wind ...
genetics - Yazscience10
... • Viruses attack our cells by substituting their own genes into the cellular apparatus of human cells • Instead of making human protein, our infected cells make viral protein • Because of similarities in genetics a virus can spread from a bird to a pig to a human ...
... • Viruses attack our cells by substituting their own genes into the cellular apparatus of human cells • Instead of making human protein, our infected cells make viral protein • Because of similarities in genetics a virus can spread from a bird to a pig to a human ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.