aphelion
... The ________________ is the region of space that is affected by Earth’s magnetic field when it extends into space. ...
... The ________________ is the region of space that is affected by Earth’s magnetic field when it extends into space. ...
Space Unit Exam /31
... d. a blast of particles and magnetic fields flowing out from the Sun at speeds of up to 1000 km/sec. ...
... d. a blast of particles and magnetic fields flowing out from the Sun at speeds of up to 1000 km/sec. ...
Earth Science 2nd 9 wk review
... One of the softest minerals is talc (powder). A naturally occurring, inorganic solid substance with a definite chemical composition and structure is called a mineral. The mineral Pyrite is also known as “fool’s gold”. The diagram that relates absolute magnitude of a Star to its temperature is calle ...
... One of the softest minerals is talc (powder). A naturally occurring, inorganic solid substance with a definite chemical composition and structure is called a mineral. The mineral Pyrite is also known as “fool’s gold”. The diagram that relates absolute magnitude of a Star to its temperature is calle ...
Earth in the Solar System - San Diego Unified School District
... c. Know how to use _________________________________ and ___________________________________ as measures of _________________________ between the _______________, ________________ and ____________________ 8. What is a light year (LY)? 9. What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)? 10. Which measurement woul ...
... c. Know how to use _________________________________ and ___________________________________ as measures of _________________________ between the _______________, ________________ and ____________________ 8. What is a light year (LY)? 9. What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)? 10. Which measurement woul ...
Space
... 1. To bring stars closer to the observer 2. To detect radio waves from distant stars 3. To magnify the image produced by the eyepiece 4. To produce an image that is magnified by the eyepiece 5. To split light from stars into different colours. ...
... 1. To bring stars closer to the observer 2. To detect radio waves from distant stars 3. To magnify the image produced by the eyepiece 4. To produce an image that is magnified by the eyepiece 5. To split light from stars into different colours. ...
Where does the sun`s energy come from?
... is that it is big. If it were smaller, it would be just be a sphere of hydrogen, like Jupiter. But the sun is much bigger than Jupiter. It would take 433,333 Jupiters to fill it up! That’s a lot of hydrogen. That means it’s held together by a whole lot of gravity. And THAT means there is a whole lot ...
... is that it is big. If it were smaller, it would be just be a sphere of hydrogen, like Jupiter. But the sun is much bigger than Jupiter. It would take 433,333 Jupiters to fill it up! That’s a lot of hydrogen. That means it’s held together by a whole lot of gravity. And THAT means there is a whole lot ...
Document
... known as the Large Magellanic Cloud that lies just beyond the Milky Way. The star, known in modern times as Sanduleak 69202, was a blue supergiant 25 times more massive than the Sun. Such explosions distribute all the common elements such as Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Calcium and Iron into interstell ...
... known as the Large Magellanic Cloud that lies just beyond the Milky Way. The star, known in modern times as Sanduleak 69202, was a blue supergiant 25 times more massive than the Sun. Such explosions distribute all the common elements such as Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Calcium and Iron into interstell ...
Patterns in the night sky - Laureate International College
... that produces and gives off light, heat, and other kinds of energy. Our Sun is a star. Stars vary in size, colour, temperature and density. ...
... that produces and gives off light, heat, and other kinds of energy. Our Sun is a star. Stars vary in size, colour, temperature and density. ...
Earth, moon, and sun - Pierce: The Fantastic Four 16-17
... anything that gets pulled into it is never seen again. It can pull dust, stars, planets, and gas toward it. Scientists have found black holes in the middle of many galaxies. They have found one in our galaxy too! It is called Sagittarius. It has the mass of 4 million suns. It is 24,000 light years a ...
... anything that gets pulled into it is never seen again. It can pull dust, stars, planets, and gas toward it. Scientists have found black holes in the middle of many galaxies. They have found one in our galaxy too! It is called Sagittarius. It has the mass of 4 million suns. It is 24,000 light years a ...
The Universe
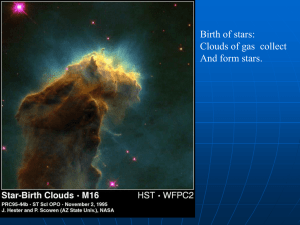
... warmer and cooler gas all around us. These ripples also show where the hydrogen clouds were slightly denser. As millions of years passed, the dense areas pulled in material because they had more gravity. Finally, about 100 million years after the Big Bang, the gas became hot and dense enough for the ...
... warmer and cooler gas all around us. These ripples also show where the hydrogen clouds were slightly denser. As millions of years passed, the dense areas pulled in material because they had more gravity. Finally, about 100 million years after the Big Bang, the gas became hot and dense enough for the ...
DOC
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) Dr. Iffat Sardharwalla ...
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) Dr. Iffat Sardharwalla ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun and Stars
... 27. _______________________ are chunks of ice and dust with long elliptical orbits. 28. Describe the life of a main sequence star. 29. What is parallax? 30. How are gas giants similar to one another? 31. How are terrestrial planets similar to one another? 32. What is the difference between comets, m ...
... 27. _______________________ are chunks of ice and dust with long elliptical orbits. 28. Describe the life of a main sequence star. 29. What is parallax? 30. How are gas giants similar to one another? 31. How are terrestrial planets similar to one another? 32. What is the difference between comets, m ...
Planets and Stars Study Guide Test Date: ______ Vocabulary to
... 6. If you see a bright object in the sky that is in a different place each night for a week, what is the object? Why does this happen? ...
... 6. If you see a bright object in the sky that is in a different place each night for a week, what is the object? Why does this happen? ...
Solar System Vocab terms geocentric — discredited theory that
... meteoroid — dust and debris that travel through space and become meteors when they enter Earth?s atmosphere. meteor shower — large number of meteors burning upon entering Earth?s atmosphere, occurring when Earth?s orbit passes through debris from a comet. moon — natural satellite of a planet. nebula ...
... meteoroid — dust and debris that travel through space and become meteors when they enter Earth?s atmosphere. meteor shower — large number of meteors burning upon entering Earth?s atmosphere, occurring when Earth?s orbit passes through debris from a comet. moon — natural satellite of a planet. nebula ...
Describe essential ideas about the composition and structure of the
... Identify equipment and instruments that explore the universe. Identify the accomplishments and contributions provided by selected past and present scientists in the field of astronomy. Identify and articulate space program efforts to investigate possibilities of living in space and on other pl ...
... Identify equipment and instruments that explore the universe. Identify the accomplishments and contributions provided by selected past and present scientists in the field of astronomy. Identify and articulate space program efforts to investigate possibilities of living in space and on other pl ...
See flyer
... and terrestrial weathers impact its conditions, which in turn affect a number of modern technologies and infrastructures, including satellite, aircraft and spacecraft operations as well as telecommunication, navigation and positioning. To fully address the predictability of the aerospace environment ...
... and terrestrial weathers impact its conditions, which in turn affect a number of modern technologies and infrastructures, including satellite, aircraft and spacecraft operations as well as telecommunication, navigation and positioning. To fully address the predictability of the aerospace environment ...
File
... Moons revolve around planets, which revolve around stars, which revolve around the center of a galaxy, which is a typical unit of the universe. 2. Explain what is meant by this statement. "When you look at a star, it might not actually be there." Many stars are thousands of light years away. The lig ...
... Moons revolve around planets, which revolve around stars, which revolve around the center of a galaxy, which is a typical unit of the universe. 2. Explain what is meant by this statement. "When you look at a star, it might not actually be there." Many stars are thousands of light years away. The lig ...
Trimble_v3
... at Irvine and University of Maryland Is the universe finite or infinite? Is there anything special about our star, the sun, or our planet, the Earth, except of course that we live here? Does the stuff out there in the cosmos behave in ways we can understand using the science we learn on earth? Peopl ...
... at Irvine and University of Maryland Is the universe finite or infinite? Is there anything special about our star, the sun, or our planet, the Earth, except of course that we live here? Does the stuff out there in the cosmos behave in ways we can understand using the science we learn on earth? Peopl ...
Astronomy Vocabulary File
... Astronomical unit (AU)—the average age distance between the Earth and the sun, or approximately 150,000,000 km Terrestrial planets—the small, dense, rocky planets of the inner solar system Prograde rotation—the counter-clockwise spin of a planet or moon as seen from above the planet’s North Pole Ret ...
... Astronomical unit (AU)—the average age distance between the Earth and the sun, or approximately 150,000,000 km Terrestrial planets—the small, dense, rocky planets of the inner solar system Prograde rotation—the counter-clockwise spin of a planet or moon as seen from above the planet’s North Pole Ret ...
Our Solar System
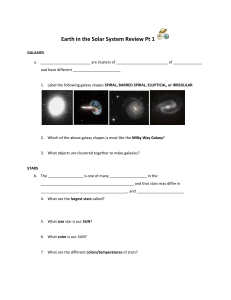
... 1. Universe- contains everything that may or may not exist in space 2. Galaxy- system of stars held together by gravity. 3 types: Spiral, Elliptical, and Irregular. Ex: Milky Way 3. Nebula= interstellar cloud of gas 4. Star- self luminous sphere of gas. Ex: sun 5. Planet- celestial object moving in ...
... 1. Universe- contains everything that may or may not exist in space 2. Galaxy- system of stars held together by gravity. 3 types: Spiral, Elliptical, and Irregular. Ex: Milky Way 3. Nebula= interstellar cloud of gas 4. Star- self luminous sphere of gas. Ex: sun 5. Planet- celestial object moving in ...
No Slide Title - steadyserverpages.com
... Why do optical telescopes work better when they are in space? ...
... Why do optical telescopes work better when they are in space? ...
Organize Your Space PowerPoint.
... crashing into each other at high speeds and sending clouds of dust into space. The combined mass of all the asteroids would only be 1/1000 the mass of the earth and if all the asteroids were combined together their diameter would be only half the diameter of ...
... crashing into each other at high speeds and sending clouds of dust into space. The combined mass of all the asteroids would only be 1/1000 the mass of the earth and if all the asteroids were combined together their diameter would be only half the diameter of ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.