* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Layers of the Atmosphere
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
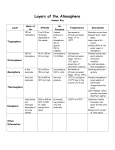
Layers of the Atmosphere Check your JIGSAW! Do you have all of these facts? Troposphere 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Tropo = turning or changing 0 to 12 km from earth’s surface Where weather occurs We live here. Contains almost all of the mass of the atmosphere. 6. As altitude increase temperature decreases Ozonosphere 1. Ozone = O3 2. Ozone is produce by lightning 3. 90% of ozone is in the stratosphere 4. Protect the earth from UV rays from the sun. Stratosphere 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Strato = spread out From the top of troposphere to 50 km. As altitude increase, temperature increases. Contains the ozone layer Planes fly here to avoid weather Mesosphere 1. Meso = middle 2. 50 – 80 km above earth’s surface 3. As altitude increase, temperature decrease. 4. Meteorites burn up in the mesosphere – leaving a shooting star Thermosphere 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Divided into two sections Begins at 80 km from the earth’s surface Ends in outer space Therm – heat As altitude increases, temp. increases Air is very thin – molecules spread out Ionosphere 1. 80 to 550 km 2. Energy from the sun causes gas molecules to have a charge + or – 3. Aurora Borealis occur here. Particles from the sun enter near the poles. (See Magnetosphere) How Auroras are caused: • Charged particles from the sun interact with the earth’s magnetic field • The particles (or ions) enter the atmosphere near the poles • The ions smash into the air molecules • The air molecules release energy from the crash as light • Northern Hemisphere – Northern Lights • Southern Hemisphere – Aurora Australis Aurora Borealis Exosphere 1. Exo = Outer 2. 2nd layer of the thermosphere 3. 550 km above earth to outer space 4. Satellites orbit here Magnetosphere 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The earth acts as a large magnet All magnetic objects produce invisible lines of force and creates charged molecules Earth’s magnetic line run from North to South Pole The magnetic field stops solar winds The charged molecules create auroras in the ionosphere