Homework 1 - Course Pages of Physics Department
... (d) Calculate r1/2 and f for galaxies, using nG = 3 × 10−3 Mpc−3 , rG = 10kpc, and tG = 1010 a. 3. Newtonian cosmology. Use Euclidean geometry and Newtonian gravity, so that we interpret the expansion of the universe as an actual motion of galaxies instead of an expansion of space itself. Consider t ...
... (d) Calculate r1/2 and f for galaxies, using nG = 3 × 10−3 Mpc−3 , rG = 10kpc, and tG = 1010 a. 3. Newtonian cosmology. Use Euclidean geometry and Newtonian gravity, so that we interpret the expansion of the universe as an actual motion of galaxies instead of an expansion of space itself. Consider t ...
ch. 5 study guide
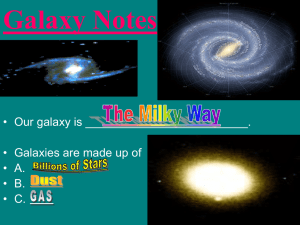
... o Know all of the following about the outer planets. (You will be asked to identify one which is not true about them.) They are the farthest from the Sun. They are all bigger than the inner planets. They all have rings. o The Sun is a medium-sized star in the universe. o Our galaxy is called the Mil ...
... o Know all of the following about the outer planets. (You will be asked to identify one which is not true about them.) They are the farthest from the Sun. They are all bigger than the inner planets. They all have rings. o The Sun is a medium-sized star in the universe. o Our galaxy is called the Mil ...
Astronomical Unit (AU)
... between the distance of the galaxies and the speed at which they are moving away from us • The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is receding (moving away) from the Earth. ...
... between the distance of the galaxies and the speed at which they are moving away from us • The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is receding (moving away) from the Earth. ...
Colorado State Science Content Standards
... 12. the ocean has a certain composition and physical characteristics (for example: currents, waves, features of the ocean floor, salinity, and tides) Solar System and the Universe 13. there are characteristics (components, composition, size) and scientific theories of origin of the solar system 14. ...
... 12. the ocean has a certain composition and physical characteristics (for example: currents, waves, features of the ocean floor, salinity, and tides) Solar System and the Universe 13. there are characteristics (components, composition, size) and scientific theories of origin of the solar system 14. ...
Document
... Only planet with adaptable sources for life. Only planet with water 71% of the surface is water ...
... Only planet with adaptable sources for life. Only planet with water 71% of the surface is water ...
Name: Astronomy Study Guide Part 1 Define Astronomy
... Day- 24 hours for Earth to rotate once about its axis Month- Length of time for the moon to revolve around earth Year- Length of time for Earth to revolve around sun 365.25 days Calendar- years, months, and days based on our celestial objects Leap Year- Feb 29 once every 4 years to make up for our 3 ...
... Day- 24 hours for Earth to rotate once about its axis Month- Length of time for the moon to revolve around earth Year- Length of time for Earth to revolve around sun 365.25 days Calendar- years, months, and days based on our celestial objects Leap Year- Feb 29 once every 4 years to make up for our 3 ...
Slide 1
... • A spectroscope works by breaking light into the wavelengths (or spectra) that make it up. Different wavelengths of light bend by different amounts, so it splits the light into its colors. Scientists can tell the elements present in a star by looking at its light through a spectroscope. Each eleme ...
... • A spectroscope works by breaking light into the wavelengths (or spectra) that make it up. Different wavelengths of light bend by different amounts, so it splits the light into its colors. Scientists can tell the elements present in a star by looking at its light through a spectroscope. Each eleme ...
Study Guide for Earth/ Space Science Test 1. Rotation – The Earth
... 5. Seasons – opposite in hemispheres and caused by the tilt toward or away from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar ...
... 5. Seasons – opposite in hemispheres and caused by the tilt toward or away from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar ...
What do we see in the night sky - Laureate International College
... Sun’s gravity exerts a powerful pulling force on the planets. This ________________ is a force of attraction that keeps the planets moving in a ___________ pattern around it. The circular pattern is called an ________. Planets ____________ around the Sun which means that they move in an orbit around ...
... Sun’s gravity exerts a powerful pulling force on the planets. This ________________ is a force of attraction that keeps the planets moving in a ___________ pattern around it. The circular pattern is called an ________. Planets ____________ around the Sun which means that they move in an orbit around ...
Monday – October 29th - East Hanover Township School District
... • Asteroids are small, rocky worlds. • Most asteroids revolve around the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. (asteroid belt) • WRITE in also known as planetoid ...
... • Asteroids are small, rocky worlds. • Most asteroids revolve around the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. (asteroid belt) • WRITE in also known as planetoid ...
Quiz
... ten to twenty billion years ago and began expanding in all directions _____ 3. galaxy moving away from Earth _____ 4. apparent shift toward shorter wavelengths of light when a luminous object moves toward the viewer ...
... ten to twenty billion years ago and began expanding in all directions _____ 3. galaxy moving away from Earth _____ 4. apparent shift toward shorter wavelengths of light when a luminous object moves toward the viewer ...
1 PS 3.9 Grade 9 Review
... Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ supernova □ nebula ...
... Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ supernova □ nebula ...
The Big Bang Theory
... Once scientists understood that the universe was expanding, they immediately realized that it would have been smaller in the past. At some point in the past, the entire universe would have been a single point. This point, later called the big bang, was the beginning of the universe as we understand ...
... Once scientists understood that the universe was expanding, they immediately realized that it would have been smaller in the past. At some point in the past, the entire universe would have been a single point. This point, later called the big bang, was the beginning of the universe as we understand ...
File
... You need a powerful telescope to see the distant galaxies. A hundred years ago, two American astronomers made an amazing discovery when they looked at galaxies through a big telescope. Henrietta Leavitt measured how far away the galaxies were. Edwin Hubble measured how fast the galaxies were mov ...
... You need a powerful telescope to see the distant galaxies. A hundred years ago, two American astronomers made an amazing discovery when they looked at galaxies through a big telescope. Henrietta Leavitt measured how far away the galaxies were. Edwin Hubble measured how fast the galaxies were mov ...
a naturally occuring object in space such as a star, planet, moon
... object in space such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid, galaxy, or a comet corona - the outermost layer of the Sun. It stretches far into space, appears very thin and faint and can only be seen from Earth during a total solar eclipse. ...
... object in space such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid, galaxy, or a comet corona - the outermost layer of the Sun. It stretches far into space, appears very thin and faint and can only be seen from Earth during a total solar eclipse. ...
Chapter 2
... 20. True/False. Evidence that all planets formed from the same swirling mass of gas and dust are based on the orbital direction of the planets around their sun. ...
... 20. True/False. Evidence that all planets formed from the same swirling mass of gas and dust are based on the orbital direction of the planets around their sun. ...
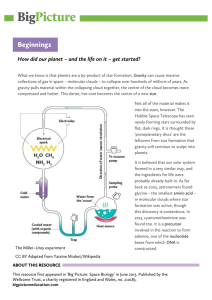
Beginnings - Big Picture
... gravity pulls material within the collapsing cloud together, the centre of the cloud becomes more compressed and hotter. This dense, hot core becomes the centre of a new star. Not all of the material makes it into the stars, however. The Hubble Space Telescope has seen newly forming stars surrounded ...
... gravity pulls material within the collapsing cloud together, the centre of the cloud becomes more compressed and hotter. This dense, hot core becomes the centre of a new star. Not all of the material makes it into the stars, however. The Hubble Space Telescope has seen newly forming stars surrounded ...
An Introduction - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... •At t=10-6 second, the temperature in the universe dropped to the threshold temperature of 1013 K, at which the photons can not produce proton and anti-proton pairs (and neutron and antineutron pairs) •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to fo ...
... •At t=10-6 second, the temperature in the universe dropped to the threshold temperature of 1013 K, at which the photons can not produce proton and anti-proton pairs (and neutron and antineutron pairs) •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to fo ...
Origins of the Universe
... • Accidentally detected faint radiation on a radio telescope in 1965 • Determined that the radiation was leftover thermal energy from the “Big Bang” ...
... • Accidentally detected faint radiation on a radio telescope in 1965 • Determined that the radiation was leftover thermal energy from the “Big Bang” ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... A. In a heliocentric system, Earth revolves around ________ B. The heliocentric system gained support when Galileo observed that ____________ goes through phases similar to our moon ...
... A. In a heliocentric system, Earth revolves around ________ B. The heliocentric system gained support when Galileo observed that ____________ goes through phases similar to our moon ...
Astronomy Topics http://www.compadre.org/astronomy/search
... http://www.compadre.org/astronomy/search/browse.cfm?browse=SS ...
... http://www.compadre.org/astronomy/search/browse.cfm?browse=SS ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.