* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meteorology
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Air quality law wikipedia , lookup
Satellite temperature measurements wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Surface weather analysis wikipedia , lookup
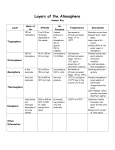
METEOROLOGY What is the Atmosphere? • Mixture of gases that surround the Earth. • Composition • 78% Nitrogen • 21% Oxygen • 1%: other argon, carbon dioxide • What is the purpose of the atmosphere? • Makes conditions suitable for us to live • Protects us from space What is the Atmosphere: continued • Why is it Important? • Stores Oxygen • Keeps us warm: Greenhouse effect • Protects us from sun’s radiation, cold of space, meteoroids Air Pressure • Does air have mass? • How could you prove/demonstrate that air has mass? • Measure of force with which air molecules push on a surface • Air pushes in all directions • Gases will fill the volume of space they are contained • Density of air effects the amount of pressure, why? • How is pressure measured? Altitude and Air pressure • Altitude = Elevation • Air pressure decreases as altitude increases • Air pressure decreases, density decreases Layers of Atmosphere • 4 main layers • Troposphere • Stratosphere • Mesosphere • Thermosphere Troposphere • Tropo = Change • Layer in which we live • Weather occurs here • What is the difference between weather and climate? • Majority of mass of atmosphere • Altitude increases, temperature decreases • Top temp. = -60 degrees Celsius • 0 to 12 km Stratosphere • Contains the Ozone • What is ozone? • 3 oxygen molecules bonded together • Top of Stratosphere is warm, but bottom is cold, Why? • Ozone absorbs Suns radiation • Ranges from 12km to 50 in elevation Mesosphere • Layer protects us from meteoroids and space junk • Meteoroids burn up = Shooting stars Thermosphere • Divided into 2 layers • Exosphere • Ionosphere • Outermost layer of atmosphere • Temp can reach up to 1,800°C • Suns radiation strikes this layer first • Thermometer would read 0°C, Why? • Density and distance between molecules. Molecules have a lot of energy but there isn’t a lot of molecules and they are spread out • Temperature = Average amount of energy of motion of each particle Thermosphere: Ionosphere • Sun’s energy innervates gas molecules to become electrically charged Ions • We see this as Auroa Borealis: Northern Lights • Layers reflects back radio waves Thermosphere: Exosphere • 400 km and beyond • Layer in which satellites orbit Earth