RNA
... • Genotype = genetic constitution • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
... • Genotype = genetic constitution • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
Protein Synthesis
... DNA carries the genetic code (genes) The code is a triplet code – 3 nucleotides (grouped together as a codon) code for one amino acid. That code is translated into proteins (each gene codes for one protein) Each protein results in one trait (or is responsible for one part of one trait) Proteins resu ...
... DNA carries the genetic code (genes) The code is a triplet code – 3 nucleotides (grouped together as a codon) code for one amino acid. That code is translated into proteins (each gene codes for one protein) Each protein results in one trait (or is responsible for one part of one trait) Proteins resu ...
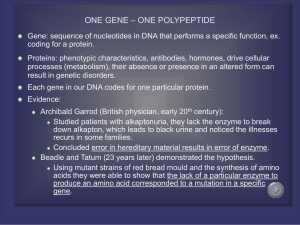
ONE GENE – ONE POLYPEPTIDE
... GENETIC CODE There are 20 amino acids found in proteins, only 4 bases in mRNA (U C A G) Codons: sequences of three bases used to code for an a.a. 43=64 possible codons (some amino acids have more than one codon) Ex. UUU UUC, UCU, UCC all code for phenylalanine (a.a.) This redundancy helps to reduce ...
... GENETIC CODE There are 20 amino acids found in proteins, only 4 bases in mRNA (U C A G) Codons: sequences of three bases used to code for an a.a. 43=64 possible codons (some amino acids have more than one codon) Ex. UUU UUC, UCU, UCC all code for phenylalanine (a.a.) This redundancy helps to reduce ...
Translation
... Genetic code • Each codon codes for a single amino acid the code is “nonoverlapping”. • The same amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon the genetic code is ...
... Genetic code • Each codon codes for a single amino acid the code is “nonoverlapping”. • The same amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon the genetic code is ...
242140_Fx_DNA-RNA
... Go back to Mr. Mason’s website and click on the link labeled “Genetics – Translation” 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there ...
... Go back to Mr. Mason’s website and click on the link labeled “Genetics – Translation” 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there ...
Protein Synthesis (Gene Expression) Notes
... (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reacAon) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
... (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reacAon) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA red. ...
... Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA red. ...
The Genetic Code: The most fundamental concept in all biology
... The Genetic Code: The most fundamental concept in all biology. Shortly after the discovery of the structure of DNA by Watson and Crick, scientists were faced with a significant problem: How does the information encoded in DNA get translated into a protein. In 1954, our old friend Francis Crick hypot ...
... The Genetic Code: The most fundamental concept in all biology. Shortly after the discovery of the structure of DNA by Watson and Crick, scientists were faced with a significant problem: How does the information encoded in DNA get translated into a protein. In 1954, our old friend Francis Crick hypot ...
Translation (Protein Synthesis)
... • Use your mRNA sequence and determine the amino acid sequence: ...
... • Use your mRNA sequence and determine the amino acid sequence: ...
Lesson 4 Protein Synthesis.notebook
... code to the ribosome to be read tRNA (transfer RNA) - transports the amino acids needed to make the protein that is coded for rRNA (ribosomal RNA) - will order the amino acids in the proper sequence when they arrive at the ribosome. ...
... code to the ribosome to be read tRNA (transfer RNA) - transports the amino acids needed to make the protein that is coded for rRNA (ribosomal RNA) - will order the amino acids in the proper sequence when they arrive at the ribosome. ...
Biology Molecular Genetic Review
... 13. Draw a piece of mRNA 5 codons long. Draw the pieces of tRNA that would match up. ...
... 13. Draw a piece of mRNA 5 codons long. Draw the pieces of tRNA that would match up. ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... 1. What is the first step in decoding a cell's genetic information? _______________________ 2. List one way that RNA is different from DNA. ____________________________________________ 3. What is the function of mRNA? ________________________________________________________ 4. What is the function o ...
... 1. What is the first step in decoding a cell's genetic information? _______________________ 2. List one way that RNA is different from DNA. ____________________________________________ 3. What is the function of mRNA? ________________________________________________________ 4. What is the function o ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 4 of 14
... Unambiguous refers to the fact that each codon only code for one specific amino acids and no others. The idea of redundancy refers to the fact that more than one codon can code for the same amino acid since there are only 20 and many combinations of codons. ...
... Unambiguous refers to the fact that each codon only code for one specific amino acids and no others. The idea of redundancy refers to the fact that more than one codon can code for the same amino acid since there are only 20 and many combinations of codons. ...
Protein Synthesis - Doral Academy High School
... stop sign), the RNA polymerase releases the RNA and DNA ...
... stop sign), the RNA polymerase releases the RNA and DNA ...
notes
... The coding region always starts with a START codon (AUG) and terminates with a STOP codon ...
... The coding region always starts with a START codon (AUG) and terminates with a STOP codon ...
Fishy Genetics: From DNA to Protein: The Central Dogma of Biology
... different amino acids. Protein synthesis is the process of reading the DNA code and building the protein called for by the code. The molecule RNA is a key player in the process. RNA is a nucleic acid just like DNA but there are several differences. ...
... different amino acids. Protein synthesis is the process of reading the DNA code and building the protein called for by the code. The molecule RNA is a key player in the process. RNA is a nucleic acid just like DNA but there are several differences. ...
Lecture #19 - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... e.g., Ser & Leu each have 6 codons whereas Tyr & Asp have only 2 apiece •Redundant Codons Reduce Potential Deleterious Effects of Mutations Particularly in 3rd position e.g., CCC, CCU, CCG & CCA All Code for Pro Therefore, such mutations are Silent or Synonymous •Several "functionally" equivalent Am ...
... e.g., Ser & Leu each have 6 codons whereas Tyr & Asp have only 2 apiece •Redundant Codons Reduce Potential Deleterious Effects of Mutations Particularly in 3rd position e.g., CCC, CCU, CCG & CCA All Code for Pro Therefore, such mutations are Silent or Synonymous •Several "functionally" equivalent Am ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
DNA and Proteins
... occur in sequences of 3 . For example, 3 U’s in a row codes as UUU and equals the amino acid Penylalanine. The letter code is called a Codon. With the letters available – U, A, G, and C; there are 64 possible combinations. There are only 20 amino acids that occur in nature. This means that some amin ...
... occur in sequences of 3 . For example, 3 U’s in a row codes as UUU and equals the amino acid Penylalanine. The letter code is called a Codon. With the letters available – U, A, G, and C; there are 64 possible combinations. There are only 20 amino acids that occur in nature. This means that some amin ...
Protein synthesis and Enzyme test review
... 3. If a DNA strand read AAT-CAT-GAT what would the mRNA strand look like? UUA-GUA-CUA 4. What is the function of mRNA? Copy the DNA code from the nucleus (transcription) and takes it to the ribosome 5. Where is the site of protein synthesis? The ribosome Use the following mRNA sequence to answer que ...
... 3. If a DNA strand read AAT-CAT-GAT what would the mRNA strand look like? UUA-GUA-CUA 4. What is the function of mRNA? Copy the DNA code from the nucleus (transcription) and takes it to the ribosome 5. Where is the site of protein synthesis? The ribosome Use the following mRNA sequence to answer que ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.