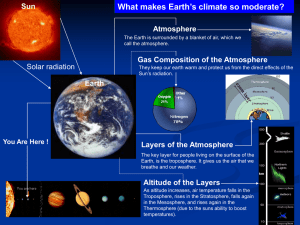
Layers of the Atmosphere
... Where weather occurs We live here. Contains almost all of the mass of the ...
... Where weather occurs We live here. Contains almost all of the mass of the ...
EarthClimate
... Troposphere, rises in the Stratosphere, falls again in the Mesosphere, and rises again in the Thermosphere (due to the suns ability to boost ...
... Troposphere, rises in the Stratosphere, falls again in the Mesosphere, and rises again in the Thermosphere (due to the suns ability to boost ...
Worksheet
... Objective – After watching a DVD, I can compare the distance of objects within the universe. ...
... Objective – After watching a DVD, I can compare the distance of objects within the universe. ...
Common Settings in Science Fiction and Fantasy
... the world. The space between the earth and the moon. Stories can be set on space stations, spaceships, space colonies, and other artificial constructs in near space. Interplanetary space—Anywhere within the solar system, the ring of planets that revolve about the sun. Beyond the orbit of the outermo ...
... the world. The space between the earth and the moon. Stories can be set on space stations, spaceships, space colonies, and other artificial constructs in near space. Interplanetary space—Anywhere within the solar system, the ring of planets that revolve about the sun. Beyond the orbit of the outermo ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun
... 22. What did Galileo observe about Venus that led him to his theory of the heliocentric system? ___________________________________________________________________________ 23. Before Galileo’s refining of the telescope, what did early astronomers think was the center of the solar system? ___________ ...
... 22. What did Galileo observe about Venus that led him to his theory of the heliocentric system? ___________________________________________________________________________ 23. Before Galileo’s refining of the telescope, what did early astronomers think was the center of the solar system? ___________ ...
History of Astronomy Scavenger Hunt
... Who am I? Stephen Hawking 24. I developed the laws of planetary motion and realized the orbits were elliptical. Who am I? Johannes Kepler 25. I showed that other galaxies existed and observed that the universe is expanding because the other galaxies are all moving away from the Milky Way. Who am I? ...
... Who am I? Stephen Hawking 24. I developed the laws of planetary motion and realized the orbits were elliptical. Who am I? Johannes Kepler 25. I showed that other galaxies existed and observed that the universe is expanding because the other galaxies are all moving away from the Milky Way. Who am I? ...
Space Review 2
... 28) What are 2 ethical, 2 political and 2 environmental issues concerning space exploration. ...
... 28) What are 2 ethical, 2 political and 2 environmental issues concerning space exploration. ...
Introduction - Jeopardy
... implodes (i.e., collapse in on itself) at the end of its lifetime, and once formed, its gravitational pull is so large that light is not emitted ...
... implodes (i.e., collapse in on itself) at the end of its lifetime, and once formed, its gravitational pull is so large that light is not emitted ...
Name: 2014/2015 Earth Space Final Exam Review Guide Directions
... Tools used to measure weather and climate (including those used for our WeatherSTEM unit) Vocabulary associated with Chapter 15 (air pressure, tropical zone, jet stream, land breeze etc.) How does altitude affect air pressure and density? What causes wind? CLIMATE STUDY PROJECT (ABOUT PHOENIX) Chapt ...
... Tools used to measure weather and climate (including those used for our WeatherSTEM unit) Vocabulary associated with Chapter 15 (air pressure, tropical zone, jet stream, land breeze etc.) How does altitude affect air pressure and density? What causes wind? CLIMATE STUDY PROJECT (ABOUT PHOENIX) Chapt ...
View as Printable PDF
... The astronomical unit is used for measuring ‘local’ distances in the solar system. It is equal to the distance from the center of the Sun to the center of the Earth (approximately 149,599,000 kms). A light year is equal to the distance light travels in 1 year (approximately 9.5 trillion kms). It is ...
... The astronomical unit is used for measuring ‘local’ distances in the solar system. It is equal to the distance from the center of the Sun to the center of the Earth (approximately 149,599,000 kms). A light year is equal to the distance light travels in 1 year (approximately 9.5 trillion kms). It is ...
What is the difference between geocentric and heliocentric theories?
... circles that also moved in bigger circles. • This belief persisted for about 1500 years. ...
... circles that also moved in bigger circles. • This belief persisted for about 1500 years. ...
Name: Date of Test: Astronomy Study Guide Words/Phrases to know
... Words/Phrases to know: gravitationally bound object (objects held together by gravity) ex Galaxy, solar system, galactic cluster 1. If the average distance between the Earth and the Sun were reduced by half, what changes would occur in the Sun’s gravitational pull on Earth and the Earth’s period of ...
... Words/Phrases to know: gravitationally bound object (objects held together by gravity) ex Galaxy, solar system, galactic cluster 1. If the average distance between the Earth and the Sun were reduced by half, what changes would occur in the Sun’s gravitational pull on Earth and the Earth’s period of ...
Space Exploration Space Travel
... • The sun produces large amounts of solar radiation • The closer to the sun, the more radiation • Too much solar radiation can kill humans • Atmospheres help block solar radiation ...
... • The sun produces large amounts of solar radiation • The closer to the sun, the more radiation • Too much solar radiation can kill humans • Atmospheres help block solar radiation ...
The Diversity and Unity of Life- A Paradox
... that, by comparison, planets and stars and galaxies seem achingly rare and lovely. If we were randomly inserted into the Cosmos, the chance that we would find ourselves on or near a planet would be less than one in a billion trillion trillion. In everyday life such odds are called compelling. Worlds ...
... that, by comparison, planets and stars and galaxies seem achingly rare and lovely. If we were randomly inserted into the Cosmos, the chance that we would find ourselves on or near a planet would be less than one in a billion trillion trillion. In everyday life such odds are called compelling. Worlds ...
What is the cosmic microwave background radiation
... Erik M. Leitch of the University of Chicago explains. The Cosmic Microwave Background radiation, or CMB for short, is a faint glow of light that fills the universe, falling on Earth from every direction with nearly uniform intensity. It is the residual heat of creation--the afterglow of the big bang ...
... Erik M. Leitch of the University of Chicago explains. The Cosmic Microwave Background radiation, or CMB for short, is a faint glow of light that fills the universe, falling on Earth from every direction with nearly uniform intensity. It is the residual heat of creation--the afterglow of the big bang ...
File - Ms. Feffer 6th and 7th Grade Science
... Our planet resides within the Milky Way Galaxy Our universe consists of systems within systems Solar System includes the Sun, planets, natural satellites of planets (moons) and minor objects, called asteroids, comets and meteoroids ...
... Our planet resides within the Milky Way Galaxy Our universe consists of systems within systems Solar System includes the Sun, planets, natural satellites of planets (moons) and minor objects, called asteroids, comets and meteoroids ...
Gravity/An invisible force that pulls a less massive object - Zoe-s-wiki
... galaxy/a system that is made up of billions of stars, star clusters and glowing clouds of dust and gas universe/all of the galaxies and the space around them; everything in space nebula/a cloud of dust and gas within a galaxy Big Bang Theory/the theroy that the universe was created by a huge explosi ...
... galaxy/a system that is made up of billions of stars, star clusters and glowing clouds of dust and gas universe/all of the galaxies and the space around them; everything in space nebula/a cloud of dust and gas within a galaxy Big Bang Theory/the theroy that the universe was created by a huge explosi ...
Ch. 20-2 Sun Study Gd. Revised
... called a(n) _______________________________ . 9. The region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter is known as the _________________. 10. Clouds of gas and dust on a comet form a fuzzy outer layer called a _______________________. 11. A spherical region of comets on the outer edg ...
... called a(n) _______________________________ . 9. The region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter is known as the _________________. 10. Clouds of gas and dust on a comet form a fuzzy outer layer called a _______________________. 11. A spherical region of comets on the outer edg ...
supplementary notes for space
... planets and other bodies in space (e.g. comets) orbit the Sun in predictable pathways – elliptical orbits… because we can use math to understand the pathways we can make accurate predictions about the position of bodies in space and about events such as solar eclipses (Moon moves between Earth and S ...
... planets and other bodies in space (e.g. comets) orbit the Sun in predictable pathways – elliptical orbits… because we can use math to understand the pathways we can make accurate predictions about the position of bodies in space and about events such as solar eclipses (Moon moves between Earth and S ...
Page 48
... 8. Meteoroid – A meteoroid is small pieces of comet that move through space. 9. Meteorite – A meteorite is a meteoroid that strikes the earth. Page 54 10. Meteor – A meteor is a small meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. 11. Asteroid Belt – the Asteroid Belt is a region between Mars and Ju ...
... 8. Meteoroid – A meteoroid is small pieces of comet that move through space. 9. Meteorite – A meteorite is a meteoroid that strikes the earth. Page 54 10. Meteor – A meteor is a small meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. 11. Asteroid Belt – the Asteroid Belt is a region between Mars and Ju ...
7.1 Space Flight to the Stars
... A light year is a unit of distance, not time! There is a reason why it is called a light-year: it is equal to the distance that a beam of light can travel through space in 1 year. It is equivalent to: -63 000 AU -9000 billion kilometres ...
... A light year is a unit of distance, not time! There is a reason why it is called a light-year: it is equal to the distance that a beam of light can travel through space in 1 year. It is equivalent to: -63 000 AU -9000 billion kilometres ...
What part of the sun can we see only during a solar eclipse?
... summer and further away in the winter. ...
... summer and further away in the winter. ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.