A fascinating tour of the cosmos — from Earth orbit.
... to the most distant galaxies at limits of the observable universe. We've taken the best and most exciting Hubble images and woven them into an engaging story of cosmic exploration, bringing the wonders of the universe to audiences everywhere. In this all-new production, major themes in current astro ...
... to the most distant galaxies at limits of the observable universe. We've taken the best and most exciting Hubble images and woven them into an engaging story of cosmic exploration, bringing the wonders of the universe to audiences everywhere. In this all-new production, major themes in current astro ...
Astroparticle physics 1. stellar astrophysics and solar neutrinos
... • Gravitational waves: not today... • Elementary particles: cosmic-rays. ...
... • Gravitational waves: not today... • Elementary particles: cosmic-rays. ...
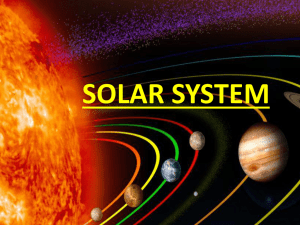
Solar System Review-KEY
... they revolve around the star/a star. Stars only APPEAR to move because Earth revolves around the Sun. Planets are in a different position each night. 7. Explain the difference between a planet and a star. Stars are huge balls of superheated gases. Planets are large objects that orbit a star. In the ...
... they revolve around the star/a star. Stars only APPEAR to move because Earth revolves around the Sun. Planets are in a different position each night. 7. Explain the difference between a planet and a star. Stars are huge balls of superheated gases. Planets are large objects that orbit a star. In the ...
exercise 1
... Earth, supports life. But there are countless other suns throughout countless galaxies scattered across the expanse of the universe. We still don’t know if life exists on another planet in some other galaxy. During the past 15 years, space probes such as the Mariner and Voyager missions have given u ...
... Earth, supports life. But there are countless other suns throughout countless galaxies scattered across the expanse of the universe. We still don’t know if life exists on another planet in some other galaxy. During the past 15 years, space probes such as the Mariner and Voyager missions have given u ...
document
... An iron meteorite 100 feet across and 70,000 tons slammed into the Earth at about 43,000mph in the Arizona desert near Flagstaff 40,000 ...
... An iron meteorite 100 feet across and 70,000 tons slammed into the Earth at about 43,000mph in the Arizona desert near Flagstaff 40,000 ...
As a pure solid, elemental carbon occurs in two distinct chemical forms
... accumulate and interact with the dust particles, forming larger particles. As these particles grow larger, they start producing a gravitational pull that attracts even more particles, creating big clumps of matter. As the cloud is rotating while all this is happening, it collapses inward, going from ...
... accumulate and interact with the dust particles, forming larger particles. As these particles grow larger, they start producing a gravitational pull that attracts even more particles, creating big clumps of matter. As the cloud is rotating while all this is happening, it collapses inward, going from ...
Space Test: Practice Questions and Answers 1. Who discovered
... 19. How are the surfaces of early planets heated? a. Asteroids b. Volcanoes c. The sun d. Solar flares 20. In redshift, the light’s wavelength… a. Get bigger b. Gets smaller c. Doesn’t change d. Goes away compl ...
... 19. How are the surfaces of early planets heated? a. Asteroids b. Volcanoes c. The sun d. Solar flares 20. In redshift, the light’s wavelength… a. Get bigger b. Gets smaller c. Doesn’t change d. Goes away compl ...
SEM 1.4_Astronomy
... Neptune) are gas giants consisting of thick, outer layers of gaseous materials (perhaps with small rocky cores). The fifth outer planet (Pluto) has an unknown composition, but it appears to be solid. Moons are natural satellites of planets that vary widely in composition. Comets orbit the sun ...
... Neptune) are gas giants consisting of thick, outer layers of gaseous materials (perhaps with small rocky cores). The fifth outer planet (Pluto) has an unknown composition, but it appears to be solid. Moons are natural satellites of planets that vary widely in composition. Comets orbit the sun ...
Space – Science 6 Outcomes - Learning Resources and
... identify and use a variety of sources and technologies to gather pertinent information about a planet, moon, asteroid, or comet, and display their findings using diagrams, pictures and/or ...
... identify and use a variety of sources and technologies to gather pertinent information about a planet, moon, asteroid, or comet, and display their findings using diagrams, pictures and/or ...
Unit Review Name
... 10. _________________________ is the name we give to the process that satellites use ...
... 10. _________________________ is the name we give to the process that satellites use ...
Science 9 Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a
... Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a-i a) Neptune b) Jupiter c) Mercury ...
... Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a-i a) Neptune b) Jupiter c) Mercury ...
Our Solar System
... • Our sun is 1 of trillions of stars in the universe. Stars are found in groups held together by gravity. • A huge group of stars is called a galaxy. • Our entire universe is made up of thousands of galaxies. • The images below show you how small we are compared to the entire universe. ...
... • Our sun is 1 of trillions of stars in the universe. Stars are found in groups held together by gravity. • A huge group of stars is called a galaxy. • Our entire universe is made up of thousands of galaxies. • The images below show you how small we are compared to the entire universe. ...
NASA Space Place
... times as great as our own star. The Bubble Nebula, discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, is perhaps the classic example of this phenomenon. At a distance of 7,100 light years away in the constellation of Cassiopeia, a molecular gas cloud is actively forming stars, including the massive Oclass star ...
... times as great as our own star. The Bubble Nebula, discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, is perhaps the classic example of this phenomenon. At a distance of 7,100 light years away in the constellation of Cassiopeia, a molecular gas cloud is actively forming stars, including the massive Oclass star ...
solar system - Teaching Children
... +the closer to the sun the smallest +has the most tenuous atmosphere +you do not have moons ...
... +the closer to the sun the smallest +has the most tenuous atmosphere +you do not have moons ...
Science Astronomy Name
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
Beyond our Sol. System
... Universe today was created in that explosion. Just like after any explosion, matter was thrown out in all directions. The same matter is still traveling outward today. It is believed that the matter closer to the center of the explosion came together to form stars and planets first. It seems like th ...
... Universe today was created in that explosion. Just like after any explosion, matter was thrown out in all directions. The same matter is still traveling outward today. It is believed that the matter closer to the center of the explosion came together to form stars and planets first. It seems like th ...
Science Astronomy Name
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
... 2. The universe is very big. It may extend to infinity. 3. Most astronomers believe that the universe began as an explosion called the “Big Bang.” 4. A constellation is a group of stars that seems to make a pattern in the sky. 5. The North Star is over the North Pole in the Little Dipper and appears ...
Gravitation Worksheet
... 5. Derive expression for escape velocity. 6. State and prove Kepler’s second and third law of planetary motion 7. How much faster than its present rate should earth rotate about its axis so that the weight of a body at equator becomes zero? 8. A spaceship is stationed on mars. How much energy must b ...
... 5. Derive expression for escape velocity. 6. State and prove Kepler’s second and third law of planetary motion 7. How much faster than its present rate should earth rotate about its axis so that the weight of a body at equator becomes zero? 8. A spaceship is stationed on mars. How much energy must b ...
The Sun - rosedalegrade9astronomy
... years old. – It will last another 5 billion years – Has the mass of more than 300 000 Earths – So big that gravity forces everything together so tight that there are nuclear reactions and a great amount of heat. -Hydrogen atoms are squashed together to form helium (a nuclear fusion reaction). ...
... years old. – It will last another 5 billion years – Has the mass of more than 300 000 Earths – So big that gravity forces everything together so tight that there are nuclear reactions and a great amount of heat. -Hydrogen atoms are squashed together to form helium (a nuclear fusion reaction). ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.