Giant Gathering of Galaxies @ 8.5 billion Light
... mountain, about 150 km across and 4 km high, with a 56 km wide, deep summit depression. Similar in shape to volcanoes on Earth and Mars. This may have been a volcano that erupted molten ice (=water?) from within the ice cold planet. ...
... mountain, about 150 km across and 4 km high, with a 56 km wide, deep summit depression. Similar in shape to volcanoes on Earth and Mars. This may have been a volcano that erupted molten ice (=water?) from within the ice cold planet. ...
Unit 1
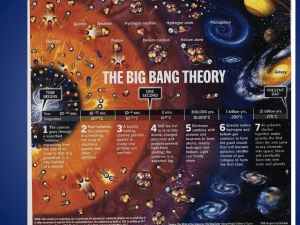
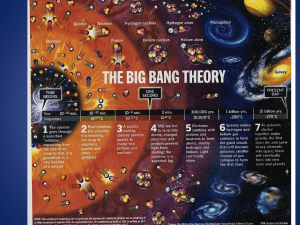
... nuclei of the simplest elements hydrogen, helium, and lithium. 300 million years later, stars and galaxies began to appear (such as our galaxy, the Milky Way). ...
... nuclei of the simplest elements hydrogen, helium, and lithium. 300 million years later, stars and galaxies began to appear (such as our galaxy, the Milky Way). ...
1)2 A light year is a) about six trillion miles. b) the distance to the star
... d) the polar front. 8)2 The “solar neutrino problem” was resolved because a) neutrinos experience time. b) long days in Sudbury allow longer collection times c) an improvement in nuclear fusion theory. 9)2 Temperature is essentially a measure of gas molecules’ a) size. b) speed. c) mass. ...
... d) the polar front. 8)2 The “solar neutrino problem” was resolved because a) neutrinos experience time. b) long days in Sudbury allow longer collection times c) an improvement in nuclear fusion theory. 9)2 Temperature is essentially a measure of gas molecules’ a) size. b) speed. c) mass. ...
Universe, Earth, and The Solar System Characteristics of Stars
... A white dwarf is only about the size of the Earth but as much as mass as the sun. A neutron star is the remains of high-mass stars. A black hole is an object with gravity so strong that not even light can escape. These are usually formed from the death of the most massive stars. ...
... A white dwarf is only about the size of the Earth but as much as mass as the sun. A neutron star is the remains of high-mass stars. A black hole is an object with gravity so strong that not even light can escape. These are usually formed from the death of the most massive stars. ...
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
SCI 2201: Concepts in Science
... By the end of the 8th grade, students should know that Nine planets of very different size, composition, and surface features move around the sun in nearly circular orbits. Some planets have a great variety of moons and even flat rings of rock and ice particles orbiting around them. Some of these ...
... By the end of the 8th grade, students should know that Nine planets of very different size, composition, and surface features move around the sun in nearly circular orbits. Some planets have a great variety of moons and even flat rings of rock and ice particles orbiting around them. Some of these ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... persisted for over 1500 years and did accurately predict the motions of the planets. • Nicholai Copernicus – Developed a new theory that placed the sun at the center of the universe (heliocentric) and had the Earth and other planets orbiting it. • Tycho Brahe – Used a mural to get precise measuremen ...
... persisted for over 1500 years and did accurately predict the motions of the planets. • Nicholai Copernicus – Developed a new theory that placed the sun at the center of the universe (heliocentric) and had the Earth and other planets orbiting it. • Tycho Brahe – Used a mural to get precise measuremen ...
The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies
... interstellar cloud of gas and dust. Most of the material becomes part of the young Sun, but some debris forms a disk. Within this disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the outer solar system, where miniature disks fo ...
... interstellar cloud of gas and dust. Most of the material becomes part of the young Sun, but some debris forms a disk. Within this disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the outer solar system, where miniature disks fo ...
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
Studying Space Chapter 26 Notes
... of planets, stars, black holes, formation of our earth Benefits to humans may include finding new sources of energy May help protect us from disasters such as collisions between Earth and Asteroids ...
... of planets, stars, black holes, formation of our earth Benefits to humans may include finding new sources of energy May help protect us from disasters such as collisions between Earth and Asteroids ...
Cells The Basic Unit of Life
... kilometres in length. These celestial wonders of ice, cock, and organic compounds travel around the Sun in elongated orbits called an _________________. In 1997, Hale-Bopp was one of the most brilliant to recently enter the inner solar system, and was visible to the unaided eye for months. However, ...
... kilometres in length. These celestial wonders of ice, cock, and organic compounds travel around the Sun in elongated orbits called an _________________. In 1997, Hale-Bopp was one of the most brilliant to recently enter the inner solar system, and was visible to the unaided eye for months. However, ...
File
... The earth rotates around in 24 hours, but revolves around the sun in 365 days. In the earths rotation its takes 24 hours but has time zones ...
... The earth rotates around in 24 hours, but revolves around the sun in 365 days. In the earths rotation its takes 24 hours but has time zones ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... 3. Nuclear reactions that give off electromagnetic radiation take place within these objects. Many are visible at night, and they are A. stars. B. black holes. C. nebulae. D. planets. 4. A black hole is an invisible, highly dense celestial body with gravity strong enough to keep light from escaping. ...
... 3. Nuclear reactions that give off electromagnetic radiation take place within these objects. Many are visible at night, and they are A. stars. B. black holes. C. nebulae. D. planets. 4. A black hole is an invisible, highly dense celestial body with gravity strong enough to keep light from escaping. ...
Chapter 14 - Heritage Christian School
... superstitions and religions centered on the sun, moon and stars. True science began when men began to track the movements of these heavenly lights. As result very complex and accurate calendars were developed, allowing the ancients to predict events and assist in planting of crops and keeping track ...
... superstitions and religions centered on the sun, moon and stars. True science began when men began to track the movements of these heavenly lights. As result very complex and accurate calendars were developed, allowing the ancients to predict events and assist in planting of crops and keeping track ...
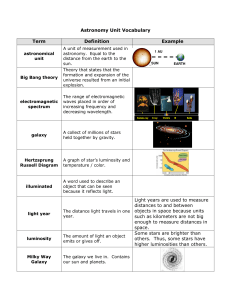
Astronomy Unit Vocabulary Term Definition Example Light years are
... Light years are used to measure distances to and between The distance light travels in one objects in space because units year. such as kilometers are not big enough to measure distances in space. Some stars are brighter than The amount of light an object others. Thus, some stars have ...
... Light years are used to measure distances to and between The distance light travels in one objects in space because units year. such as kilometers are not big enough to measure distances in space. Some stars are brighter than The amount of light an object others. Thus, some stars have ...
Space Review
... o A Comet is comparable to a ‘dirty snowball’. It usually has a ‘tail’ that can be seen caused by the comet being heated up by the sun, evaporating the ice from the comet. The tail of a comet points away from the sun. Comets may be either short period or long period comets. A short period comet orbi ...
... o A Comet is comparable to a ‘dirty snowball’. It usually has a ‘tail’ that can be seen caused by the comet being heated up by the sun, evaporating the ice from the comet. The tail of a comet points away from the sun. Comets may be either short period or long period comets. A short period comet orbi ...
Unit Review Answers - click here
... 6. e. dark matter 7. d. dark energy 8. star, globular cluster, galaxy, galaxy cluster, universe. 9. Using one of his best telescopes, Herschel was able to break up the fuzzy regions of the Milky Way into individual stars. 10. A: spiral galaxy, B: elliptical galaxy, C: irregular galaxy, D: globular c ...
... 6. e. dark matter 7. d. dark energy 8. star, globular cluster, galaxy, galaxy cluster, universe. 9. Using one of his best telescopes, Herschel was able to break up the fuzzy regions of the Milky Way into individual stars. 10. A: spiral galaxy, B: elliptical galaxy, C: irregular galaxy, D: globular c ...
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... 22. A ____________ is a huge collection of gas, dust, and hundreds of billions of stars. Our galaxy is called the _________ _________ and is ____________ shaped. 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the ...
... 22. A ____________ is a huge collection of gas, dust, and hundreds of billions of stars. Our galaxy is called the _________ _________ and is ____________ shaped. 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the ...
Astronomy Unit Study Guide
... I. the idea that the earth is the center of the universe J. he developed a law that other galaxies are moving away from us ...
... I. the idea that the earth is the center of the universe J. he developed a law that other galaxies are moving away from us ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.1 2011 Night Sky
... Getting Started in Space Space is fun to explore. What do you already know? Answer the following questions. 1. What is a star? 2. Can you see a planet without a telescope? 3. You are looking into the night sky and think you see a planet. How do you know it is a planet and not a star? Provide two re ...
... Getting Started in Space Space is fun to explore. What do you already know? Answer the following questions. 1. What is a star? 2. Can you see a planet without a telescope? 3. You are looking into the night sky and think you see a planet. How do you know it is a planet and not a star? Provide two re ...
Project topics
... Include information about a spectroscope, spectrums of different gases, the Doppler Effect with emphases on what a”red shift” is, and how Edwin Hubble used the” red shift” to determine stellar distance and movement. 4. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 5. Constellations and how they change daily, n ...
... Include information about a spectroscope, spectrums of different gases, the Doppler Effect with emphases on what a”red shift” is, and how Edwin Hubble used the” red shift” to determine stellar distance and movement. 4. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 5. Constellations and how they change daily, n ...
Outer Space Study Guide
... Voyager 1 and 2 where the first probes to see each of the nine planets in our solar system: VIDEO LINK The main thing to know is that outer space is cool! Know the vocabulary terms listed below. Know that the moon causes the tides. Know that Earth’s tilt causes the seasons. When it’s summer in the n ...
... Voyager 1 and 2 where the first probes to see each of the nine planets in our solar system: VIDEO LINK The main thing to know is that outer space is cool! Know the vocabulary terms listed below. Know that the moon causes the tides. Know that Earth’s tilt causes the seasons. When it’s summer in the n ...
lung volumes and capacities
... Small fragments of matter moving in space that sometimes enter Earth’s atmosphere. METEOROIDS When they strike the Earth, they are called Meteorites. A system of stars, gases and dust appearing as a bright white path across the sky. Our MILKY WAY solar system is in part of this galaxy. GALAXY The pa ...
... Small fragments of matter moving in space that sometimes enter Earth’s atmosphere. METEOROIDS When they strike the Earth, they are called Meteorites. A system of stars, gases and dust appearing as a bright white path across the sky. Our MILKY WAY solar system is in part of this galaxy. GALAXY The pa ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.